| 83% |
With palladium diacetate; sodium carbonate; triphenylphosphine; In 1,2-dimethoxyethane; water; for 6h;Reflux; |
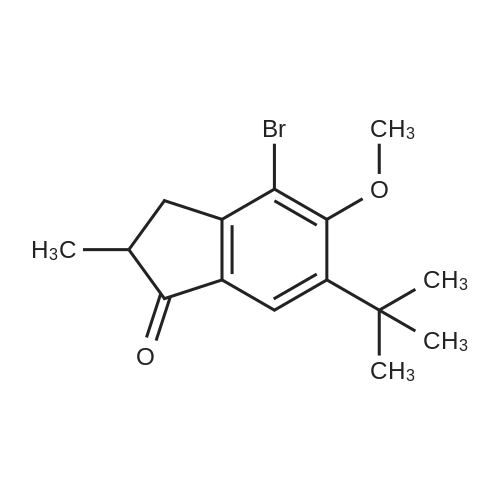
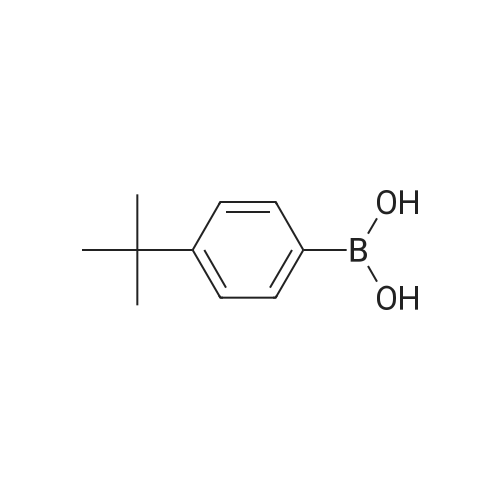
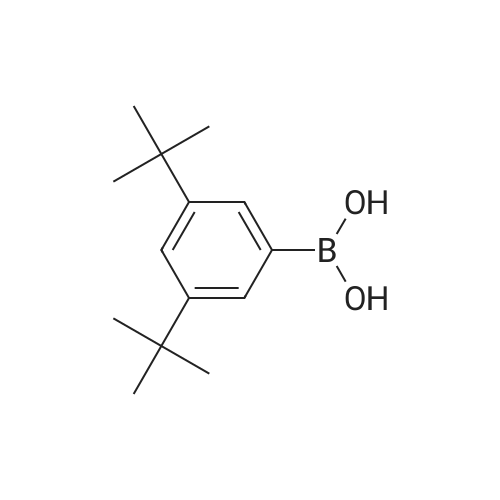
A mixture of71.8 g (231 mmol) of 4-bromo-6-tert-butyl-5-methoxy-2-methylindan-1-one, 67.3 g (287 mmol, 1.25 eq.) of<strong>[197223-39-5](3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl)boronic acid</strong>, 65.3 g(616 mmol) ofNa2C03, 2.70 g (12 mmol, 5 mol.percent) ofPd(OAc)2, 6.30 g (24 mmol,10 mol.percent) ofPPh3, 290 ml of water and 700 ml of 1,2-dimethoxyethane was refluxed for 6 h. The formed mixture was kept overnight at 0°C. The formed darkprecipitate was filtered off, then 1 liter of dichloromethane and 1 liter of water wereadded to the precipitate. The organic layer was separated, the aqueous layer wasadditionally extracted with 2 x 200 ml of dichloromethane. The combined organicextract was dried over K2C03 and then evaporated to dryness to give 108 g of black solid mass. This crude product was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel 60 ( 40-63 )liD, hexanes-dichloromethane = 1:1, vol., then, 1 :2) to give 80.8 g (83percent)of a slightly yellowish solid.Anal. calc. for C29H4o02: C, 82.81; H, 9.59. Found: C, 83.04; H, 9.75.1H NMR (CDCh): b 7.74 (s, 1H), 7.41 (t, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (d, J = 1.6 Hz 2H), 3.24 (s, 3H), 3.17 (dd,J= 17.3 Hz,J= 8.0 Hz, 1H), 2.64 (m, 1H), 2.47 (dd,J= 17.3Hz, J= 3.7 Hz, 1H), 1.43 (s, 9H), 1.36 (s, 18H), 1.25 (d, J= 7.3 Hz 3H). |
| 43% |
With palladium diacetate; sodium carbonate; triphenylphosphine; In 1,2-dimethoxyethane; water; for 12h;Reflux; |
tei"i-Butyl-4-(3,5-di-tei"i-butylphenyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindan-l-oneA mixture of 30.7g (98.6 mmol) of 4-bromo-6-tertbutyl-5-methoxy-2- methylindanone, 30.6 g (128 mmol) 3,5-di-tert-butylphenylboronic acid, 29.7 g (280 mmol) of Na2C03, 1.35 g (5.92 mmol; 6 mol.percent) of Pd(OAc)2, 3.15 g (1 1.8 mmol; 12 mol.percent) of PPh3, 130 ml of water, and 380 ml of 1 ,2-dimethoxyethane was re fluxed for 12 h. Further on, the reaction mixture was quenched with water, solvents were evaporated. The residue was dissolved in 500 ml of dichloromethane, and this solution was washed by 500 ml of water. The organic layer was separated, the aqueous layer was additionally extracted with 100 ml of dichloromethane. The combined organic extract was dried over Na2S04, then evaporated to dryness. The crude product isolated from the residue using flash chromatography on silica gel 60 (40-63 um, hexanes-dichloromethane = 2: 1, vol.) was then re-crystallized from n- hexane to give 18.5 g (43percent) of a white solid.Anal. calc. for C29H40O2: C, 82.81; H, 9.59. Found: C, 83.04; H, 9.75. 1H NMR (CDCI3): delta 7.74 (s, 1H, 7-H in indan-l-one), 7.41 (t, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, 4-H in 3.24 (s, 3H, OMe), 3.17 (dd, J = 17.3 Hz, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, 3-H in indan-l-one), 2.64 (m, 1H, 2-H in indan-l-one), 2.47 (dd, J = 17.3 Hz, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H, 3-H' in indan-l-one), 1.43 (s, 9H, 6-lBu in indan-l-one), 1.36 (s, 18H, ¾u in CgH^Bu^, 1.25 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H, 2-Me in indan- l-one). |
| 43% |
With palladium diacetate; sodium carbonate; triphenylphosphine; In 1,2-dimethoxyethane; water; for 12h;Reflux; Inert atmosphere; Schlenk technique; Glovebox; |
A mixture of 30.7g (98.6 mmol) of 4-bromo-6-tertbutyl-5-methoxy-2- methylindanone, 30.6 g (128 mmol) 3,5-di-tert-butylphenylboronic acid, 29.7 g (280 mmol) ofNa2CO3, 1.35 g (5.92 mmol; 6 mol.percent) ofPd(OAc)2, 3.15 g (11.8 mmol; 12 mol.percent) of PPh3, 130 ml of water, and 380 ml of 1,2-dimethoxy ethane was refluxed for 12 h. Further on, the reaction mixture was quenched with water, solvents were evaporated. The residue was dissolved in 500 ml of dichloromethane, and this solution was washed by 500 ml of water. The organic layer was separated, the aqueous layer was additionally extracted with 100 ml of dichloromethane. Thecombined organic extract was dried over Na2S04, then evaporated to dryness. The crude product isolated from the residue using flash chromatography on silica gel 60 (40-63 um, hexanes-dichloromethane = 2: 1 , vol.) was then re-crystallized from n- hexane to give 18.5 g (43percent) of a white solid. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 110K+ Compounds
110K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping