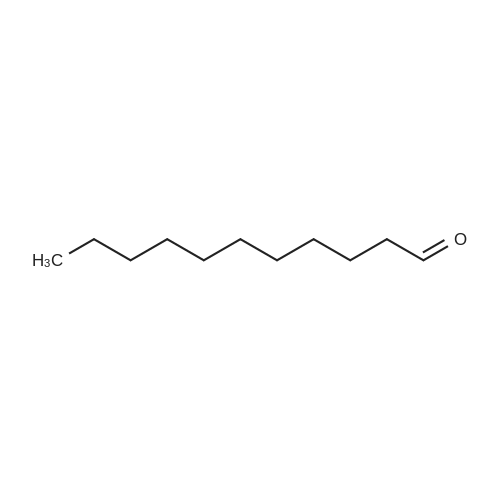
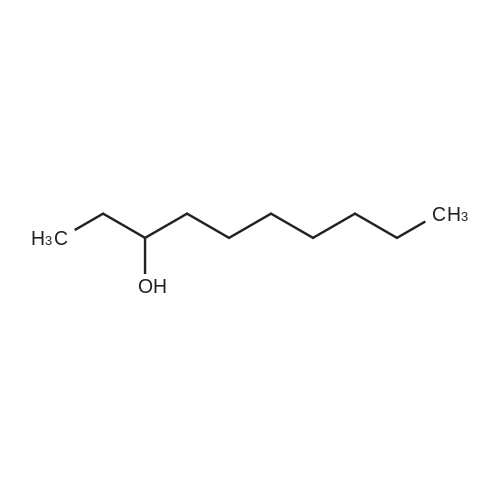
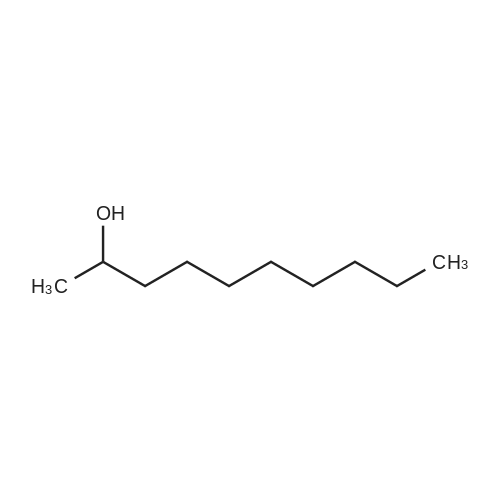
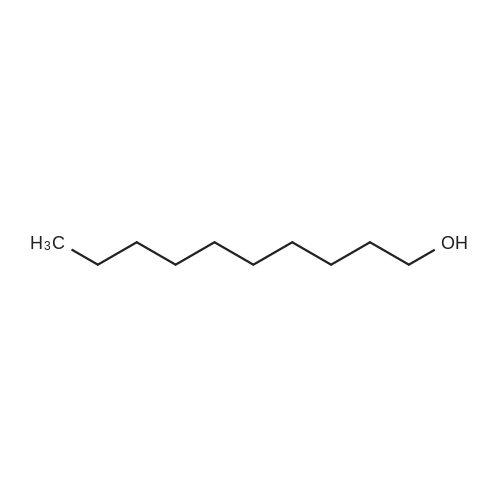
| 62.2% |
With chloro(1,5-cyclooctadiene)(pentamethylcyclopentadiene)ruthenium(II); potassium <i>tert</i>-butylate; hydrogen; (2-aminoethyl)diphenylphosphane In 1,4-dioxane at 120℃; for 18h; Inert atmosphere; Autoclave; |
1
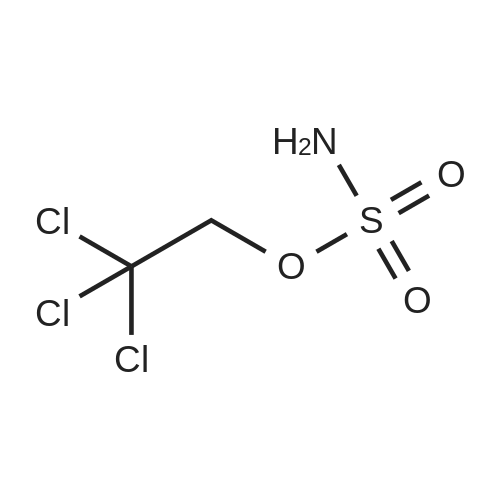
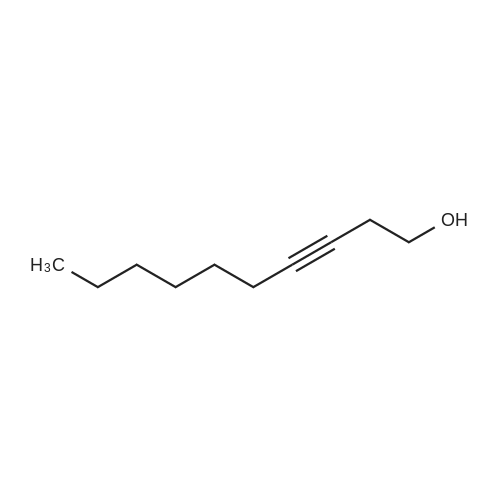
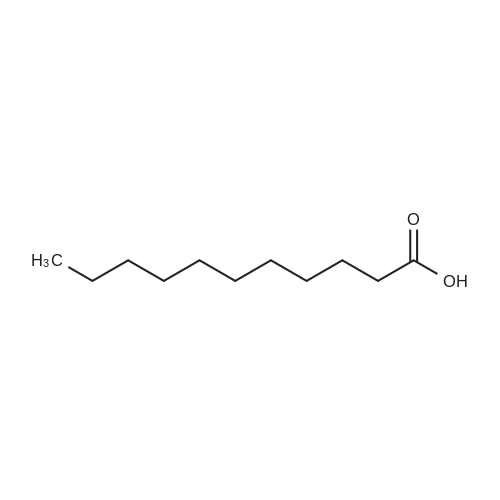
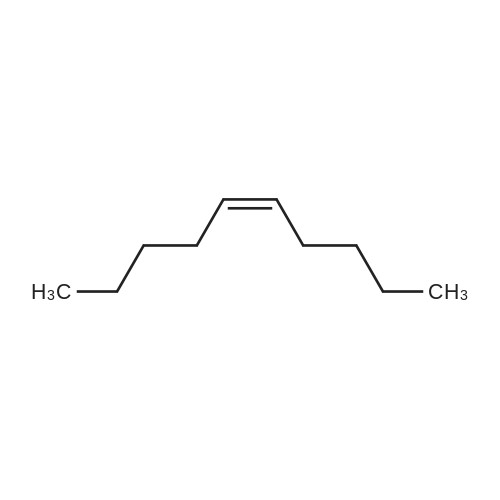
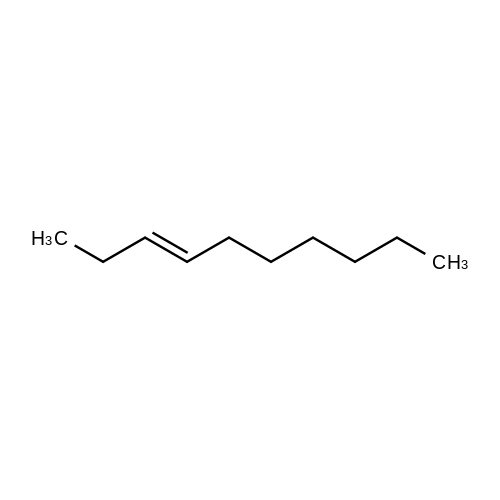
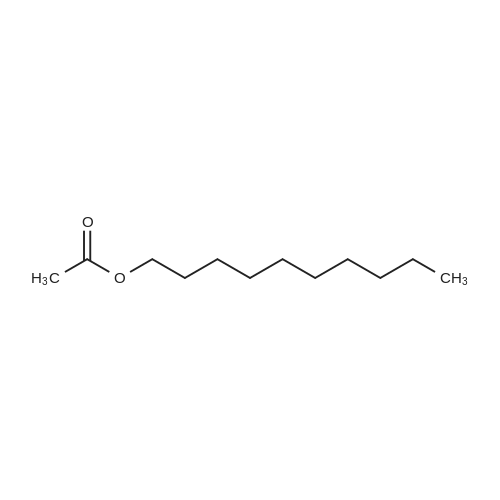
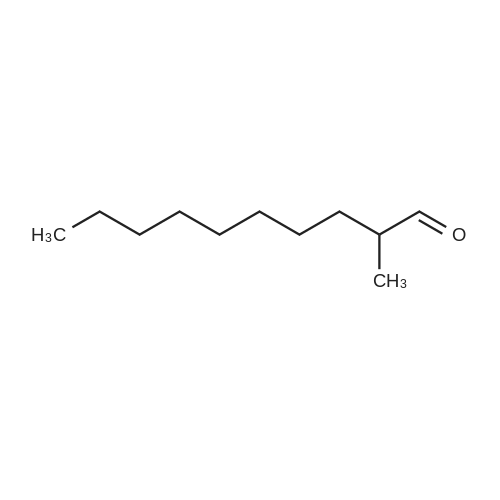
Three glass containers for catalyst preparation were prepared, Cp * Ru (cod) Cl (5.7 mg, 0.015 mmol)as transition metal compound for hydrogenation catalyst of selective hydrogenation reaction catalyst material, the compound A-46 (3.5 mg, 0.015 mmol) auxiliaries hydrogenation reaction catalyst, as a basic compound, potassium t-butoxide (1.7 mg, 0.015 mmol) were added. These were sequentially made into a glass container A (transition metal compound for hydrogenation catalyst), B (auxiliary agent) and C (basic compound). Separately, Rh (acac) (CO) 2 (5.2 mg, 0.020 mmol) was used as a rhodium compound for the hydroformylation reaction catalyst in a stainless steel autoclave having an internal volume of 50 ml containing a magnetic stirrer in a container and the bidentate organophosphorus compound L-22 (42.9 mg, 0.040 mmol) was weighed out as a ligand of the hydroformylation reaction catalyst. Next, 1, 4-dioxane (0.5 ml) was added as a solvent to each of the above-mentioned glass containers A, B, C under a nitrogen atmosphere to dissolve each component, and then the solution of the glass container A was charged into a glass transferred to a container B, after stirring at room temperature for 5 minutes, the solution in the glass container B was further transferred to a glass container C with a cannula and stirred for 5 minutes. In addition, 1, 4-dioxane (0.5 ml) as a solvent was added to the autoclave under a nitrogen atmosphere and stirred for 5 minutes. Subsequently, the solution of the glass container C was transferred to an autoclave with a cannula, the inside of the glass container C was washed with 1, 4-dioxane (2.0 ml), and the washing liquid was also transferred to the autoclave. Further, 448.9 mg (cis-2-decene: 2.0 mmol, 1 mol / mol) of a mixed solution of cis-2-decene (reaction raw material) and n-dodecane (internal standard substance for GC analysis) N-dodecane: 1.0 mmol) was added. After sealing the autoclave, quickly hydrogen from a gas supply valve/ carbon monoxide mixed gas (mixing ratio: 1/1) was introduced up to 0.5 Mpa, Under stirring at 800 rpm with a magnetic stirrer, reacted for 18 hours while heating at 120°C in an electric furnace (the amount of 1,4-dioxane used is 88% by weight based on the total weight of the reaction medium). After completion of the reaction, the reaction was cooled down to room temperature and the residual gas was released, and then the reaction results were analyzed by NMR and gas chromatography. As a result, undecanal yield was 4.0%, undecanol yield was 62.2%. In addition, the ratio (L / B ratio) of linear alcohol (1-undecanol) to branched alcohol (2-methyl-1-decanol etc.) in undecanol was 17 (linear selectivity = 94% |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science












 HazMat Fee +
HazMat Fee +

 For Research Only
For Research Only
 110K+ Compounds
110K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping