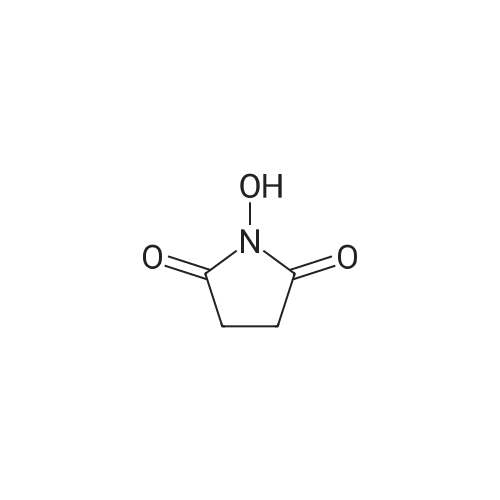
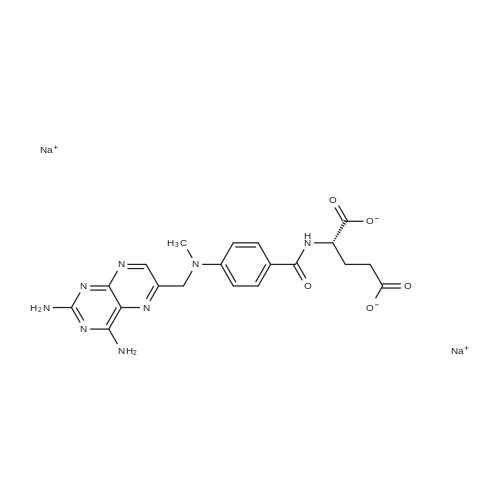
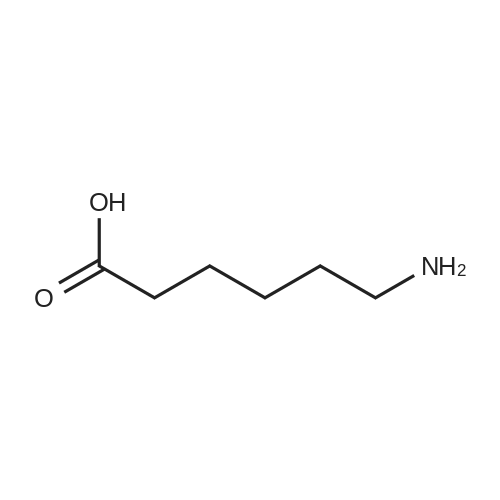
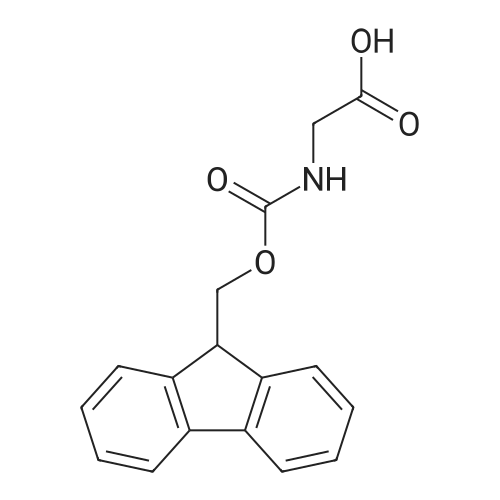
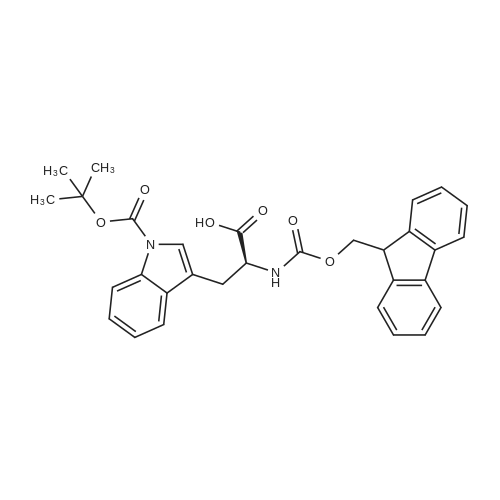
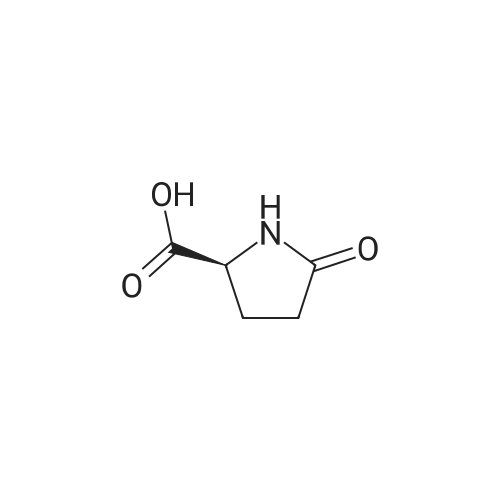
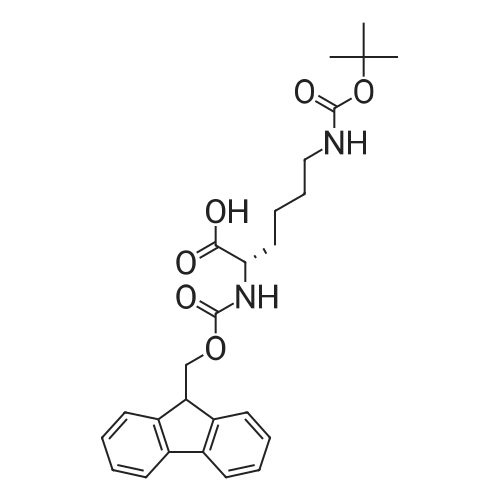
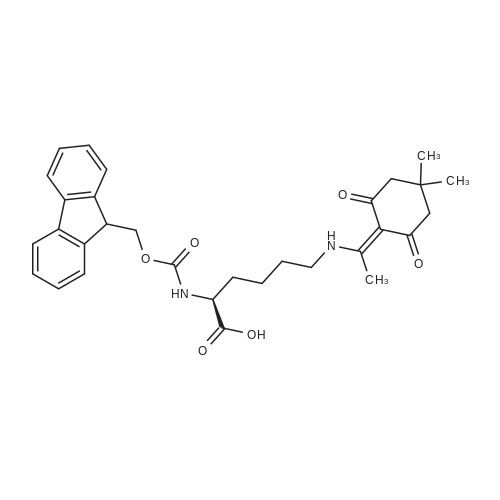
| 35% |
|
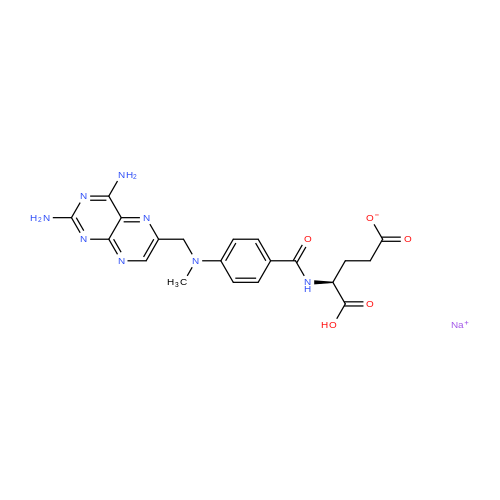
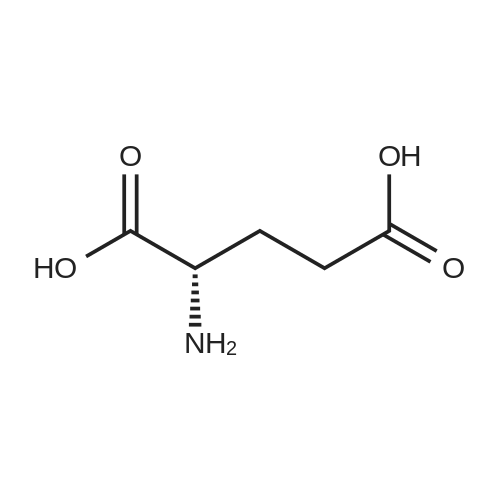
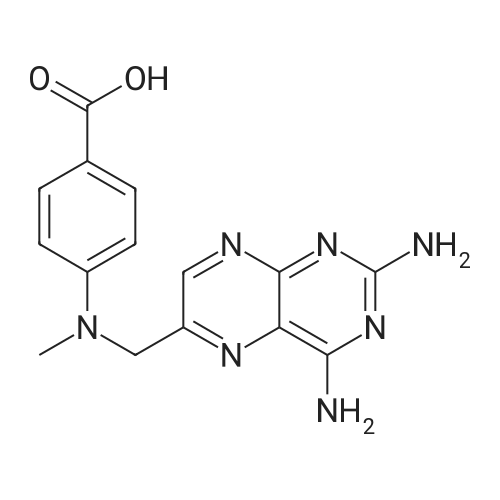
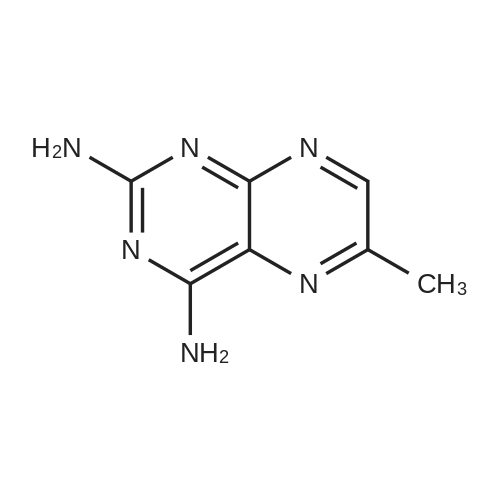
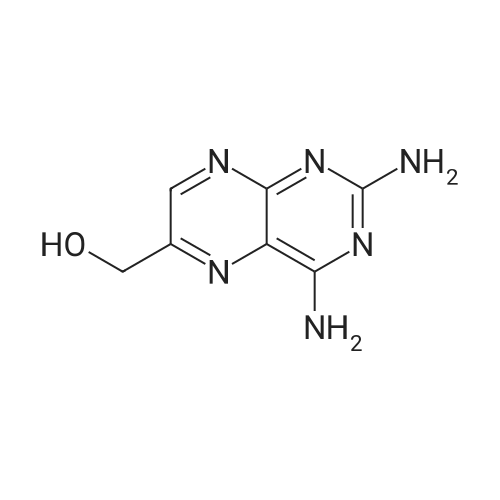
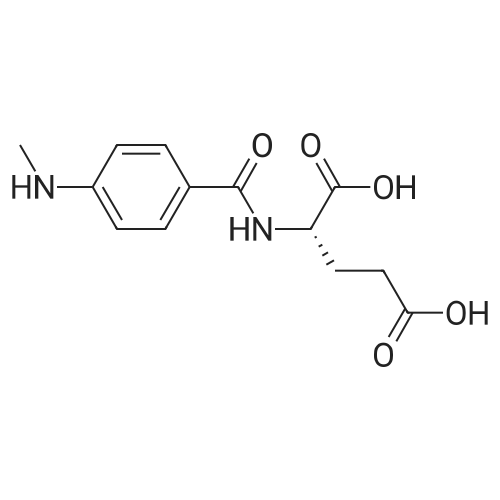
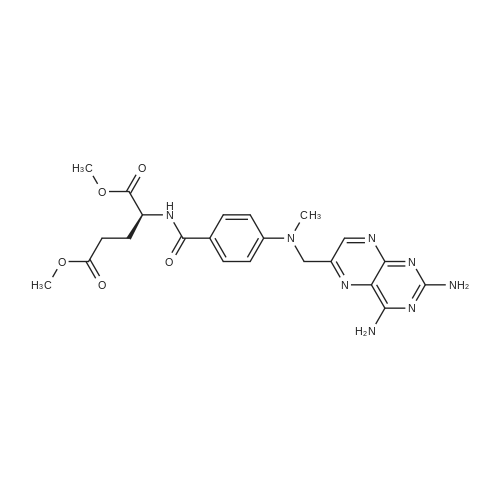
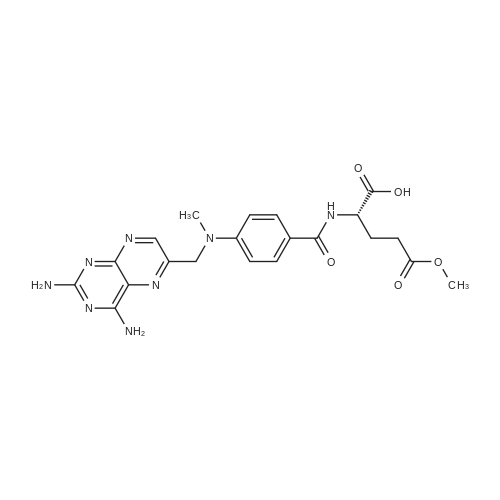
A solution comprising the corresponding 1-stearoyl-2-omega-aminoacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine of stage 4, acetic acid (0.589 g., 0.9 mmol) and triethylamine (0.182 g., 239 mul, 1.8 mmol) in 30 ml of dry freshly distilled chloroform is added dropwise to the reaction mixture of stage 5 for 30 min at -25 C. The reaction mixture is stirred for additional one hour at -25 C., and then for overnight at room temperature. The solvents are removed in evaporator under reduced pressure. The obtained residue is a thick viscous liquid. Diethyl ether (50 ml) is added to this liquid and the mixture is stirred. The product is gradually transformed into a yellow powder which is filtered and washed with diethyl ether (3×20 ml). The crude product is purified by column chromatography as follows: 450 g. crude product is dissolved in 50 ml of methanol, followed by addition of 11.0 g. dry silica gel. The mixture is swirled, and then the volatile liquid is evaporated under reduced pressure to yield free-flowing yellow finely divided solid. The obtained solid is packed on top of a silica column (3×30 cm) (100 g. silica gel per 1 g of crude product). The product is eluted in succession with the solution MeOH:H2O of variable composition: first fraction is 100:0 (v/v) (1L), second fraction is 99:1 (v/v) (1L), third fraction is 98:2 (v/v) (1L), and fourth fraction is 98:3 (v/v) (2L). The fractions, which contain the product (the determination is carried out by TLC analysis), are combined and the solvent is evaporated under reduced pressure. The obtained product (about 250 mg) is dissolved in mixture of methanol (10 ml) and chloroform (250 ml). The solution is washed with 1% HCl (3×20 ml) and then with water (3×20 ml). To achieve better separation of the aqueous and organic phases, isopropanol (about 25% of the volume of solution) is added. Isopropanol addition also promotes transition of the product into the organic phase. The organic layers are combined and dried over sodium sulfate. The sodium sulfate is filtered off and the solvent is distilled under reduced pressure. The obtained product is dried under vacuum for 3 hours. [00146] Examples of resulted final products and their analyses are: [00147] 1-Stearoyl-2-[3-(alpha-MTX amido)]-proponoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, C49H79N10O12P. [00148] Yield 35%. Yellow solid. Decompose at 200 C. without melting. pH 5.1. TLC analysis: Silica gel on aluminium plates. Eluent is CH3OH:H2O (98:2, v/v). Indication by UV-Vis spectrum. One spot. Rf0.16. MS(FAB). C49H79N10O12P. Main peak (+FAB) is 1031.2. 1H NMR (CD3OD), delta (ppm): 0.89 (t, 3H), 1.22-1.29 (broad s, 30H), 1.53 (m, 2H), 2.08 (m, 2H), 2.35 (m, 2H), 2.60 (t, 2H), 2.50 (t, 2H), 3.21 (s, 3H), 3.38 (s, 9H), 3.47 (t, 2H), 3.93-4.31 (m, 8H), 4.41 (m, 1H), 4.80 (s, 2H), 5.21 (m, 1H), 6.84 (d, 2H), 7.76 (d, 2H), 8.60 (s, 1H). 31P NMR (CD3OD), delta (ppm): -3.3 (s). Chemical analysis: C49H79N10O12P.HCl.3H2O. Calculated: C 52.47%, H 7.55%, N 12.49%, P 2.76%, Cl 3.16%. Found: C 52.92% , H 7.76%, N 12.21%, P 2.46%, Cl 30 3.08%. [00149] 1-Stearoyl-2-[6-(alpha-MTX amido)]-hexanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine C25H85N10O12P. [00150] Yield 40%. Yellow solid. Decomposes without melting at 200 C. pH 5.0. TLC analysis: Silica gel on aluminium plates. Eluent is MeOH:H2O (98:2, v/v). Indication is UV-Vis spectra. One spot Rf0.18. MS (FAB): C52H85N10O12P 1073.3 (+FAB) is main peak. 1H NMR (CD3OD), delta (ppm): 0.86-0.89 (t, 3H), 1.22-1.30 (broad s, 32H), 1.51-1.55 (m, 4H), 2.06-2.10 (m, 4H), 2.33-2.36(m, 2H), 2.58-2.62 (t, 2H), 2.49-2.52 (t, 2H), 3.22 (s, 3H), 3.38 (s, 9H), 3.45-3.48 (t, 2H), 3.92-4.35 (several m, 8H), 4.40-4.42 (m, 1H), 4.79 (s, 2H), 5.20 (n, 1H), 6.82-6.84 (d, 2H), 7.74-7.76 (d, 2H0, 8.58 (s, 1H). 31P NMR (CD3OD), delta (ppm): -3.7 (s). Chemical analysis: C52H85N10O12P.2HCl.5H2O: Calculated: C 50.48%, H 7.84%, N 11.33%/, P 2.51%, Cl 5.74%. Found: C 50.45%, H 7.220/a, N 11.46%, P 2.43%, Cl 5.43%. [00151] 1-Stearoyl-2-[3-(alpha-dodecylate-gamma-MTX amido)]-proponoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. C61H103N10O12P. [00152] Yield 40%. Yellow solid. Decompose at 200 C. without melting. TLC analysis: Silica gel on aluminium plates. Eluent is CHCl3:CH3OH:H2O (65:35:5, v/v). Indication by UV-Vis spectrum. One spot. Rf0.17. MS(FAB). C61H103N10O12P. Main peak (+FAB) is 1198.4. 1H NMR (CD3OD+CDCL3), delta (ppm): 0.82-0.85 (t, 3H), 1.23 (broad s, 46H), 1.53-1.58 (m, 2H), 2.24-2.34 (m, 3H), 2.50-2.52 (m, H), 3.17 (s, 9H), 3.41 (t, 1H) 3.54 (s, 1H), 4.04-4.18 (m, 4H), 4.32-4.47 (m, 1H), 4.80 (s, 2H), 5.21 (m, 1H), 6.79-6.82 (d, 2H), 7.76 (d, 2H), 8.54 (s, 1H). 31P NMR (CD3OD+CDCL3), delta (ppm): +0.71 (s). Chemical analysis: C61H103N10O12P.3H2O. Calculated: C 58.47%, H 8.71%, N 11.18%, P 2.47%. Found: C 58.67%, H 8.88%, N 11. 15%, P 2.47%. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 110K+ Compounds
110K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping