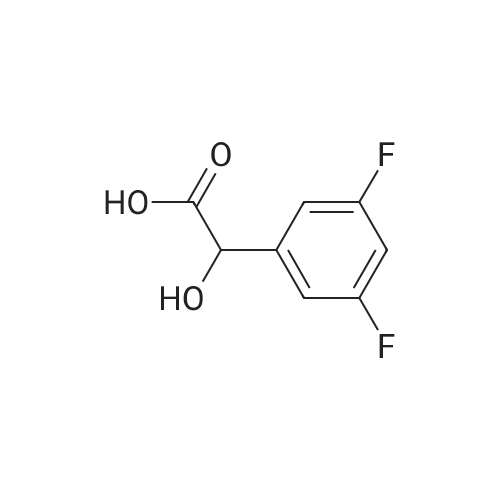
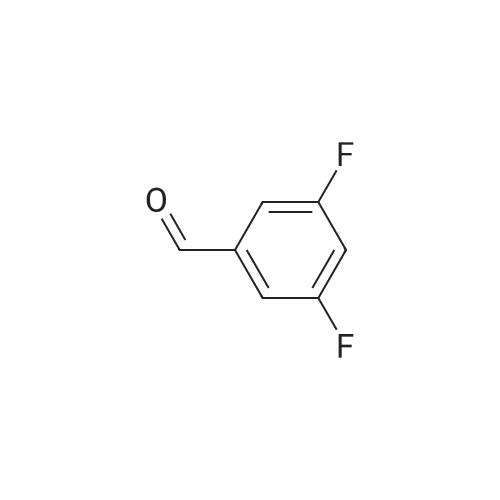
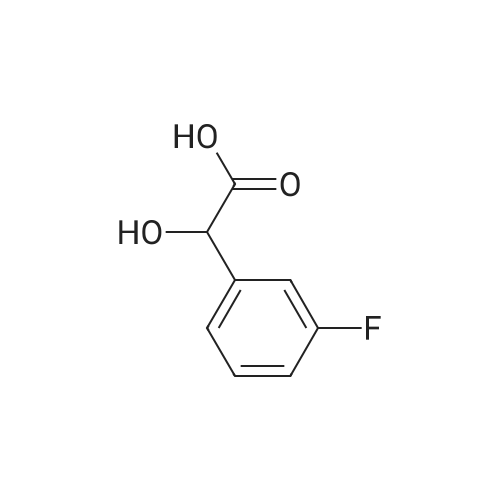
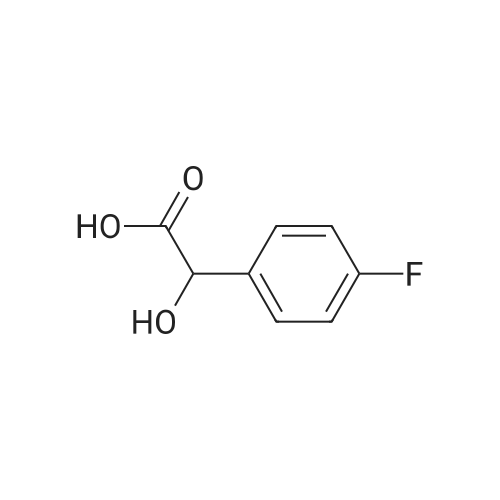
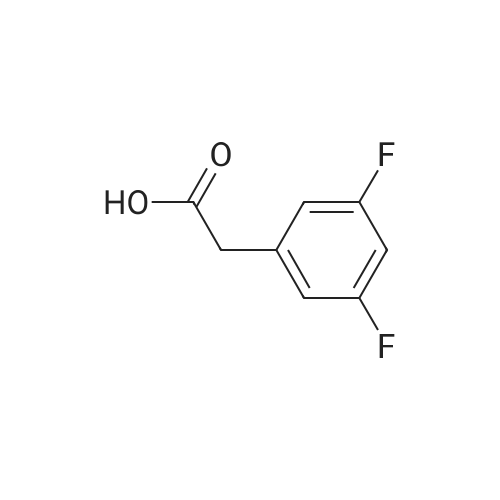
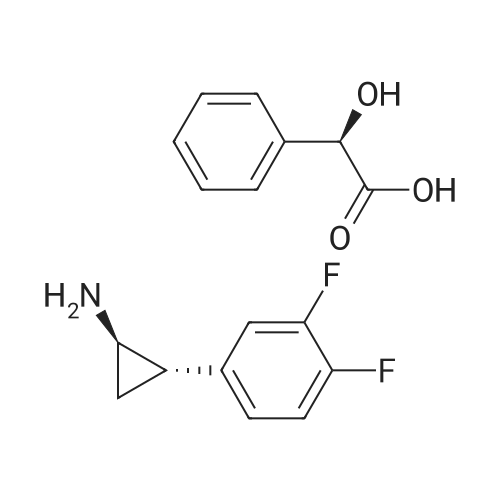
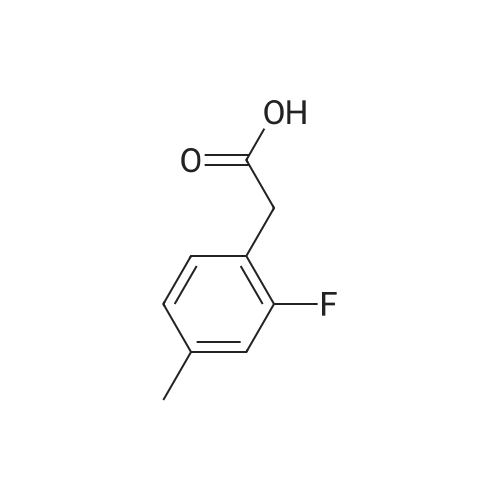
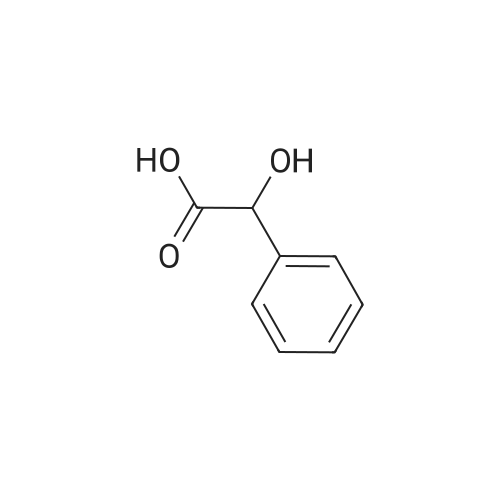
Heterocyclic Building Blocks
Aliphatic Heterocycles (103)
(1R,5S)-3-Azabicyclo[3.1.0]Hexane (11)1,2-Dithiolane (6)1,4-Diazepan-2-One (5)1,4-Diazepan-5-One (9)1,4-Dioxane (17)1,4-Oxazepane (8)10,11-Dihydro-5H-Dibenzo[B,F]Azepine (9)11,12-Didehydro-5,6-Dihydrodibenz[B,F]Azocine (14)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Glycyl)-2,2-Dimethyloxazolidine-4-Carboxylic Acid (8)3H-Diazirine (11)4-Benzyl-1,4-Oxazepane (5)Tetrahydro-2H-Thiopyran 1,1-Dioxide (8)
Azetidines (2997)
1-(Azetidin-1-Yl)-2-Bromoethan-1-One (3)1-(Azetidin-3-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole (7)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)Azetidine (7)1-Benzhydrylazetidine (13)1-Benzylazetidine (6)1-Methylazetidine (6)1-Phenylazetidine (8)2,7-Diazaspiro[3.5]Nonane (7)2-Azaspiro[3.3]Heptane (11)2-Imino-N-((6R,7R)-8-Oxo-5-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[4.2.0]Oct-2-En-7-Yl)-2-(Thiazol-4-Yl)Acetamide (3)3-Bromoazetidine (3)3-Methylazetidin-3-Ol (3)3-Methyleneazetidine (8)3-Phenylazetidine (5)4-(Azetidin-1-Yl)Piperidine (6)Azetidin-2-One (11)Azetidin-2-Ylmethanol (7)Azetidin-3-Amine (4)Azetidin-3-Ol (11)Azetidin-3-Yl Acetate (3)Azetidin-3-Ylmethanamine (3)Azetidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)Azetidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (5)Benzyl Azetidine-1-Carboxylate (9)Methyl Azetidine-2-Carboxylate (3)N-((6R,7R)-8-Oxo-5-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[4.2.0]Oct-2-En-7-Yl)-2-Phenylacetamide (5)Tert-Butyl Azetidine-1-Carboxylate (64)
Benzimidazoles (4428)
Benzimidazole-Carboxylic Acid (43)(1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Yl)Methanamine (7)(1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Yl)Methanol (14)1,2-Diphenyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (7)1-Benzyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (6)1-Ethyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (4)1-Methyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (47)1-Phenyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (4)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Amine (7)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-5-Amine (4)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-6-Amine (6)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-2-Carbaldehyde (5)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-2-Carboxylic Acid (7)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-2-Thiol (10)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (6)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (4)2-((Pyridin-2-Ylmethyl)Thio)-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (7)2-(1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (6)2-(Chloromethyl)-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (9)2-Benzyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (7)2-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (4)2-Chloro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (17)2-Methyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (20)4-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (14)4-Methyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (7)5,6-Dichloro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (4)5-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (13)5-Chloro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (14)5-Methoxy-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (2)5-Methyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (10)6-Chloro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (25)Methyl (1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Yl)Carbamate (5)Methyl 1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-2-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl 1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-1-Carboxylate (5)
Benzofurans (3713)
Benzofuran-Carboxylic Acid (67)Dimethoxyisobenzofuran (4)Epoxyisobenzofuran (1)Fluorobenzofuran (19)Fluoroisobenzofuran (5)Methoxyisobenzofuran (4)Methylbenzofuran (25)1-(Benzofuran-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (3)2,2-Dimethyl-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (7)2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran-3-Amine (11)2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran-5-Amine (3)2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran-7-Amine (5)2-(Benzofuran-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (3)2-Bromodibenzo[B,D]Furan (6)2-Ethylbenzofuran (3)2-Methylbenzofuran (5)3-Methylbenzofuran (4)4-Bromobenzofuran (3)4-Phenyldibenzo[B,D]Furan (8)5,7,8-Trimethylchromane (3)5-Bromo-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (6)5-Chloro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (5)5-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (5)5-Methoxyisobenzofuran-1(3H)-One (5)6-Bromo-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (6)6-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (6)6-Methoxybenzofuran (4)7-Bromo-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (6)7-Bromobenzofuran (6)7-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (6)Benzofuran-2(3H)-One (7)Benzofuran-2-Carbaldehyde (5)Benzofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (21)Benzofuran-2-Ylboronic Acid (8)Benzofuran-3(2H)-One (15)Benzofuran-3-Carboxylic Acid (6)Benzofuran-3-Yl(Phenyl)Methanone (11)Methyl Benzofuran-2-Carboxylate (6)
Benzothiazoles (2422)
Benzothiazole-Carboxylic Acid (27)Bromobenzothiazole (7)Dichlorobenzothiazole (10)Methoxybenzothiazole (4)Methylbenzothiazole (7)2-(Methylthio)Benzo[D]Thiazole (6)2-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (28)2-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (21)2-Methylbenzo[D]Thiazole (26)4-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (9)4-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (7)4-Fluorobenzo[D]Thiazole (6)4-Methylbenzo[D]Thiazole (10)5-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (5)5-Nitrobenzo[D]Thiazole (3)6-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (7)6-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (6)6-Fluorobenzo[D]Thiazole (5)6-Methoxybenzo[D]Thiazole (6)6-Methylbenzo[D]Thiazole (6)6-Nitrobenzo[D]Thiazole (3)7-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (8)7-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (6)7-Fluorobenzo[D]Thiazole (9)Benzo[D]Thiazol-2-Amine (29)Benzo[D]Thiazol-5-Amine (3)Benzo[D]Thiazol-6-Amine (3)Benzo[D]Thiazol-6-Ol (2)Benzo[D]Thiazole-2-Carbonitrile (11)Benzo[D]Thiazole-2-Thiol (11)Benzo[D]Thiazole-6-Carboxylic Acid (5)Methyl Benzo[D]Thiazole-6-Carboxylate (5)
Benzothiophenes (1116)
Benzothiophene-Carboxylic Acid (58)2-(Benzo[B]Thiophen-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (10)2-Methylbenzo[B]Thiophene (4)3-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (5)3-Chlorobenzo[B]Thiophene (6)3-Methylbenzo[B]Thiophene (4)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrobenzo[B]Thiophene (21)5-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (3)5-Chlorobenzo[B]Thiophene (4)6-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (4)7-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (5)Benzo[B]Thiophen-2-Amine (5)Benzo[B]Thiophen-2-Ylboronic Acid (5)Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carbaldehyde (7)Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carbonitrile (3)Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carboxylic Acid (32)Benzo[B]Thiophene-3-Carbaldehyde (6)Ethyl Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carboxylate (9)Methyl Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carboxylate (27)
Benzoxazoles (2804)
Benzoxazole-Carboxylic Acid (25)2-Chlorobenzo[D]Oxazole (11)2-Methylbenzo[D]Oxazole (26)2-Phenylbenzo[D]Oxazole (22)3-Phenylbenzo[D]Oxazol-3-Ium (8)5-Bromobenzo[D]Oxazole (3)5-Chlorobenzo[D]Oxazole (5)5-Methylbenzo[D]Oxazole (3)6-Chlorobenzo[D]Oxazole (4)Benzo[D]Oxazol-2-Amine (16)Benzo[D]Oxazole-2-Thiol (6)Methyl Benzo[D]Oxazole-2-Carboxylate (3)
Carbazole Series (482)
Carbazolyl-Phenyl-Boronic Acid/Ester (14)1-Methyl-9H-Carbazole (7)2,3,4,9-Tetrahydro-1H-Carbazol-1-One (7)2-Bromo-9H-Carbazole (4)3,9-Diphenyl-9H-Carbazole (7)3-(Tert-Butyl)-9H-Carbazole (3)3-Bromo-9-Phenyl-9H-Carbazole (16)3-Bromo-9H-Carbazole (4)3-Chloro-9H-Carbazole (3)3-Methyl-9H-Carbazole (3)7H-Benzo[C]Carbazole (5)9-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Yl)-9H-Carbazole (9)9-(P-Tolyl)-9H-Carbazole (5)9-Benzyl-9H-Carbazole (7)9-Ethyl-9H-Carbazole (10)
Dioxolanes (1580)
(3As,6As)-Tetrahydrofuro[3,4-D][1,3]Dioxole (6)1,3-Dioxolan-2-One (11)2,2-Difluorobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (24)2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-Dioxolane (29)2,2-Dimethylbenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (7)2-Phenyl-1,3-Dioxolane (18)4-Bromobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (6)4-Methyl-1,3-Dioxolane (5)5,6-Dihydro-[1,3]Dioxolo[4,5-G]Isoquinolino[3,2-A]Isoquinolin-7-Ium (4)5-Bromobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (12)5-Chlorobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (5)5-Nitrobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (4)9-((3As,4R,6Ar)-Tetrahydrofuro[3,4-D][1,3]Dioxol-4-Yl)-9H-Purine (7)Benzo[D][1,3]Dioxol-5-Amine (3)
Furans (7000)
Aminodihydrofuran (7)Bromofuran (32)Chlorofuran (2)Chlorofuro (11)Cyanofuran (53)Dibromofuran (5)Dihydrofuran (31)Dihydrofuro (15)Dihydroxydihydrofuran (8)Dimethylfuran (10)Formylfuran (10)Hexahydrofuro (6)Hydroxydihydrofuran (31)Methyldihydrofuran (11)Methylfuran (58)Nitrofuran (10)2,3-Dihydrofuran-3-One (9)2-(Bromomethyl)Furan (3)2-(Chloromethyl)Furan (3)2-(Furan-2-Yl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (6)2-Bromofuran (21)2-Chlorofuran (3)2-Methylfuran (37)2-Nitrofuran (9)3-Bromofuran (13)4-Methylisobenzofuran-1(3H)-One (3)5-Nitro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (3)5-Phenylfuran-2-Carbaldehyde (9)5-Phenylfuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)6-Chloro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (3)6-Fluoroisobenzofuran-1(3H)-One (3)7-Chloro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (3)Ethyl Furan-2-Carboxylate (6)Furan-2,5-Dione (8)Furan-2-Carbaldehyde (22)Furan-2-Carbonitrile (8)Furan-2-Carboxylic Acid (31)Furan-2-Ylmethanol (5)Furan-3-Carboxylic Acid (11)Furo[3,2-B]Pyridine (7)Furo[3,2-C]Pyridine (7)Methyl Furan-2-Carboxylate (20)N-(Furan-2-Ylmethyl)Aniline (5)
Imidazoles (833)
Biimidazole (5)Bromoimidazo (102)Dibromoimidazo (8)Dichloroimidazo (9)Dihydroimidazo (25)Imidazol-Amine (1)Methoxyimidazo (13)Methylimidazo (121)Tetrahydroimidazo (40)1,1'-Diphenyl-4,4',5,5'-Tetrahydro-1H,1'H-2,2'-Biimidazole (11)1,2-Dimethyl-1H-Imidazole (6)1,3-Diphenyl-1H-Imidazol-3-Ium (14)1,3-Diphenyl-4,5-Dihydro-1H-Imidazol-3-Ium (5)1-(Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (3)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-Imidazole (5)1-Benzyl-1H-Imidazole (19)1-Decyl-3-Methyl-1H-Imidazol-3-Ium (14)1-Ethyl-1H-Imidazole (3)1-Isopropyl-1H-Imidazole (5)1-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (5)1-Trityl-1H-Imidazole (15)1H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine (14)1H-Imidazo[4,5-C]Pyridine (12)1H-Imidazol-2-Amine (6)1H-Imidazole-2-Carboxylic Acid (7)1H-Imidazole-4-Carbonitrile (2)1H-Imidazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (4)2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (5)2-Bromo-1H-Imidazole (13)2-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (5)2-Ethyl-1H-Imidazole (3)2-Methyl-1-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (11)2-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (8)2-Phenyl-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (26)2-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (26)2-Phenylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (12)2-Propyl-1H-Imidazole (5)3-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrazine (6)3-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (26)3-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrimidine (6)3-Iodoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (10)3-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-C]Pyridine (5)4-(1H-Imidazol-1-Yl)Benzaldehyde (7)4-Bromo-1-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (9)4-Methyl-1-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (7)4-Methyl-1H-Imidazole (6)4-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (8)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrazine (15)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (12)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroimidazo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (11)5-Benzyl-1H-Imidazole (1)5-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (6)5-Chloro-1H-Imidazole (2)5-Fluoro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (12)5-Iodo-1H-Imidazole (4)5-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (4)5-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (6)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Pyrrolo[1,2-A]Imidazole (9)6-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrazine (11)6-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (14)6-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrimidine (5)6-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (4)6-Chloroimidazo[1,2-B]Pyridazine (30)7-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)8-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrazine (7)8-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (15)8-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrazine (8)8-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (7)8-Fluoroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)8-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (9)Ethyl 1H-Imidazole-2-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl 2-(Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-3-Yl)Acetate (3)Ethyl Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-2-Carboxylate (25)Ethyl Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (13)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-3-Amine (7)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-8-Amine (7)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-8-Ol (3)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-2-Carbaldehyde (8)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-2-Carboxylic Acid (21)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-3-Carbaldehyde (9)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-7-Carboxylic Acid (5)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-8-Carboxylic Acid (6)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyrimidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (5)Imidazo[1,2-C]Pyrimidine (6)Imidazo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (9)Imidazo[2,1-B]Thiazole (14)Methyl 1H-Imidazole-2-Carboxylate (4)Methyl 1H-Imidazole-5-Carboxylate (8)Methyl Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-8-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl 1H-Imidazole-1-Carboxylate (6)
Indazoles (3081)
Indazol-Amide (3)(1H-Indazol-4-Yl)Boronic Acid (3)(1H-Indazol-6-Yl)Boronic Acid (4)1-(1H-Indazol-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (7)1-(Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)-1H-Indazole (17)1-Benzyl-1H-Indazole (7)1-Ethyl-1H-Indazole (7)1H-Indazol-3-Amine (23)1H-Indazol-3-Ol (10)1H-Indazol-4-Amine (12)1H-Indazol-4-Ol (4)1H-Indazol-5-Amine (3)1H-Indazol-6-Amine (5)1H-Indazol-6-Ol (6)1H-Indazol-7-Amine (6)1H-Indazole-3-Carbaldehyde (19)1H-Indazole-3-Carbonitrile (9)1H-Indazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (27)1H-Indazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (9)1H-Indazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Indazole-7-Carboxylic Acid (6)2,3-Dimethyl-2H-Indazole (4)2-Methyl-2H-Indazole (34)3-(Piperidin-4-Yl)-1H-Indazole (5)3-Chloro-1H-Indazole (13)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H-Indazole (12)4-Chloro-1H-Indazole (18)4-Fluoro-1H-Indazole (22)4-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (7)4-Methyl-1H-Indazole (12)4-Nitro-1H-Indazole (10)5-Bromo-1H-Indazole (14)5-Chloro-1H-Indazole (9)5-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (5)5-Nitro-1H-Indazole (5)6-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Indazole (6)6-Bromo-1H-Indazole (23)6-Chloro-1H-Indazole (14)6-Fluoro-1H-Indazole (15)6-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (14)6-Methyl-1H-Indazole (9)6-Nitro-1H-Indazole (9)7-Bromo-1H-Indazole (18)7-Chloro-1H-Indazole (7)7-Fluoro-1H-Indazole (12)7-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (5)7-Nitro-1H-Indazole (11)Methyl 1H-Indazole-3-Carboxylate (23)Methyl 1H-Indazole-4-Carboxylate (10)Methyl 1H-Indazole-5-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 1H-Indazole-6-Carboxylate (9)Methyl 1H-Indazole-7-Carboxylate (8)Methyl 2-Methyl-2H-Indazole-3-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl 1H-Indazole-1-Carboxylate (29)
Indoles (7683)
Azaindole (44)Benzyloxyindole (1)Biindolinylidene (1)Bromo-Indole-Carboxylic Acid (28)Cyanoindole (5)Dihydroindolo (14)Fluoroindole (5)Formylindole (44)Hydroxyindole (7)Hydroxyisoindoline (2)Indolecarboxylic (2)Isoindole (26)Methoxyindole (9)Nitroindole (6)(1-(Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-1H-Indol-2-Yl)Boronic Acid (17)(1H-Indol-2-Yl)Boronic Acid (3)(1H-Indol-2-Yl)Methanol (8)(3As,7As)-Octahydro-1H-Indole (5)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethyl)Carbamate (12)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydrocyclopenta[B]Indole (5)1,2-Dimethyl-1H-Indole (4)1-(1H-Indol-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (6)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-Indole (26)1-(Triisopropylsilyl)-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (8)1-Benzyl-1H-Indole (10)1-Ethyl-1H-Indole (7)1-Methyl-1H-Indole (85)1-Methyl-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylic Acid (8)1-Methyl-1H-Indole-3-Carbaldehyde (9)1-Methyl-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (14)1-Phenyl-1H-Indole (5)1H-Indol-3-Ol (5)1H-Indol-3-Yl Acetate (4)1H-Indol-4-Amine (10)1H-Indol-4-Ol (7)1H-Indol-5-Ol (4)1H-Indol-6-Amine (21)1H-Indol-6-Ol (6)1H-Indol-7-Amine (10)1H-Indole-2-Carbaldehyde (20)1H-Indole-2-Carbonitrile (9)1H-Indole-3-Carbonitrile (17)1H-Indole-3-Carboxylic Acid (32)1H-Indole-4-Carboxylic Acid (10)1H-Indole-5-Carbonitrile (5)1H-Indole-5-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Indole-6-Carbonitrile (4)1H-Indole-6-Carboxylic Acid (5)1H-Indole-7-Carbonitrile (6)1H-Indole-7-Carboxylic Acid (7)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-3-Carbaldehyde (14)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-5-Carbaldehyde (5)2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrido[4,3-B]Indole (12)2,3,4,9-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrido[3,4-B]Indole (12)2,3-Dimethyl-1H-Indole (9)2-(1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1-Methyl-1H-Indole (6)2-(1H-Indol-1-Yl)Acetic Acid (5)2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (28)2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (4)2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (10)2-(2-Methyl-1H-Indol-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (5)2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1H-Indole (4)2-Methyl-1H-Indole-3-Carbaldehyde (3)2-Methyl-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (12)3-(1-Oxoisoindolin-2-Yl)Piperidine-2,6-Dione (21)3-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Propanoic Acid (4)3-(Piperidin-4-Yl)-1H-Indole (8)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (11)3-Methyl-1H-Indole (41)3H-Indole (8)4-Bromo-1H-Indole (25)4-Chloro-1H-Indole (21)4-Fluoro-1H-Indole (24)4-Fluoro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (6)4-Fluoroindoline-2,3-Dione (3)4-Methoxy-1H-Indole (11)4-Methyl-1H-Indole (23)4-Nitro-1H-Indole (6)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Indole (5)5-(Benzyloxy)-1H-Indole (8)5-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Indole (4)5-Chloro-1H-Indole (64)5-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)5-Fluoro-1H-Indole (50)5-Fluoro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (9)5-Fluoroindolin-2-One (4)5-Methoxy-1H-Indole (11)5-Methoxy-2-Methyl-1H-Indole (5)5-Methyl-1H-Indole (33)5-Nitro-1H-Indole (6)6-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Indole (5)6-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Indole (3)6-Bromo-1H-Indole (15)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (6)6-Chloro-1H-Indole (19)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)6-Fluoro-1H-Indole (17)6-Methoxy-1H-Indole (12)6-Methyl-1H-Indole (29)6-Methyl-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (8)6-Nitro-1H-Indole (8)7-Bromo-1H-Indole (28)7-Bromoindoline-2,3-Dione (3)7-Chloro-1H-Indole (29)7-Fluoro-1H-Indole (24)7-Fluoro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylic Acid (5)7-Methoxy-1H-Indole (8)7-Methyl-1H-Indole (34)7-Nitro-1H-Indole (11)9H-Pyrido[3,4-B]Indole (5)Benzo[Cd]Indol-2(1H)-One (5)Ethyl 1H-Indole-3-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl 5-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 5-Fluoro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 6-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 7-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 1H-Indole-3-Carboxylate (21)Methyl 1H-Indole-4-Carboxylate (9)Methyl 1H-Indole-5-Carboxylate (7)Methyl 1H-Indole-6-Carboxylate (9)Methyl 1H-Indole-7-Carboxylate (7)Methyl 2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Acetate (3)N-(2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethyl)Acetamide (5)Spiro[Indoline-3,4'-Piperidin]-2-One (18)Tert-Butyl 1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (18)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-1-Carboxylate (9)Tert-Butyl 2-(1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (6)Tert-Butyl 3-(Hydroxymethyl)-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (10)Tert-Butyl 3-Bromo-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (9)Tert-Butyl 3-Iodo-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (7)Tert-Butyl 5-Methoxy-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (6)Tryptophan (21)
Indolines (4489)
Aminoindoline (10)Bromoindoline (17)Bromoisoindolin (5)Bromoisoindoline (6)Chloroindolin (4)Chloroisoindoline (3)Dibromoindoline (12)Dichloroindoline (16)Difluoroindoline (1)Dimethylindoline (21)Dioxoindoline (8)Dioxoisoindolin (72)Fluoroindolin (9)Fluoroindoline (9)Fluoroisoindoline (10)Hydroxyindolin (5)Indoline-Carboxylate (1)Isoindoline (20)Methoxyindoline (12)Methoxyisoindoline (9)Methylindoline (46)Methylisoindoline (18)Nitroindolin (6)Nitroindoline (11)Nitroisoindoline (8)Oxoindoline (32)Oxoisoindoline (16)Spiro-Indoline-Piperidine (34)(E)-[3,3'-Biindolinylidene]-2,2'-Dione (5)(Z)-3-((1H-Pyrrol-2-Yl)Methylene)Indolin-2-One (8)(Z)-3-(Phenyl(Phenylamino)Methylene)Indolin-2-One (5)(Z)-3-Benzylideneindolin-2-One (7)1-(Indolin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-Benzylindoline-2,3-Dione (5)1-Methylindolin-2-One (14)1-Methylindoline (3)1-Methylindoline-2,3-Dione (8)2-(1,3-Dioxoisoindolin-2-Yl)Propanoic Acid (3)2-Methylindoline (7)2-Methylisoindolin-1-One (7)3,3-Dimethylindolin-2-One (5)3,3-Dimethylindoline (7)4-Bromoindoline (4)4-Chloroindoline-2,3-Dione (6)4-Methylindoline (3)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Indoline (5)5-Bromoindolin-2-One (5)5-Bromoindoline (8)5-Bromoisoindoline-1,3-Dione (3)5-Chloroindolin-2-One (3)5-Fluoroindoline (3)5-Methoxyindoline (4)5-Methylindolin-2-One (3)5-Methylindoline (3)6-Bromoindolin-2-One (8)6-Bromoindoline-2,3-Dione (4)6-Chloroindolin-2-One (5)6-Chloroindoline (3)6-Chloroindoline-2,3-Dione (5)6-Fluoroindolin-2-One (5)6-Fluoroindoline-2,3-Dione (3)7-Bromoindoline (3)7-Fluoroindolin-2-One (3)7-Fluoroindoline-2,3-Dione (6)7-Methylindoline-2,3-Dione (7)Indoline-2-Carboxylic Acid (3)Methyl Indoline-6-Carboxylate (3)Spiro[Cyclopropane-1,3'-Indolin]-2'-One (6)Tert-Butyl Indoline-1-Carboxylate (24)
Isoquinolines (2729)
Bromoisoquinoline (69)Chloroisoquinoline (101)Dibromoisoquinoline (9)Dichloroisoquinoline (14)Dihydroisoquinoline (107)Fluoroisoquinoline (78)Methoxyisoquinoline (59)Methylisoquinoline (59)Nitroisoquinoline (23)1,3-Dichloroisoquinoline (14)1-Bromoisoquinoline (20)1-Chloroisoquinoline (20)1-Methylisoquinoline (9)1H-Benzo[De]Isoquinoline-1,3(2H)-Dione (14)2-Methyl-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (6)3-Bromoisoquinoline (10)3-Chloroisoquinoline (20)3-Methylisoquinoline (8)4-Bromoisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (3)4-Bromoisoquinoline (33)4-Chloroisoquinoline (11)4-Fluoroisoquinoline (6)5,6-Dihydro-[1,3]Dioxolo[4,5-G]Isoquinolino[3,2-A]Isoquinolin-7-Ium (4)5-Bromoisoquinoline (17)5-Chloroisoquinoline (6)5-Methoxyisoquinoline (6)5-Nitroisoquinoline (7)6-Bromo-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (6)6-Bromoisoquinoline (9)6-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (3)7-Bromo-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (6)7-Bromoisoquinoline (6)7-Chloroisoquinoline (6)7-Fluoroisoquinoline (3)7-Methoxyisoquinoline (5)8-Bromoisoquinoline (17)8-Chloroisoquinoline (7)8-Fluoroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (3)8-Fluoroisoquinoline (10)8-Methoxyisoquinoline (7)Isoquinolin-1-Amine (18)Isoquinolin-1-Ol (9)Isoquinolin-3-Amine (13)Isoquinolin-3-Ol (6)Isoquinolin-4-Amine (16)Isoquinolin-4-Ol (9)Isoquinolin-4-Ylboronic Acid (3)Isoquinolin-5-Amine (9)Isoquinolin-5-Ol (7)Isoquinolin-8-Amine (6)Isoquinoline-1-Carbonitrile (7)Isoquinoline-1-Carboxylic Acid (10)Isoquinoline-3-Carboxylic Acid (7)Isoquinoline-4-Carboxylic Acid (12)Isoquinoline-5-Carboxylic Acid (5)Isoquinoline-5-Sulfonyl Chloride (3)Isoquinoline-6-Carboxylic Acid (3)Methyl Isoquinoline-3-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Isoquinoline-4-Carboxylate (6)Tert-Butyl 3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-Carboxylate (19)
Isoxazoles (3403)
Aminoisoxazole (7)Bromoisoxazole (5)Dihydroisoxazol (2)Dimethylisoxazole (17)Phenylisoxazole (28)(3-Phenylisoxazol-5-Yl)Methanol (7)3-Bromoisoxazole (7)3-Methyl-5-Phenylisoxazole (6)3-Methylisoxazole (30)3-Phenylisoxazol-5-Amine (8)5-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Isoxazole (5)5-Cyclopropylisoxazole (5)5-Methyl-3-Phenylisoxazole (4)5-Methylisoxazole (16)5-Phenylisoxazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (15)Ethyl Isoxazole-3-Carboxylate (8)Ethyl Isoxazole-4-Carboxylate (5)Isoxazol-3-Amine (7)Isoxazol-3-Ylmethanol (3)Isoxazol-5-Amine (15)Isoxazol-5-Ylmethanol (5)Isoxazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (8)Isoxazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (7)Methyl 5-Phenylisoxazole-3-Carboxylate (6)N-((5R,6R)-7-Oxo-4-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[3.2.0]Heptan-6-Yl)-3-Phenylisoxazole-4-Carboxamide (1)
Morpholines (4988)
Benzylmorpholine (25)Cyanomorpholine (6)Dimorpholine (3)Ethylmorpholine (9)Isopropylmorpholine (9)Methylmorpholine (68)Morpholinobenzaldehyde (11)Morpholinobenzo (13)Morpholinobenzoic (8)Morpholinoethanone (5)Morpholinoethoxy (1)Morpholinoethyl (5)Morpholinomethyl (16)Morpholinophenyl (14)Morpholinopropoxy (6)Morpholinopyrimidin (6)Morpholinosulfonyl (7)Oxomorpholine (6)(R)-3-Phenylmorpholine (7)(S)-3-Phenylmorpholine (10)2,2-Dimethylmorpholine (5)2,6-Dimethylmorpholine (5)2-(Methoxymethyl)Morpholine (4)2-(Morpholin-2-Yl)Acetic Acid (5)2-Ethylmorpholine (3)2-Isopropylmorpholine (4)2-Methylmorpholine (7)2-Phenylmorpholine (8)3-(4-Morpholinophenyl)Oxazolidin-2-One (4)3-(Methoxymethyl)Morpholine (4)3-Ethylmorpholine (4)3-Isopropylmorpholine (5)3-Methylmorpholine (13)3-Phenylmorpholine (8)4-(2-Fluorophenyl)Morpholine (8)4-(3-Phenoxypropyl)Morpholine (7)4-(O-Tolyl)Morpholine (6)4-(Pyrazin-2-Yl)Morpholine (5)4-(Pyridin-4-Yl)Morpholine (5)4-(Pyrimidin-2-Yl)Morpholine (9)4-Benzylmorpholin-3-One (6)4-Morpholinoaniline (4)4-Morpholinobenzaldehyde (8)4-Morpholinobenzoic Acid (5)4-Phenylmorpholin-3-One (6)6,6-Dimethylmorpholine-3-Carboxylic Acid (5)Benzyl Morpholine-4-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Morpholine-2-Carboxylate (4)Methyl 2-(Morpholin-3-Yl)Acetate (3)Methyl Morpholine-2-Carboxylate (4)Methyl Morpholine-3-Carboxylate (10)Morpholin-2-Ylmethanamine (8)Morpholin-2-Ylmethanol (12)Morpholin-3-Ylmethanol (14)Morpholine-2-Carbonitrile (4)Morpholine-2-Carboxylic Acid (12)Morpholine-3-Carboxylic Acid (10)Morpholino(Phenyl)Methanone (11)Tert-Butyl (Morpholin-2-Ylmethyl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl 2-(Bromomethyl)Morpholine-4-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl Morpholine-4-Carboxylate (23)
Oxazines (235)
2,2-Dimethyl-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (3)2-Methyl-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (3)2H-Pyrido[3,2-B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (8)3,4-Dihydro-2H-Pyrido[3,2-B][1,4]Oxazine (5)6-Amino-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (3)6-Bromo-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (7)6-Bromo-3,4-Dihydro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazine (5)6-Chloro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (8)6-Chloro-3,4-Dihydro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazine (5)7-Bromo-3,4-Dihydro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazine (7)Spiro[Benzo[D][1,3]Oxazine-4,4'-Piperidin]-2(1H)-One (5)
Oxazoles (2026)
Bioxazole (12)2-Bromooxazole (7)2-Chlorooxazole (7)2-Methyloxazole (19)2-Phenyloxazole (16)3,4-Diphenylisoxazole (8)4,5-Diphenyloxazole (7)4-(Oxazol-5-Yl)Aniline (3)4-Methyloxazole (9)5-(4-Nitrophenyl)Oxazole (3)5-Methyloxazole (5)6-Bromobenzo[D]Oxazole (3)Ethyl Oxazole-4-Carboxylate (8)Ethyl Oxazole-5-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Oxazole-4-Carboxylate (9)Oxazol-2-Amine (8)Oxazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (4)Oxazolo[4,5-B]Pyridine (7)Oxazolo[5,4-B]Pyridine (5)
Oxazolidines (1298)
Dimethyloxazolidin (6)Dioxooxazolidin (2)Oxazolidinone (5)Phenyloxazolidin (9)Propionyloxazolidin (5)(R)-4-Benzyloxazolidin-2-One (5)(S)-4-Benzyloxazolidin-2-One (11)3-(4-Morpholinophenyl)Oxazolidin-2-One (4)3-Phenyloxazolidin-2-One (4)4-Isopropyloxazolidine (6)Oxazolidine (21)Oxazolidine-2,5-Dione (9)
Oxazolines (1577)
(3Ar,8As)-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-3A,8A-Dihydro-8H-Indeno[1,2-D]Oxazole (6)(3As,8Ar)-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-3A,8A-Dihydro-8H-Indeno[1,2-D]Oxazole (7)(4R,5S)-4,5-Diphenyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (5)(R)-4-Benzyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (7)(R)-4-Phenyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (7)(S)-4-Benzyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (8)(S)-4-Phenyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (6)1,3-Bis(4,5-Dihydrooxazol-2-Yl)Benzene (8)2,2'-(1,3-Diphenylpropane-2,2-Diyl)Bis(4,5-Dihydrooxazole) (5)2,2'-(2-Phenylethane-1,1-Diyl)Bis(4,5-Dihydrooxazole) (5)2,3-Dihydropyrazolo[5,1-B]Oxazole (7)2,6-Bis(4,5-Dihydrooxazol-2-Yl)Pyridine (12)2-(6-Benzhydrylpyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (10)2-(6-Cyclopropylpyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (10)2-(Benzo[B]Thiophen-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (10)2-(Pyridin-2-Ylmethyl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (14)2-(Quinolin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (7)2-Phenyl-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (18)4,4',5,5'-Tetrahydro-2,2'-Bioxazole (10)4-(Tert-Butyl)-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (16)4-Isopropyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (16)Bis((3Ar,8As)-3A,8A-Dihydro-8H-Indeno[1,2-D]Oxazol-2-Yl)Methane (5)Bis((3As,8Ar)-3A,8A-Dihydro-8H-Indeno[1,2-D]Oxazol-2-Yl)Methane (5)Bis(4,5-Dihydrooxazol-2-Yl)Methane (22)
Piperazines (7427)
Isobutylpiperazine (6)Propylpiperazine (10)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (7)(R)-2-Benzylpiperazine (5)1,4-Diphenylpiperazine (7)1-(2-Chlorophenyl)Piperazine (4)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Piperazine (8)1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Piperazine (4)1-(4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenyl)Piperazine (10)1-(5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine (6)1-(Methylsulfonyl)Piperazine (5)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)Piperazine (17)1-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Piperazine (6)1-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Piperazine (13)1-(Pyridin-3-Ylmethyl)Piperazine (6)1-Benzhydryl-4-Benzylpiperazine (1)1-Benzhydrylpiperazine (9)1-Benzyl 4-(Tert-Butyl) Piperazine-1,4-Dicarboxylate (10)1-Benzyl-4-Methylpiperazine (10)1-Ethyl-4-Phenylpiperazine (4)1-Ethylpiperazine (5)1-Isopropylpiperazine (4)1-Methyl-4-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine (5)1-Methyl-4-Phenylpiperazine (22)1-Methylpiperazin-2-One (6)1-Methylpiperazine (21)10-(3-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Propyl)-10H-Phenothiazine (2)2-(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (10)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Benzonitrile (6)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (8)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (10)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyrazine (9)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (11)2-Phenylpiperazine (17)3-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Aniline (3)3-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Benzoic Acid (3)3-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyridazine (7)3-Methylpiperazin-2-One (7)4-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Benzaldehyde (5)4-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (13)Benzyl 2-Methylpiperazine-1-Carboxylate (7)Benzyl 3-(Hydroxymethyl)Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (6)Benzyl 3-Methylpiperazine-1-Carboxylate (5)Phenyl(Piperazin-1-Yl)Methanone (20)Piperazine-2,5-Dione (9)Tert-Butyl 3-Oxopiperazine-1-Carboxylate (7)Tert-Butyl 4-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (12)Tert-Butyl 4-Benzylpiperazine-1-Carboxylate (13)Tert-Butyl 4-Phenylpiperazine-1-Carboxylate (23)Tert-Butyl Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (30)
Piperidines (21889)
Bipiperidine (12)Chloropiperidine (6)Dimethylpiperidine (46)Ethynylpiperidine (5)Fluoropiperidine (33)Formylpiperidine (9)Isopropylpiperidine (11)Piperidine-Carboxylate (3)Piperidineacetic (5)Piperidinecarboxylic (6)Piperidinyl-Phenyl-Boronic Acid/Ester (32)Propylpiperidine (8)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl Piperidine-1-Carboxylate (16)(E)-N-(3-Oxo-1-Phenyl-3-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Prop-1-En-2-Yl)Benzamide (6)(R)-2-Phenylpiperidine (10)(R)-3-Aminopiperidin-2-One (3)(R)-N-(Piperidin-3-Yl)-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidin-4-Amine (5)(S)-2-Phenylpiperidine (11)(S)-N-Phenylpiperidine-2-Carboxamide (1)1,3-Dihydrospiro[Indene-2,4'-Piperidine] (5)1,4'-Bipiperidine (8)1-((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Piperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (5)1-((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Piperidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (3)1-(Methylsulfonyl)Piperidine (6)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)Piperidine (23)1-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (13)1-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Piperazine (6)1-Benzyl 3-Methyl Piperidine-1,3-Dicarboxylate (3)1-Benzyl-N-Methylpiperidin-3-Amine (6)1-Benzylpiperidin-3-One (5)1-Benzylpiperidin-4-Amine (8)1-Benzylpiperidin-4-One (8)1-Isopropylpiperidine (5)1-Methyl-4-Phenylpiperidine (4)1-Methylpiperidin-2-One (3)1-Oxa-8-Azaspiro[4.5]Decane (5)1-Phenylpiperidin-2-One (8)2,2-Dimethylpiperidin-4-One (6)2,2-Dimethylpiperidine (21)2,7-Diazaspiro[3.5]Nonane (7)2,8-Diazaspiro[4.5]Decan-3-One (6)2,8-Diazaspiro[4.5]Decane (5)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (8)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (10)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyridine (11)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (16)2-(Piperidin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (8)2-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (5)2-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-Methylpiperidin-4-One (6)2-Methylpiperidine (14)2-Phenylpiperidine (14)3,3-Difluoropiperidin-4-One (3)3,3-Difluoropiperidine (29)3,3-Dimethylpiperidin-4-One (3)3,3-Dimethylpiperidine (5)3-(1-Oxoisoindolin-2-Yl)Piperidine-2,6-Dione (21)3-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyridine (5)3-(Piperidin-4-Yl)-1H-Indazole (5)3-(Piperidin-4-Yl)-1H-Indole (8)3-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Pyridine (5)3-Fluoropiperidin-4-One (3)3-Fluoropiperidine (26)3-Methoxypiperidine (7)3-Methylpiperidin-4-One (3)3-Methylpiperidine (10)3-Phenylpiperidine (6)4,4-Difluoropiperidine (5)4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Piperidine (11)4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (11)4-(Azetidin-1-Yl)Piperidine (6)4-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (8)4-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Piperidine (6)4-Benzylpiperidine (18)4-Hydrazineylpiperidine (5)4-Hydroxypiperidin-2-One (3)4-Methyl-1-Phenylpiperidine (6)4-Methylenepiperidine (14)4-Oxopiperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (3)4-Phenylpiperidin-4-Ol (10)5-Hydroxypiperidin-2-One (3)6-Azaspiro[2.5]Octane (10)6-Oxopiperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (3)7-Azaspiro[3.5]Nonane (7)Azepane (25)Benzyl 3-Hydroxypiperidine-1-Carboxylate (7)Benzyl 4-Oxopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (12)Benzyl Piperidin-4-Ylcarbamate (7)Benzyl Piperidine-1-Carboxylate (50)Benzyl-3-Aminopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl Piperidine-1-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Piperidine-2-Carboxylate (9)Ethyl Piperidine-3-Carboxylate (14)Ethyl Piperidine-4-Carboxylate (10)Methyl 4-Oxopiperidine-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Piperidine-2-Carboxylate (12)Methyl Piperidine-3-Carboxylate (19)N-Benzylpiperidin-4-Amine (3)N-Methylpiperidin-3-Amine (5)N-Phenylpiperidine-2-Carboxamide (2)Phenyl(Piperidin-1-Yl)Methanone (21)Phenyl(Piperidin-4-Yl)Methanone (21)Piperidin-2-Ylmethanamine (6)Piperidin-2-Ylmethanol (11)Piperidin-3-Amine (17)Piperidin-3-Ol (27)Piperidin-3-One (13)Piperidin-3-Ylmethanamine (5)Piperidin-3-Ylmethanol (15)Piperidin-4-Amine (14)Piperidin-4-Ol (44)Piperidin-4-Ylmethanamine (7)Piperidin-4-Ylmethanol (11)Piperidine-2,4-Dione (5)Piperidine-2,6-Dione (13)Piperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (26)Piperidine-3-Carboxamide (5)Piperidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)Piperidine-4-Carboxylic Acid (11)Quinuclidine (5)Spiro[Benzo[D][1,3]Oxazine-4,4'-Piperidin]-2(1H)-One (5)Spiro[Chromane-2,4'-Piperidin]-4-One (6)Spiro[Indene-2,4'-Piperidin]-1(3H)-One (5)Spiro[Indoline-3,4'-Piperidin]-2-One (18)Spiro[Indoline-3,4'-Piperidine] (5)Tert-Butyl (2-Oxopiperidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (4)Tert-Butyl (6-Oxopiperidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (Piperidin-3-Ylmethyl)Carbamate (5)Tert-Butyl 2-Oxopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl 3-Bromopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (4)Tert-Butyl 4-Oxopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (16)Tert-Butyl 4-Phenoxypiperidine-1-Carboxylate (12)Tert-Butyl 4-Phenylpiperidine-1-Carboxylate (16)Tert-Butyl Piperidin-3-Ylcarbamate (9)
Purines (2020)
(R)-N-(9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purin-6-Yl)Benzamide (5)2-(Acetoxymethyl)-5-(9H-Purin-9-Yl)Tetrahydrofuran-3,4-Diyl Diacetate (6)2-(Hydroxymethyl)-5-(9H-Purin-9-Yl)Tetrahydrofuran-3,4-Diol (27)2-Chloro-7H-Purine (3)2-Chloro-9H-Purine (5)7H-Purin-2-Amine (6)7H-Purin-6-Amine (9)9-((3As,4R,6Ar)-Tetrahydrofuro[3,4-D][1,3]Dioxol-4-Yl)-9H-Purine (7)9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purin-6-Amine (30)9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purin-6-Ol (6)9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purine (2)9H-Purin-6-Amine (3)
Pyrans (1095)
Chromene-Carboxylic Acid (1)Thioglucopyranoside (4)(S)-2-Phenylchroman-4-One (17)1-(Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)-1H-Indazole (17)2,2-Dimethylchromane (5)2-(2-Oxo-2H-Chromen-4-Yl)Acetic Acid (4)2-Oxo-2H-Chromene-3-Carbonitrile (4)2-Oxo-2H-Chromene-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)2H-Chromene (16)3,4-Dihydro-2H-Pyran (11)3,6-Dihydro-2H-Pyran (8)3-Acetyl-2H-Chromen-2-One (3)3-Hydroxy-2-Phenyl-4H-Chromen-4-One (21)4-(Trifluoromethyl)-2H-Chromen-2-One (6)4-Hydroxy-2H-Chromen-2-One (10)4-Methyl-2H-Chromen-2-One (27)5-Fluorochroman-4-One (3)5-Fluorochromane (6)5-Hydroxy-2-Phenyl-4H-Chromen-4-One (36)5-Methoxy-2-Phenyl-4H-Chromen-4-One (10)6-Bromochroman-4-One (6)6-Chlorochroman-4-One (6)6-Chlorochromane (6)6-Fluorochroman-4-One (5)6-Fluorochromane (6)6-Methoxychromane (5)7-(Diethylamino)-2H-Chromen-2-One (9)7-Bromochroman-4-One (4)7-Bromochromane (7)7-Chlorochromane (5)7-Fluorochroman-4-One (5)7-Hydroxy-2H-Chromen-2-One (23)7-Methoxy-2H-Chromen-2-One (12)7-Methoxychroman-4-One (3)8-Bromochroman-4-One (4)8-Bromochromane (6)8-Chlorochromane (5)8-Fluorochromane (5)8-Methylchroman-4-One (4)8-Methylchromane (10)Chroman-2-One (5)Chroman-2-Ylmethanamine (3)Chroman-3-Amine (3)Chroman-4-Amine (20)Chroman-4-Ol (4)Chromane-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)Chromane-3-Carboxylic Acid (4)Dihydro-2H-Pyran-2,6(3H)-Dione (5)Ethyl 2-Oxo-2H-Chromene-3-Carboxylate (5)Isochromane (11)Spiro[Chromane-2,4'-Piperidin]-4-One (6)Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-One (15)Tetrahydro-2H-Thiopyran (10)Tetrahydro-4H-Pyran-4-One (12)Thiochroman-4-One (10)
Pyrazines (3359)
Dibromopyrazine (7)Dichloropyrazine (21)Dihydropyrazine (6)Dimethylpyrazine (30)Ethoxypyrazine (5)Ethylpyrazine (7)Fluoropyrazine (6)Hydroxypyrazine (4)Iodopyrazine (17)Methoxypyrazine (36)Phenylpyrazin (5)Pyrazino (5)Pyrazino-Nitrile (50)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydropyrido[2,3-B]Pyrazine (5)1-(Pyrazin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyrazine (5)2,3-Diphenylpyrazine (5)2,5-Dibromopyrazine (4)2,5-Dichloropyrazine (4)2,6-Dibromopyrazine (9)2,6-Dichloropyrazine (14)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyrazine (9)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrazine (6)2-Bromo-3-Methoxypyrazine (5)2-Bromo-3-Methylpyrazine (5)2-Bromo-5-Chloropyrazine (6)2-Bromo-6-Chloropyrazine (5)2-Bromo-6-Methylpyrazine (5)2-Bromopyrazine (15)2-Chloro-3-Methylpyrazine (7)2-Chloro-6-Methylpyrazine (12)2-Chloropyrazine (24)2-Ethoxypyrazine (3)2-Ethylpyrazine (9)2-Fluoropyrazine (7)2-Iodopyrazine (25)2-Methoxypyrazine (45)2-Methylpyrazine (16)2-Phenylpyrazine (12)3-Chloropyrazin-2-Amine (6)3-Chloropyrazine-2-Carbonitrile (6)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (7)4-(Pyrazin-2-Yl)Morpholine (5)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydro-[1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A]Pyrazine (11)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrazine (15)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroimidazo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (11)5-Bromopyrazin-2-Amine (13)5-Bromopyrazin-2-Ol (5)5-Chloropyrazin-2-Amine (9)5H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyrazine (14)6-Bromopyrazin-2-Amine (5)6-Chloropyrazin-2-Amine (11)[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (9)[1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A]Pyrazine (11)Ethyl Pyrazine-2-Carboxylate (10)Imidazo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (9)Methyl 3-Bromopyrazine-2-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 6-Bromopyrazine-2-Carboxylate (7)Methyl 6-Chloropyrazine-2-Carboxylate (5)Methyl Pyrazine-2-Carboxylate (19)Pyrazin-2-Amine (22)Pyrazin-2-Ol (7)Pyrazin-2-Ylmethanamine (12)Pyrazine-2-Carbaldehyde (17)Pyrazine-2-Carbohydrazide (3)Pyrazine-2-Carbonitrile (15)Pyrazine-2-Carboxamide (10)Pyrazine-2-Carboxylic Acid (34)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (5)Pyrido[2,3-B]Pyrazine (12)Pyrido[3,4-B]Pyrazine (11)Tert-Butyl Pyrazin-2-Ylcarbamate (8)
Pyrazoles (16157)
Bipyrazole (5)Chloropyrazolo (33)Dichloropyrazolo (11)Dihydropyrazolo (28)Dimethylpyrazolo (6)Ethylpyrazole (7)Fluoropyrazolo (9)Hydroxypyrazolo (10)Methoxypyrazolo (16)Methyl-Pyrazole-Carboxylic Acid (147)Methyl-Pyrazolone (87)Methylpyrazolo (32)Pyrazolopyridine-Carboxylic Acid (48)Tetrahydropyrazolo (23)(1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Yl)Methanol (7)(1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-4-Yl)Boronic Acid (4)1,3-Dimethyl-1H-Pyrazole (28)1,3-Diphenyl-1H-Pyrazole (6)1,4,5,6-Tetrahydropyrrolo[3,4-C]Pyrazole (6)1,5-Diphenyl-1H-Pyrazole (13)1-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1H-Pyrazole (3)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-1H-Pyrazole (3)1-(4-Methoxybenzyl)-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-(Azetidin-3-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole (7)1-(Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole (9)1-(Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-4-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole (6)1-Benzyl-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (9)1-Benzyl-4-Bromo-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-Benzyl-4-Iodo-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-Cyclopentyl-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-Cyclopropyl-1H-Pyrazole (9)1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Amine (14)1-Methyl-3-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (21)1-Methyl-4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole (6)1-Methyl-5-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (7)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Amine (3)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Ol (3)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-5-Amine (4)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (10)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbaldehyde (8)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbonitrile (17)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (19)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (3)1-Phenyl-3-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-Trityl-1H-Pyrazole (5)1H-Pyrazol-4-Amine (6)1H-Pyrazol-4-Ol (3)1H-Pyrazol-5-Amine (19)1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbaldehyde (30)1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbonitrile (5)1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (9)1H-Pyrazole-4-Sulfonyl Chloride (8)1H-Pyrazole-5-Carboxamide (3)1H-Pyrazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (10)1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyrazine (5)1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridin-5-Amine (3)1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidin-4-Amine (5)1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-D]Pyrimidine (5)2,3-Dihydropyrazolo[5,1-B]Oxazole (7)2,4-Dihydro-3H-Pyrazol-3-One (10)2,6-Di(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Pyridine (16)2-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (6)2-(1H-Pyrazol-3-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-Phenyl-2,4-Dihydro-3H-Pyrazol-3-One (23)3-(Tert-Butyl)-1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (4)3-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (16)3-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (6)3-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (11)3-Chloro-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (7)3-Cyclopropyl-1H-Pyrazole (5)3-Iodo-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (6)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (4)3-Methyl-1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (23)3-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-5-Amine (11)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-C]Pyridine (7)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-C]Pyridine (14)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (7)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydropyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (6)4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Benzoic Acid (3)4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Piperidine (11)4-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (14)4-Bromo-1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (11)4-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (4)4-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (8)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazole (10)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (5)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (5)4-Iodo-1H-Pyrazole (9)4-Methyl-1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (6)4-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (11)4-Nitro-1H-Pyrazole (8)4-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (18)5,6-Dihydro-4H-Pyrrolo[1,2-B]Pyrazole (8)5-(Difluoromethyl)-1H-Pyrazole (6)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrazole (11)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (11)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-C]Pyridine (5)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrazole (8)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (3)5-Chloropyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (24)5-Cyclopropyl-1H-Pyrazole (6)5-Iodo-1H-Pyrazole (4)5-Nitro-1H-Pyrazole (9)5-Nitro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (3)5-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (15)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Pyrazolo[5,1-B][1,3]Oxazine (13)6-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (8)6-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (7)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (12)7-Chloropyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (8)Ethyl 1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-3-Carboxylate (4)Ethyl 1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylate (13)Ethyl 1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylate (11)Ethyl Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (11)Ethyl Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine-3-Carboxylate (6)Methyl 1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylate (10)Methyl 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine-5-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (16)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (5)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-2-Carboxylic Acid (5)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (13)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (7)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine-1-Carboxylate (7)Tert-Butyl 4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole-1-Carboxylate (3)
Pyridazines (2753)
Aminopyridazine (12)Dihydropyridazine (26)Dimethylpyridazine (9)Hexahydropyridazines (10)Pyridazinecarboxylic (1)2-Methylpyridazin-3(2H)-One (7)3,6-Dichloropyridazine (20)3-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyridazine (7)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridazine (3)3-Bromopyridazine (25)3-Chloro-4-Methylpyridazine (7)3-Chloropyridazine (44)3-Iodopyridazine (5)3-Methoxypyridazine (17)3-Methylpyridazine (6)3-Phenylpyridazine (8)4-Aminopyridazin-3(2H)-One (4)4-Bromopyridazin-3(2H)-One (3)4-Bromopyridazine (5)4-Chloropyridazin-3(2H)-One (4)4-Chloropyridazine (16)4-Methoxypyridazine (8)4-Methylpyridazine (3)6-Chloropyridazin-3(2H)-One (5)6-Chloropyridazin-3-Amine (5)[1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-B]Pyridazine (10)Ethyl Pyridazine-3-Carboxylate (6)Methyl Pyridazine-3-Carboxylate (7)Pyridazin-3-Amine (18)Pyridazin-3-Ol (3)Pyridazin-4-Amine (10)Pyridazine-3-Carboxylic Acid (7)
Pyridines (70617)
Acetylpyridin (5)Aminopicolinate (8)Benzyloxypyridine (36)Bipyridine (202)Bromopicolinate (19)Bromopicolinic (4)Bromopicolinic Acid (5)Bromopicolinonitrile (6)Bromopyrido (13)Butylpyridine (5)Chloroisonicotinic Acid (5)Chloronicotinaldehyde (23)Chloronicotinamide (11)Chloronicotinate (45)Chloronicotinic (41)Cyanopicolinate (7)Cyanopicolinic (6)Cyanopyridine (34)Cyclopropoxypyridine (6)Cyclopropylpyridine (30)Dibromopicolinate (4)Dibromopicolinic Acid (3)Dibromopyridine (36)Dichloropicolinate (9)Dichloropicolinonitrile (4)Dichloropyridine (120)Difluoropicolinic Acid (3)Difluoropyridine (58)Dihydropyrido (27)Diiodopyridine (13)Dimethoxypicolinic Acid (5)Dimethoxypyridine (33)Dimethylpyridine (143)Diphenylpyridine (6)Dipyridine (28)Ethoxypicolinic Acid (3)Ethoxypyridine (35)Ethylpyridine (36)Ethynylpicolinate (3)Fluoro-Pyridine--Boronate (79)Fluoropicolinaldehyde (8)Fluoropicolinamide (8)Fluoropicolinate (22)Fluoropyridine (288)Fluoropyrido (3)Formylpyridine (23)Hexahydropyrido (7)Hydrazinylpyridine (22)Hydroxymethylpyridine (26)Hydroxypicolinate (13)Hydroxypicolinic (9)Hydroxypicolinonitrile (7)Iodopicolinate (5)Iodopicolinic Acid (4)Iodopyridine (167)Isopropoxypyridine (20)Isopropylpyridine (32)Methoxyisonicotinaldehyde (10)Methoxynicotinaldehyde (18)Methoxypicolinaldehyde (13)Methoxypicolinamide (13)Methoxypicolinate (21)Methoxypicolinic (18)Methoxypicolinic Acid (16)Methoxypicolinimidamide (5)Methoxypicolinonitrile (13)Methoxypyridine (342)Methylisonicotinamide (8)Methylnicotinaldehyde (30)Methylnicotinamide (13)Methylpicolinaldehyde (16)Methylpicolinamide (15)Methylpicolinate (27)Methylpicolinic (23)Methylpicolinonitrile (28)Methylpyrido (13)Nitropyridine (393)Oxopyridin (2)Phenoxypyridin (1)Picolinate (42)Pyridinecarbonitrile (50)Pyridyl-Benzene-Boronic Acid/Ester (16)Pyridyl-Phenyl-Boronate (2)Pyridylmethyl (6)Terpyridine (32)Tetrachloropyridine (5)Tetrafluoropyridine (21)Tetrahydropyridine (49)Tetrahydropyrido (32)Tribromopyridine (9)Trichloropyridine (17)Trifluoropyridine (8)Trimethylpyridine (5)(2-Chloropyridin-4-Yl)Boronic Acid (6)(3-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (7)(3-Chloropyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (6)(3-Fluoropyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(3-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(3-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (10)(3Ar,8As)-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-3A,8A-Dihydro-8H-Indeno[1,2-D]Oxazole (6)(3As,8Ar)-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-3A,8A-Dihydro-8H-Indeno[1,2-D]Oxazole (7)(4R,5S)-4,5-Diphenyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (5)(5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-3-Yl)Boronic Acid (4)(5-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(5-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (5)(5-Chloropyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(6-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (6)(6-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (5)(6-Phenoxypyridin-3-Yl)Boronic Acid (5)(R)-3-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Pyridine (9)(R)-4-Benzyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (7)(R)-4-Phenyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (7)(S)-4-Benzyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (8)(S)-4-Phenyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (6)1,1'-Diphenyl-[4,4'-Bipyridine]-1,1'-Diium (7)1,10-Phenanthrolin-4-Ol (3)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydropyrido[2,3-B]Pyrazine (5)1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (22)1,3-Dihydro-2H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridin-2-One (19)1,3-Dihydro-2H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridin-2-One (5)1,3-Dihydro-2H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridin-2-One (11)1,4-Di(Pyridin-4-Yl)Benzene (5)1-(5-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine (6)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (30)1-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (15)1-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (36)1-(Pyridin-2-Yl-L2-Azaneyl)Ethan-1-One (12)1-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (17)1-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (29)1-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Piperazine (13)1-(Pyridin-3-Ylmethyl)Piperazine (6)1-(Pyridin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (23)1-(Pyridin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-One (14)1-Benzyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (9)1-Benzyl-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (9)1-Methyl-4-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine (5)1-Methylpyridin-1-Ium Iodide (5)1-Phenyl-3-(4-(Pyridin-4-Yloxy)Phenyl)Urea (8)1H-Imidazo[4,5-B]Pyridine (14)1H-Imidazo[4,5-C]Pyridine (12)1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridin-5-Amine (3)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridin-7-Ol (3)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (6)2,2':6',2''-Terpyridine (15)2,2-Dimethyl-1-(Pyridin-2-Yl-L2-Azaneyl)Propan-1-One (7)2,3'-Bipyridine (11)2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrido[4,3-B]Indole (12)2,3,4,9-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrido[3,4-B]Indole (12)2,3,5-Trichloropyridine (13)2,3,6-Trichloropyridine (16)2,3-Dibromopyridine (21)2,3-Dichloropyridine (38)2,3-Difluoropyridine (13)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (10)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (7)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,4-C]Pyridine (5)2,3-Dihydro-[1,4]Dioxino[2,3-B]Pyridine (5)2,3-Dihydropyridin-2-One (5)2,3-Dimethoxypyridine (7)2,3-Dimethylpyridine (8)2,4,6-Trichloropyridine (5)2,4,6-Triphenylpyridine (7)2,4-Dibromopyridine (5)2,4-Dichloro-6-Methylpyridine (8)2,4-Dichloropyridine (50)2,4-Dimethylpyridine (5)2,5-Dibromopyridine (26)2,5-Dichloropyridine (32)2,5-Difluoropyridine (8)2,6-Bis(4,5-Dihydrooxazol-2-Yl)Pyridine (12)2,6-Di(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Pyridine (5)2,6-Dibromo-3-Fluoropyridine (3)2,6-Dibromopyridin-4-Amine (3)2,6-Dibromopyridine (28)2,6-Dichloro-3-Fluoropyridine (10)2,6-Dichloro-3-Methylpyridine (5)2,6-Dichloro-3-Nitropyridine (6)2,6-Dichloro-4-Iodopyridine (4)2,6-Dichloro-4-Methylpyridine (5)2,6-Dichloronicotinonitrile (8)2,6-Dichloropyridin-3-Amine (11)2,6-Dichloropyridine (49)2,6-Difluoropyridine (29)2,6-Dimethoxypyridine (11)2,6-Dimethylpyridin-4-Ol (4)2,6-Dimethylpyridine (26)2-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Pyridine (16)2-(1H-Pyrazol-3-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-(2,2,2-Trifluoroethoxy)Pyridine (8)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Pyridine (3)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)2-(4-Fluorophenyl)Pyridine (11)2-(6-Benzhydrylpyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (10)2-(6-Cyclopropylpyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (10)2-(Benzyloxy)Pyridine (18)2-(Bromomethyl)Pyridine (27)2-(Chloromethyl)-3-Methylpyridine (12)2-(Chloromethyl)Pyridine (12)2-(Chloromethyl)Pyridine 1-Oxide (4)2-(Difluoromethyl)Pyridine (21)2-(Methylsulfonyl)Pyridine (11)2-(Methylthio)Pyridine (5)2-(P-Tolyl)Pyridine (6)2-(Phenoxymethyl)Pyridine (5)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyridine (11)2-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (5)2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Acetonitrile (8)2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Pyrimidine (8)2-(Pyridin-2-Ylmethyl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (14)2-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (14)2-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Acetonitrile (6)2-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Pyridine (6)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-Aminonicotinonitrile (6)2-Benzylpyridine (12)2-Bromo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (4)2-Bromo-3-Chloropyridine (25)2-Bromo-3-Fluoropyridine (26)2-Bromo-3-Iodopyridine (6)2-Bromo-3-Methoxypyridine (7)2-Bromo-3-Methylpyridine (25)2-Bromo-3-Nitropyridine (5)2-Bromo-4-Chloropyridine (7)2-Bromo-4-Methylpyridine (6)2-Bromo-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-Bromo-5-Chloropyridine (22)2-Bromo-5-Fluoropyridine (33)2-Bromo-5-Methoxypyridine (11)2-Bromo-5-Methylpyridine (19)2-Bromo-5-Nitropyridine (11)2-Bromo-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-Bromo-6-Chloropyridine (23)2-Bromo-6-Fluoropyridine (21)2-Bromo-6-Iodopyridine (5)2-Bromo-6-Methoxypyridine (15)2-Bromo-6-Methylpyridine (17)2-Bromo-6-Phenylpyridine (4)2-Bromonicotinic Acid (5)2-Bromopyridin-3-Amine (10)2-Bromopyridin-3-Ol (7)2-Bromopyridine (10)2-Bromopyridine 1-Oxide (6)2-Chloro-3,6-Dimethylpyridine (4)2-Chloro-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (4)2-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (12)2-Chloro-3-Fluoropyridin-4-Amine (3)2-Chloro-3-Fluoropyridine (20)2-Chloro-3-Iodopyridin-4-Amine (3)2-Chloro-3-Iodopyridine (13)2-Chloro-3-Methoxypyridine (12)2-Chloro-3-Methylpyridine (17)2-Chloro-3-Nitropyridine (10)2-Chloro-4,6-Dimethylpyridine (7)2-Chloro-4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (14)2-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (9)2-Chloro-4-Ethoxypyridine (5)2-Chloro-4-Fluoropyridine (10)2-Chloro-4-Iodopyridine (19)2-Chloro-4-Methoxypyridine (22)2-Chloro-4-Methylpyridine (31)2-Chloro-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)2-Chloro-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (4)2-Chloro-5-Fluoropyridin-4-Amine (3)2-Chloro-5-Fluoropyridine (16)2-Chloro-5-Iodopyridine (18)2-Chloro-5-Methylpyridine (11)2-Chloro-5-Nitropyridine (8)2-Chloro-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (16)2-Chloro-6-Fluoropyridine (14)2-Chloro-6-Iodopyridine (9)2-Chloro-6-Methoxypyridine (24)2-Chloro-6-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine (4)2-Chloro-6-Methylnicotinonitrile (10)2-Chloro-6-Methylpyridine (49)2-Chloroisonicotinaldehyde (19)2-Chloroisonicotinic Acid (17)2-Chloroisonicotinonitrile (7)2-Chloronicotinic Acid (7)2-Chloronicotinonitrile (9)2-Chloropyridin-3-Amine (11)2-Chloropyridin-3-Ol (9)2-Chloropyridin-4-Amine (28)2-Chloropyridine 1-Oxide (10)2-Cyclopropyl-4-Phenylquinoline (12)2-Cyclopropylpyridine (20)2-Ethoxypyridine (20)2-Ethylpyridine (9)2-Ethynylpyridine (31)2-Fluoro-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (7)2-Fluoro-3-Iodopyridine (8)2-Fluoro-3-Methylpyridine (14)2-Fluoro-4-Methylpyridine (6)2-Fluoro-5-Methoxypyridine (4)2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine (6)2-Fluoro-6-Methoxypyridine (6)2-Fluoro-6-Methylpyridine (20)2-Fluoropyridine (15)2-Hydrazineylpyridine (32)2-Iodo-6-Methylpyridine (5)2-Iodopyridine (27)2-Isopropoxypyridine (16)2-Isopropylpyridine (14)2-Methoxy-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (7)2-Methoxy-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-Methoxy-4-Methylpyridine (5)2-Methoxy-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-Methoxy-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (4)2-Methoxy-5-Methylpyridine (5)2-Methoxy-5-Nitropyridine (8)2-Methoxy-6-Methylpyridine (14)2-Methoxyisonicotinic Acid (13)2-Methoxypyridin-3-Amine (6)2-Methoxypyridine (436)2-Methyl-1,10-Phenanthroline (3)2-Methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine (9)2-Methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (3)2-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (8)2-Methylpyridin-3-Ol (8)2-Methylpyridin-4-Amine (7)2-Methylpyridine 1-Oxide (9)2-Nitropyridine (40)2-Phenoxy-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (7)2-Phenylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (12)2-Propoxypyridine (9)2H-Pyrido[3,2-B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (8)3,3'-Bipyridine (7)3,4-Dihydro-2H-Pyrido[3,2-B][1,4]Oxazine (5)3,5-Dibromopyridine (12)3,5-Dichloropyridine (16)3,5-Difluoropyridine (12)3,5-Dimethoxypyridine (4)3,5-Dimethylpyridine (8)3,5-Diphenylpyridine (5)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (3)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (74)3-(Benzyloxy)Pyridine (19)3-(Bromomethyl)Pyridine (18)3-(Chloromethyl)Pyridine (22)3-(Cyclopropylmethyl)Pyridine (6)3-(Difluoromethyl)Pyridine (5)3-(Methylsulfonyl)Pyridine (5)3-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyridine (5)3-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Pyridine (5)3-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)3-(Tert-Butyl)Pyridine (5)3-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (3)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Ol (5)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (52)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (6)3-Bromo-2-Chloropyridin-4-Amine (3)3-Bromo-2-Chloropyridine (20)3-Bromo-2-Fluoropyridine (21)3-Bromo-2-Methoxypyridine (20)3-Bromo-2-Methylpyridine (27)3-Bromo-4-Methylpyridine (13)3-Bromo-5-Chloropyridine (14)3-Bromo-5-Fluoropyridine (18)3-Bromo-5-Methylpyridine (14)3-Bromo-5-Nitropyridine (10)3-Bromopicolinic Acid (9)3-Bromopicolinonitrile (13)3-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (6)3-Bromopyridin-2-Amine (30)3-Bromopyridin-2-Ol (17)3-Bromopyridine 1-Oxide (8)3-Chloro-2-Fluoropyridine (13)3-Chloro-2-Methoxypyridine (16)3-Chloro-2-Methylpyridine (4)3-Chloro-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)3-Chloro-5-Fluoropyridine (10)3-Chloro-5-Methylpyridine (7)3-Chloro-5-Nitropyridine (5)3-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)3-Chloropicolinic Acid (9)3-Chloropicolinonitrile (6)3-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (17)3-Chloropyridin-2-Ol (10)3-Cyclopropylpyridine (28)3-Ethoxypyridine (12)3-Ethylpyridine (11)3-Ethynylpyridine (22)3-Fluoro-2-Methoxypyridine (14)3-Fluoro-2-Methylpyridine (15)3-Fluoro-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (7)3-Fluoropicolinic Acid (6)3-Fluoropicolinonitrile (5)3-Fluoropyridin-2-Amine (12)3-Fluoropyridin-4-Amine (4)3-Hydrazineylpyridine (8)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (4)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (6)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (4)3-Iodopyridin-2-Amine (12)3-Iodopyridin-2-Ol (4)3-Iodopyridin-4-Amine (6)3-Iodopyridin-4-Ol (4)3-Iodopyridine (37)3-Methoxypyridin-2-Amine (5)3-Methoxypyridine (52)3-Methyl-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (5)3-Methyl-2-Phenylpyridine (3)3-Methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)3-Methyl-5-Nitropyridine (4)3-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)3-Methylpicolinic Acid (13)3-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (7)3-Methylpyridine (50)3-Methylpyridine 1-Oxide (7)3-Nitropyridin-2-Ol (11)3-Nitropyridin-4-Amine (5)3-Nitropyridine (54)3-Phenoxypyridine (12)4'-Phenyl-2,2':6',2''-Terpyridine (13)4,4'-Bipyridine (10)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-C]Pyridine (7)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-C]Pyridine (14)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-3H-Imidazo[4,5-C]Pyridine (5)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothiazolo[5,4-C]Pyridine (10)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno[2,3-C]Pyridine (10)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno[3,2-C]Pyridine (9)4,6-Dichloropyridin-2-Amine (6)4,6-Dichloropyridin-3-Amine (4)4,7-Diphenyl-1,10-Phenanthroline (4)4-(2,4-Diphenyl-1H-Imidazol-5-Yl)Pyridine (5)4-(Benzyloxy)Pyridine (8)4-(Bromomethyl)Pyridine (8)4-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Morpholine (21)4-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Pyrimidine (5)4-(Pyridin-4-Yl)Morpholine (5)4-(Tert-Butyl)-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (16)4-(Tert-Butyl)Pyridine (5)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Nicotinic Acid (3)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (14)4-Bromo-2-Chloropyridine (29)4-Bromo-2-Fluoropyridine (4)4-Bromo-2-Methoxypyridine (4)4-Bromo-3-Methylpyridine (5)4-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (8)4-Bromopyridine (31)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-C]Pyridine (7)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (10)4-Chloro-2,6-Dimethylpyridine (4)4-Chloro-2-Methoxypyridine (6)4-Chloro-3-Methylpyridine (7)4-Chloronicotinic Acid (4)4-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (6)4-Chloropyridine (31)4-Cyclopropylpyridine (7)4-Ethoxypyridine (7)4-Ethynylpyridine (10)4-Iodopyridine (17)4-Isopropyl-2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (16)4-Methoxypyridine (136)4-Methyl-2,2'-Bipyridine (8)4-Methyl-2-Phenylpyridine (3)4-Methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine (8)4-Methylnicotinic Acid (5)4-Methylpyridine (24)4-Nitropyridine (11)4-Phenoxypyridine (7)4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (7)4-Phenyl-1,4-Dihydropyridine (10)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (12)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydropyrido[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (7)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydropyrido[4,3-D]Pyrimidine (17)5,6-Dichloropyridin-2-Amine (4)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Nicotinonitrile (4)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridin-2-Amine (9)5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Amine (5)5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Ol (8)5-Benzyl-4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno[3,2-C]Pyridine (7)5-Bromo-2-Chloro-4-Methylpyridine (5)5-Bromo-2-Chloropyridine (40)5-Bromo-2-Fluoropyridine (22)5-Bromo-2-Iodopyridine (5)5-Bromo-2-Methoxypyridine (29)5-Bromo-2-Methylpyridine (23)5-Bromo-2-Phenylpyridine (3)5-Bromo-4-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (5)5-Bromo-6-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (3)5-Bromonicotinaldehyde (12)5-Bromonicotinic Acid (6)5-Bromonicotinonitrile (6)5-Bromopicolinic Acid (11)5-Bromopicolinonitrile (13)5-Bromopyridin-2-Amine (35)5-Bromopyridin-2-Ol (18)5-Bromopyridin-3-Amine (10)5-Bromopyridin-3-Ol (6)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (3)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-B]Pyridine (6)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (6)5-Chloro-2-Fluoropyridine (13)5-Chloro-2-Methoxypyridine (10)5-Chloro-2-Methylpyridine (10)5-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)5-Chloropicolinic Acid (7)5-Chloropicolinonitrile (6)5-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (26)5-Chloropyridin-2-Ol (15)5-Chloropyridin-3-Amine (7)5-Fluoro-2-Methoxypyridine (15)5-Fluoro-2-Methylpyridine (8)5-Fluoropicolinonitrile (5)5-Fluoropyridin-2-Amine (15)5-Iodopyridin-2-Amine (17)5-Iodopyridin-2-Ol (8)5-Methoxy-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (4)5-Methoxypyridin-3-Amine (4)5-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (4)5-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (7)5-Methylpyridin-3-Amine (4)5-Nitronicotinic Acid (5)5-Nitropyridin-2-Amine (6)5-Phenylpicolinic Acid (4)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Cyclopenta[B]Pyridine (18)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Cyclopenta[C]Pyridine (7)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Pyrrolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (5)6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Amine (11)6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-3-Amine (5)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-B]Pyridine (4)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (7)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (5)6-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (14)6-Bromonicotinaldehyde (11)6-Bromonicotinic Acid (9)6-Bromonicotinonitrile (7)6-Bromopicolinic Acid (5)6-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (8)6-Bromopyridin-2-Amine (8)6-Bromopyridin-3-Amine (12)6-Bromopyridin-3-Ol (13)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-C]Pyridine (8)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (13)6-Chloro-3-Nitropyridin-2-Amine (4)6-Chloro-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Amine (3)6-Chloro-5-Iodopyridin-2-Amine (3)6-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (4)6-Chloronicotinaldehyde (24)6-Chloronicotinic Acid (4)6-Chloropicolinic Acid (12)6-Chloropicolinonitrile (9)6-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (21)6-Chloropyridin-2-Ol (9)6-Chloropyridin-3-Amine (4)6-Chloropyridine-3-Sulfonyl Chloride (5)6-Fluoro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (3)6-Fluoropyridin-2-Amine (8)6-Fluoropyridin-3-Amine (4)6-Methoxy-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (3)6-Methoxynicotinaldehyde (4)6-Methoxypicolinic Acid (9)6-Methoxypyridin-2-Amine (14)6-Methoxypyridin-3-Amine (8)6-Methylnicotinic Acid (6)6-Methylnicotinonitrile (7)6-Methylpicolinic Acid (12)6-Methylpicolinonitrile (10)6-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (46)6-Methylpyridin-2-Ol (23)6-Methylpyridin-3-Amine (5)6-Methylpyridin-3-Ol (7)6-Phenoxypyridin-3-Amine (5)6-Phenylnicotinic Acid (8)6-Phenylpicolinic Acid (3)7-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (4)7-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)7-Methoxy-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)7-Methylimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)9H-Pyrido[3,4-B]Indole (5)Bis(Pyridin-2-Ylmethyl)Amine (6)Dimethyl Pyridine-2,6-Dicarboxylate (7)Dimethyl(Pyridin-2-Yl)Phosphine Oxide (8)Dimethyl(Pyridin-3-Yl)Phosphine Oxide (7)Ethyl 2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Acetate (15)Ethyl 2-Methylnicotinate (6)Ethyl 4,6-Dichloronicotinate (4)Ethyl 6-Chloropicolinate (7)Ethyl Isonicotinate (12)Ethyl Nicotinate (25)Ethyl Picolinate (41)Ethyl Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (11)Furo[3,2-B]Pyridine (7)Furo[3,2-C]Pyridine (7)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-2-Ylmethanol (4)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-5-Carboxylic Acid (3)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-6-Carbonitrile (3)Isonicotinaldehyde (68)Isonicotinamide (12)Isonicotinic Acid (23)Isonicotinohydrazide (6)Isonicotinonitrile (16)Methyl 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine-5-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Acetate (9)Methyl 2-Chloroisonicotinate (11)Methyl 2-Chloronicotinate (6)Methyl 3-Bromopicolinate (9)Methyl 3-Chloropicolinate (9)Methyl 5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Nicotinate (4)Methyl 5-Hydroxypicolinate (5)Methyl 6-Bromonicotinate (6)Methyl 6-Chloropicolinate (11)Methyl 6-Fluoronicotinate (4)Methyl 6-Methoxynicotinate (4)Methyl Isonicotinate (16)Methyl Nicotinate (52)Methyl Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (16)N,N-Dimethylpyridin-2-Amine (10)N,N-Dimethylpyridin-4-Amine (6)N-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Benzamide (9)N-Benzylpyridin-2-Amine (9)N-Methylpicolinamide (10)N-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (47)N-Methylpyridin-3-Amine (15)N-Phenyl-4-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Pyrimidin-2-Amine (5)N-Phenylpicolinamide (8)N-Phenylpyridin-2-Amine (9)Nicotinaldehyde (153)Nicotinamide (64)Nicotinic Acid (53)Nicotinonitrile (82)Oxazolo[4,5-B]Pyridine (7)Oxazolo[5,4-B]Pyridine (5)Phenyl(Pyridin-2-Yl)Methanone (10)Phenyl(Pyridin-3-Yl)Methanone (9)Picolinaldehyde (98)Picolinamide (26)Picolinic Acid (22)Picolinimidamide (11)Picolinohydrazide (5)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-2-Carboxylic Acid (5)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (13)Pyridin-2-Amine (29)Pyridin-2-Ol (170)Pyridin-2-Ylboronic Acid (9)Pyridin-2-Ylmethanamine (38)Pyridin-2-Ylmethanol (65)Pyridin-3-Amine (21)Pyridin-3-Ol (13)Pyridin-3-Ylboronic Acid (49)Pyridin-3-Ylmethanamine (29)Pyridin-3-Ylmethanol (39)Pyridin-4-Amine (22)Pyridin-4-Ol (16)Pyridin-4-Ylboronic Acid (21)Pyridin-4-Ylmethanamine (12)Pyridin-4-Ylmethanol (16)Pyridine 1-Oxide (33)Pyridine-2,3-Diamine (5)Pyridine-2,6-Diamine (12)Pyridine-2,6-Dicarboxylic Acid (9)Pyridine-2,6-Diol (6)Pyridine-2-Sulfonamide (6)Pyridine-2-Sulfonyl Chloride (9)Pyridine-2-Thiol (8)Pyridine-3-Sulfonic Acid (6)Pyridine-3-Sulfonyl Chloride (25)Pyrido[2,3-B]Pyrazine (12)Pyrido[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (8)Pyrido[3,2-D]Pyrimidine (14)Pyrido[3,4-B]Pyrazine (11)Pyrido[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (10)Tert-Butyl (2-Chloropyridin-4-Yl)Carbamate (4)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine-1-Carboxylate (7)Tert-Butyl 4-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (12)Tert-Butyl Pyridin-2-Ylcarbamate (37)Tert-Butyl Pyridin-3-Ylcarbamate (16)Tert-Butyl Pyridin-4-Ylcarbamate (6)Thiazolo[4,5-B]Pyridine (12)Thiazolo[5,4-B]Pyridine (13)Thiazolo[5,4-C]Pyridine (5)Thieno[2,3-B]Pyridine (22)Thieno[2,3-C]Pyridine (14)Thieno[3,2-B]Pyridine (18)Thieno[3,2-C]Pyridine (13)
Pyrimidines (14557)
Bipyrimidine (4)Dibromopyrimidine (15)Methoxypyrimidine (107)Pyrimidinone (3)Tetraoxatetradecan (10)Trichloropyrimidine (11)(R)-7-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (8)(R)-N-(Piperidin-3-Yl)-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidin-4-Amine (5)1,4,5,6-Tetrahydropyrimidine (4)1-(3-Fluorotetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (9)1-(5-(Hydroxymethyl)Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (30)1-(Pyrimidin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)1-(Pyrimidin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-One (6)1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (46)1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidin-4-Amine (5)1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-D]Pyrimidine (5)2,4,5-Trichloropyrimidine (6)2,4,6-Trichloropyrimidine (14)2,4,6-Triphenylpyrimidine (9)2,4-Dichloro-6-Methylpyrimidine (7)2,4-Dichloropyrimidin-5-Amine (6)2,4-Dimethoxypyrimidine (13)2,4-Dimethylpyrimidine (7)2-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (6)2-(Chloromethyl)Pyrimidine (5)2-(Methylsulfonyl)Pyrimidine (25)2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidin-4-Amine (10)2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (19)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (11)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (16)2-(Propylthio)Pyrimidine (5)2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Pyrimidine (8)2-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (8)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidine (27)2-Aminopyrimidin-4(3H)-One (11)2-Bromopyrimidine (22)2-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidine (6)2-Chloro-4-Methoxypyrimidine (14)2-Chloro-4-Methylpyrimidine (16)2-Chloro-4-Phenylpyrimidine (7)2-Chloro-5-Fluoropyrimidine (6)2-Chloro-5-Methylpyrimidine (5)2-Chloro-5-Nitropyrimidine (5)2-Chloro-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (13)2-Chloropyrimidin-4-Amine (22)2-Cyclopropylpyrimidine (10)2-Ethoxypyrimidine (7)2-Ethylpyrimidine (6)2-Fluoropyrimidine (9)2-Hydrazineylpyrimidine (6)2-Iodopyrimidine (8)2-Methoxypyrimidin-4-Amine (6)2-Methoxypyrimidine (59)2-Methylpyrimidin-4-Amine (22)2-Methylpyrimidin-4-Ol (11)2-Phenoxypyrimidine (8)2-Phenylpyrimidin-5-Amine (5)3-Methylpyrimidin-4(3H)-One (6)4,5-Dichloropyrimidine (7)4,6-Dichloro-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (9)4,6-Dichloro-2-Methylpyrimidine (7)4,6-Dichloropyrimidin-2-Amine (9)4,6-Dichloropyrimidine (14)4,6-Diphenylpyrimidine (7)4-(Dimethoxymethyl)Pyrimidine (5)4-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (13)4-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (8)4-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Pyrimidine (5)4-(Pyrimidin-2-Yl)Morpholine (9)4-(Pyrimidin-4-Yl)Morpholine (13)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidin-2-Amine (6)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidine (12)4-Amino-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (19)4-Bromopyrimidine (24)4-Chloro-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (29)4-Chloro-2-Methoxypyrimidine (12)4-Chloro-2-Phenylpyrimidine (5)4-Chloro-5-Fluoro-2-Methylpyrimidine (5)4-Chloro-5-Iodopyrimidine (6)4-Chloro-5-Methoxypyrimidine (7)4-Chloro-5-Methylpyrimidine (8)4-Chloro-6-Methoxypyrimidine (5)4-Chloropyrimidin-2-Amine (23)4-Chloropyrimidin-5-Amine (7)4-Chloropyrimidine-5-Carbonitrile (6)4-Ethoxypyrimidine (6)4-Fluoropyrimidine (8)4-Iodopyrimidine (9)4-Methoxy-2-Methylpyrimidine (8)4-Methoxypyrimidin-2-Amine (6)4-Methoxypyrimidine (102)4-Methyl-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (7)4-Methylpyrimidin-2-Amine (9)4-Methylpyrimidine (22)4-Phenoxypyrimidine (5)4-Phenylpyrimidin-2-Amine (15)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydropyrido[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (7)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydropyrido[4,3-D]Pyrimidine (17)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyrimidine (27)5-(Benzyloxy)Pyrimidine (5)5-Benzylpyrimidine (7)5-Bromo-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (4)5-Bromo-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (6)5-Bromo-2-Chloropyrimidine (6)5-Bromo-2-Methylpyrimidine (5)5-Bromo-4-Chloropyrimidine (4)5-Bromo-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (3)5-Bromopyrimidin-4(3H)-One (3)5-Chloropyrimidin-4(3H)-One (4)5-Chloropyrimidine (8)5-Chloropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (3)5-Ethylpyrimidine (5)5-Fluoro-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (7)5-Fluoro-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (2)5-Fluoropyrimidin-4(3H)-One (3)5-Fluoropyrimidine (11)5-Fluoropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (3)5-Iodo-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (4)5-Iodopyrimidine (5)5-Methylpyrimidine (3)5-Phenylpyrimidine (16)5H-Pyrrolo[3,2-D]Pyrimidine (16)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Cyclopenta[D]Pyrimidine (5)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Pyrrolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (8)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (12)6-Chloropyrimidin-4-Amine (8)7-(Phenylsulfonyl)-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (7)7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidin-2-Amine (5)7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidin-4-Amine (3)[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (14)Ethyl 4-Chloropyrimidine-5-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine-3-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl Pyrimidine-4-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl Pyrimidine-5-Carboxylate (5)Imidazo[1,2-C]Pyrimidine (6)Methyl Pyrimidine-2-Carboxylate (10)Methyl Pyrimidine-4-Carboxylate (11)Methyl Pyrimidine-5-Carboxylate (5)N,N-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-Amine (10)N-(9-((2R,5S)-5-((Trityloxy)Methyl)Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purin-6-Yl)Benzamide (5)N-Benzyl-9H-Purin-6-Amine (6)N-Cyclopropylpyrimidin-2-Amine (5)N-Methyl-N-(4-Phenylpyrimidin-2-Yl)Methanesulfonamide (7)N-Methylpyrimidin-2-Amine (10)N-Methylpyrimidin-4-Amine (10)N-Phenyl-4-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Pyrimidin-2-Amine (5)N-Phenylpyrimidin-2-Amine (5)N-Phenylpyrimidin-4-Amine (7)N2,N4-Diphenylpyrimidine-2,4-Diamine (5)Pyrido[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (8)Pyrido[3,2-D]Pyrimidine (14)Pyrido[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (10)Pyrimidin-2-Ol (21)Pyrimidin-2-Ylmethanamine (7)Pyrimidin-2-Ylmethanol (5)Pyrimidin-4-Amine (29)Pyrimidin-4-Ol (25)Pyrimidin-5-Amine (6)Pyrimidin-5-Ol (5)Pyrimidin-5-Ylboronic Acid (9)Pyrimidine-2,4-Diamine (14)Pyrimidine-2-Carbonitrile (14)Pyrimidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (11)Pyrimidine-2-Thiol (6)Pyrimidine-4,6(1H,5H)-Dione (3)Pyrimidine-4-Carbonitrile (9)Pyrimidine-4-Carboxylic Acid (17)Pyrimidine-5-Carbaldehyde (38)Pyrimidine-5-Carbonitrile (6)Pyrimidine-5-Carboxylic Acid (7)Tetrahydropyrimidin-2(1H)-One (6)Thiazolo[5,4-D]Pyrimidine (5)Thieno[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (30)Thieno[3,2-D]Pyrimidine (24)
Pyrroles (4953)
Bromopyrrolo (8)Chloropyrrolo (10)Dihydropyrrolo (15)Octahydropyrrolo (6)Pyrrol-Amine (1)Pyrrolopyridine-Methylamine (6)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (26)(Z)-3-((1H-Pyrrol-2-Yl)Methylene)Indolin-2-One (8)1,3-Dihydro-2H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridin-2-One (19)1,3-Dihydro-2H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridin-2-One (11)1,4,5,6-Tetrahydropyrrolo[3,4-C]Pyrazole (6)1-(1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-Pyrrole (24)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (30)1-Benzylpyrrolidin-2-One (18)1-Methyl-1H-Pyrrole (43)1H-Pyrrol-1-Amine (7)1H-Pyrrole-2-Carbaldehyde (21)1H-Pyrrole-2-Carbonitrile (7)1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylic Acid (30)1H-Pyrrole-3-Carbaldehyde (9)1H-Pyrrole-3-Carbonitrile (9)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridin-6-Amine (4)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (5)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridin-7-Ol (3)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (10)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,4-C]Pyridine (5)2-Bromo-1H-Pyrrole (11)2-Methyl-1H-Pyrrole (49)2-Nitro-1H-Pyrrole (5)2-Phenyl-1H-Pyrrole (24)3,6-Di(Thiophen-2-Yl)-2,5-Dihydropyrrolo[3,4-C]Pyrrole-1,4-Dione (17)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrole (16)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (7)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (4)3-Methyl-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (5)3-Phenyl-1H-Pyrrole (5)3-Phenylpyrrolidine (26)4-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (9)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)4H-Thieno[3,2-B]Pyrrole (6)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)5-Methoxy-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (4)5H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyrazine (14)5H-Pyrrolo[3,2-D]Pyrimidine (16)7-(Phenylsulfonyl)-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (7)7-Methoxy-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)Ethyl 1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylate (24)Ethyl 1H-Pyrrole-3-Carboxylate (8)Methyl 1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylate (30)Methyl 1H-Pyrrole-3-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (4)Methyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-6-Carboxylate (3)Pyrrolo[2,1-F][1,2,4]Triazine (14)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrrole-1-Carboxylate (8)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylate (3)
Pyrrolidines (14879)
Acetylpyrrolidine (9)Benzylpyrrolidine (33)Bipyrrolidine (9)Bromopyrrolidine (7)Carbamoylpyrrolidine (5)Difluoropyrrolidine (16)Dimethylpyrrolidine (31)Dioxopyrrolidin (131)Ethylpyrrolidine (9)Fluoropyrrolidine (26)Formylpyrrolidine (10)Mercaptopyrrolidine (4)Methoxypyrrolidine (19)Methylenepyrrolidine (2)Methylpyrrolidine (129)Phenoxypyrrolidine (3)Pyrrolidine-Benzene-Boronic Acid/Ester (20)(3Ar,6As)-Octahydrocyclopenta[C]Pyrrole (5)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (26)(R)-3-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Pyridine (9)(R)-3-Benzylpyrrolidine (6)(R)-3-Phenylpyrrolidine (8)(S)-3-Phenylpyrrolidine (14)(S)-N-(((S)-Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Methyl)Pyrrolidine-2-Carboxamide (4)(S)-N-(4-(Thiazol-5-Yl)Benzyl)Pyrrolidine-2-Carboxamide (7)(S)-N-Phenethyl-3-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Propanamide (5)1-((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Pyrrolidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (6)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (3)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)Pyrrolidine (15)1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-Benzyl 2-Methyl Pyrrolidine-1,2-Dicarboxylate (7)1-Benzylpyrrolidin-2-One (18)1-Benzylpyrrolidine (26)1-Methylpyrrolidin-2-One (13)1-Phenylpyrrolidin-2-One (18)2,2-Dimethylpyrrolidine (4)2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-Yl ((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Glycinate (8)2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-Yl Benzoate (8)2,8-Diazaspiro[4.5]Decan-3-One (6)2-((3-Phenylpropyl)Amino)-1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (2)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (17)2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (16)2-(3-Fluorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (5)2-(Methoxymethyl)Pyrrolidine (6)2-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Benzoic Acid (3)2-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Pyridine (11)2-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Pyrimidine (8)2-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Acetic Acid (8)2-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-(Pyrrolidin-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (6)2-Amino-1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)2-Azabicyclo[2.2.1]Heptane (6)2-Methyl-1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrrole (8)2-Methylpyrrolidine (21)3,3-Difluoropyrrolidine (29)3-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)3-Aminopyrrolidin-2-One (5)3-Bromopyrrolidine (6)3-Hydroxypyrrolidin-2-One (4)3-Phenoxypyrrolidine (5)3-Phenyl-1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Propan-1-One (5)3-Phenylpyrrolidine (26)4-(Hydroxymethyl)Pyrrolidin-2-One (4)4-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Aniline (3)4-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Piperidine (6)4-Hydroxypyrrolidin-2-One (7)4-Phenylpyrrolidin-2-One (7)4H-Thieno[3,4-C]Pyrrole-4,6(5H)-Dione (7)5-(Aminomethyl)Pyrrolidin-2-One (3)5-(Hydroxymethyl)Pyrrolidin-2-One (7)5-Azaspiro[2.4]Heptane (13)5-Oxopyrrolidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)6-Azaspiro[3.4]Octane (4)Benzyl (S)-Pyrrolidin-3-Ylcarbamate (7)Benzyl 3-Hydroxypyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (5)Benzyl-2-(Hydroxymethyl)Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (9)Benzyl-3-Aminopyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl 5-Oxopyrrolidine-2-Carboxylate (3)Hexahydro-1H-Pyrrolizine (12)Methyl 5-Oxopyrrolidine-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Prolinate (43)Methyl Pyrrolidine-3-Carboxylate (9)N,N-Dimethylpyrrolidin-3-Amine (7)N-Methylpyrrolidin-3-Amine (6)Octahydrocyclopenta[C]Pyrrole (6)Phenyl(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Methanone (12)Proline (13)Pyrrolidin-2-Ylmethanamine (12)Pyrrolidin-2-Ylmethanol (26)Pyrrolidin-3-Ol (59)Pyrrolidin-3-Ylmethanamine (6)Pyrrolidin-3-Ylmethanol (13)Pyrrolidine-2-Carbonitrile (9)Pyrrolidine-2-Carboxamide (12)Pyrrolidine-3-Carbonitrile (6)Pyrrolidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)Tert-Butyl (2-Oxopyrrolidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (5-Oxopyrrolidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl 2-Oxopyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (15)Tert-Butyl 3-((Methylsulfonyl)Oxy)Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (5)Tert-Butyl 3-Hydroxypyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (20)Tert-Butyl 3-Methoxypyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (6)Tert-Butyl Pyrrolidin-3-Ylcarbamate (12)Tert-Butyl Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (21)
Pyrrolines (1763)
1,3-Dihydro-2H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridin-2-One (5)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrrole-2,5-Dione (12)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (7)2,5-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrol-2-One (5)2,5-Dihydro-1H-Pyrrole (13)2-Phenyl-2,5,6,7-Tetrahydropyrrolo[2,1-C][1,2,4]Triazol-4-Ium (6)3,4-Dihydro-2H-Pyrrole (5)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrole-2,5-Dione (3)5,6-Dihydro-4H-Pyrrolo[1,2-B]Pyrazole (8)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Pyrrolo[1,2-A]Imidazole (9)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Pyrrolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (5)6,7-Dihydro-5H-Pyrrolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (8)
Quinazolines (3143)
Dichloroquinazoline (14)Iodoquinazoline (10)Methylquinazoline (46)Nitroquinazoline (20)Trichloroquinazoline (5)2,4-Dichloroquinazoline (19)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Quinazoline (4)2-Bromoquinazoline (4)2-Chloroquinazolin-4(3H)-One (4)2-Cyclopropylquinazoline (5)2-Mercaptoquinazolin-4(3H)-One (3)2-Methylquinazoline (20)4-Chloroquinazoline (39)4-Methylquinazoline (4)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroquinazoline (8)5-Chloroquinazoline (4)6-Bromoquinazoline (7)7-Bromoquinazolin-4(3H)-One (4)7-Fluoroquinazolin-4(3H)-One (4)7-Methoxy-N-Phenylquinazolin-4-Amine (12)8-Bromoquinazoline (8)8-Chloroquinazoline (5)8-Fluoroquinazoline (4)8-Methoxyquinazoline (3)8-Methylquinazoline (3)Ethyl Quinazoline-2-Carboxylate (4)N-(3-Chlorophenyl)Quinazolin-4-Amine (9)Quinazolin-2-Amine (13)Quinazolin-2-Ol (7)Quinazolin-4-Amine (8)Quinazolin-4-Ol (10)
Quinolines (11910)
Iodoquinoline (32)1,2-Dihydroquinoline (5)1-Cyclopropyl-3-(4-(Quinolin-4-Yloxy)Phenyl)Urea (6)2,2'-Biquinoline (3)2,3,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H,5H-Pyrido[3,2,1-Ij]Quinoline (7)2-(Quinolin-2-Yl)-4,5-Dihydrooxazole (7)2-Hydroxyquinolin-4(1H)-One (3)2-Phenylquinoline (18)3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline (11)4-Oxo-1,4-Dihydroquinoline-3-Carboxylic Acid (3)4-Phenoxyquinoline (5)4-Phenylquinoline (9)6-Bromo-3,4-Dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-One (4)7,8-Dihydroquinolin-5(6H)-One (5)7-(Benzyloxy)Quinoline (6)7-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-One (3)N-Phenyl-N-(4-(Quinolin-4-Yloxy)Phenyl)Cyclopropane-1,1-Dicarboxamide (5)N-Phenylquinolin-4-Amine (11)
Quinoxalines (1411)
Dichloroquinoxaline (8)Dihydroquinoxalin (7)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoxaline (6)2-Chloroquinoxaline (39)2-Methylquinoxaline (5)2-Phenylquinoxaline (5)3,4-Dihydroquinoxalin-2(1H)-One (7)5-Bromoquinoxaline (6)6-Bromoquinoxaline (9)6-Chloroquinoxaline (3)6-Methoxyquinoxaline (6)Quinoxalin-2-Amine (3)Quinoxalin-2-Ol (4)
Spiroes (4763)
Aminospiro (4)Azaspiro (246)Bromospiro (11)Diazaspiro (182)Dihydrospiro (18)Dioxaspiro (39)Fluorospiro (4)Oxospiro (22)Triazaspiro (13)1,3-Dihydrospiro[Indene-2,4'-Piperidine] (5)1,4-Dioxaspiro[4.5]Decane (17)2,8-Diazaspiro[4.5]Decane (5)2-Oxa-8-Azaspiro[4.5]Decane (5)3-Phenyloxetane (11)6-Azaspiro[3.4]Octane (4)7-Azaspiro[3.5]Nonane (7)9,9'-Spirobi[Fluorene] (19)Spiro[Cyclopropane-1,3'-Indolin]-2'-One (6)Spiro[Indene-2,4'-Piperidin]-1(3H)-One (5)Spiro[Indoline-3,4'-Piperidine] (5)
Tetrahydrofurans (2265)
Hydroxytetrahydrofuran (16)Iodotetrahydrofuran (3)Methoxytetrahydrofuran (11)Oxotetrahydrofuran (26)(2R,3S)-2-((Benzoyloxy)Methyl)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Yl Benzoate (8)(3Ar,6Ar)-Hexahydrofuro[3,2-B]Furan (5)(3As,6As)-Tetrahydrofuro[3,4-D][1,3]Dioxole (6)(R)-7-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (8)(R)-N-(9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purin-6-Yl)Benzamide (5)(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Methanamine (4)(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Methanol (6)(Tetrahydrofuran-3-Yl)Methanamine (3)1,3-Dihydrobenzo[C][1,2]Oxaborole (20)1-(3-Fluorotetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (9)1-(5-(Hydroxymethyl)Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (30)1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (46)1-Oxa-8-Azaspiro[4.5]Decane (5)2-(Acetoxymethyl)-5-(9H-Purin-9-Yl)Tetrahydrofuran-3,4-Diyl Diacetate (6)2-(Hydroxymethyl)-5-(9H-Purin-9-Yl)Tetrahydrofuran-3,4-Diol (27)2-Oxa-8-Azaspiro[4.5]Decane (5)2-Oxabicyclo[2.1.1]Hexane (6)3-Aminodihydrofuran-2(3H)-One (4)3-Iodotetrahydrofuran (3)4-Amino-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (19)4-Fluoro-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-5-(9H-Purin-9-Yl)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Ol (4)4-Hydroxydihydrofuran-2(3H)-One (14)5-(Hydroxymethyl)Dihydrofuran-2(3H)-One (7)5-Bromo-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (4)5-Fluoro-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidin-2(1H)-One (7)5-Fluoro-1-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (2)5-Oxotetrahydrofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purin-6-Amine (30)9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purin-6-Ol (6)9-(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)-9H-Purine (2)Dihydrofuran-3(2H)-One (7)Tert-Butyl (Tetrahydrofuran-3-Yl)Carbamate (4)Tetrahydrofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Amine (6)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Carboxylic Acid (4)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Ol (7)
Tetrahydroisoquinolines (1291)
Tetrahydroisoquinoline-Carboxylic Acid (48)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl 3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-Carboxylate (7)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-5-Amine (4)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-5-Ol (3)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-6-Amine (3)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-6-Ol (6)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-Amine (3)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline-1-Carboxylic Acid (19)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-Carboxylic Acid (12)1,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-3(2H)-One (5)1-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)2-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (13)4,4-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (5)5-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)5-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)5-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)5-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)6-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)6-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)6-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)6-Methoxy-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)6-Nitro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)7-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)7-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (5)7-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)7-Methoxy-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (6)7-Nitro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)Isoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-Dione (7)
Tetrahydropyrans (3359)
Chroman-Amine (1)Difluorochroman (16)(1S,4Ar,7Ar)-1-(((S)-Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Oxy)-1,4A,5,7A-Tetrahydrocyclopenta[C]Pyran (4)(6-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Methanol (17)(R)-2-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran (7)(S)-2-(Phenylthio)Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran (5)(S)-7-(((S)-Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Oxy)-7,8,9,10-Tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-Dione (5)(S)-N-(((S)-Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Methyl)Pyrrolidine-2-Carboxamide (4)1-(Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-4-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole (6)2-(Phenoxymethyl)Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran (5)2-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran (6)2-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran-4-Yl Acetate (6)4-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran (5)9-Bromoanthracene (5)
Tetrahydroquinolines (1464)
Tetrahydroquinoline-Carboxylic Acid (18)1-Ethyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (6)1-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (6)2,3-Dihydroquinolin-4(1H)-One (19)2-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)4,4-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)4-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (2)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroquinoline (17)6-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (6)6-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)6-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)7-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)Tert-Butyl 3,4-Dihydroquinoline-1(2H)-Carboxylate (11)
Thiazoles (6687)
Acetylthiazole (7)Bromothiazolo (9)Chlorothiazole (32)Chlorothiazolo (18)Cyanothiazole (7)Cyclopropylthiazole (11)Dibromothiazole (7)Dichlorothiazole (8)Dihydrothiazole (16)Dihydrothiazolo (14)Dimethylthiazole (22)Ethylthiazole (8)Formylthiazole (7)Methylthiazole (109)Nitrothiazol (8)Tetrahydrothiazolo (8)1-(Thiazol-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (9)2,4-Dibromothiazole (5)2,4-Dichlorothiazole (4)2,4-Dimethylthiazole (7)2,5-Dibromothiazole (5)2,5-Dimethylthiazole (4)2-(Chloromethyl)Thiazole (5)2-(Methylthio)Thiazole (5)2-(Thiazol-4-Yl)Acetic Acid (9)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Thiazole (11)2-Bromo-4-Methylthiazole (7)2-Bromo-5-Methylthiazole (7)2-Chloro-4-Methylthiazole (5)2-Chloro-5-Methylthiazole (5)2-Chlorothiazole (32)2-Imino-N-((6R,7R)-8-Oxo-5-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[4.2.0]Oct-2-En-7-Yl)-2-(Thiazol-4-Yl)Acetamide (3)2-Isopropylthiazole (11)2-Methyl-4-Phenylthiazole (6)2-Phenoxythiazole (5)2-Phenylbenzo[D]Thiazole (16)2-Phenylthiazole-4-Carbaldehyde (9)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrobenzo[D]Thiazole (14)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothiazolo[5,4-C]Pyridine (10)4,5-Dihydrothiazole (8)4-(4-Fluorophenyl)Thiazole (9)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Thiazole (7)4-Bromothiazole (10)4-Cyclopropylthiazole (6)4-Methyl-2-Phenylthiazole (6)4-Methylthiazol-2-Amine (7)4-Methylthiazole (5)4-Phenylthiazol-2-Amine (37)5,6-Dihydrobenzo[D]Thiazol-7(4H)-One (5)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Thiazole (7)5-Bromothiazol-2-Amine (6)5-Bromothiazole (8)5-Methyl-4-Phenylthiazole (5)5-Methylthiazol-2-Amine (6)5-Phenylthiazole (20)Ethyl 2-Aminothiazole-4-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl 2-Aminothiazole-5-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 2-Phenylthiazole-4-Carboxylate (12)Ethyl 2-Phenylthiazole-5-Carboxylate (9)Ethyl Thiazole-2-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl Thiazole-4-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl Thiazole-5-Carboxylate (7)Methyl 2-Aminothiazole-4-Carboxylate (6)Methyl Thiazole-2-Carboxylate (6)Methyl Thiazole-4-Carboxylate (6)N-(Thiazol-2-Yl)Acetamide (9)N-(Thiazol-2-Yl)Benzamide (9)N-Phenylthiazol-2-Amine (9)Tert-Butyl Thiazol-2-Ylcarbamate (22)Thiazol-2-Ylmethanamine (5)Thiazol-2-Ylmethanol (9)Thiazol-5-Amine (6)Thiazole-2-Carbaldehyde (9)Thiazole-2-Carboxylic Acid (9)Thiazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (5)Thiazole-5-Carbaldehyde (19)Thiazole-5-Carbonitrile (7)Thiazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (10)Thiazolo[4,5-B]Pyridine (12)Thiazolo[5,4-B]Pyridine (13)Thiazolo[5,4-C]Pyridine (5)Thiazolo[5,4-D]Pyrimidine (5)
Thiophenes (960)
Acetylthiophene (5)Aminothiophene (23)Bromothieno (29)Chlorothieno (41)Chlorothiophene (61)Cyanothiophene (5)Dibromothieno (5)Dibromothiophene (17)Dichlorothieno (10)Dichlorothiophene (13)Dihydrothieno (24)Dihydrothiophene (1)Dihydroxythiophene (7)Dimethylthieno (10)Dimethylthiophene (21)Dithiophene (40)Fluorothiophene (18)Formylthiophene (16)Hydroxythiophene (7)Iodothieno (6)Iodothiophene (13)Methylthieno (27)Nitrothiophene (27)Terthiophene (10)Tetrahydrothieno (17)Thiophenecarboxaldehyde (10)Thiphen-Amine-Hydrochloride (58)Trithiophene (5)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (2-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Ethyl)Carbamate (5)1-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (17)2,2'-Bithiophene (25)2,2':5',2''-Terthiophene (9)2,3-Dihydrothieno[3,4-B][1,4]Dioxine (9)2,5-Dibromothiophene (18)2,5-Diphenylthiophene (5)2-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Thiophene (11)2-Chlorothiophene (20)2-Ethynylthiophene (8)2-Iodothiophene (14)2-Methoxythiophene (7)2-Nitrothiophene (20)3-Bromothiophene (6)3-Chlorothiophene (17)3-Fluorothiophene (6)3-Methoxythiophene (9)3-Methylthiophene (14)3-Nitrothiophene (6)3-Phenylthiophene (13)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(Thiophen-2-Yl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (23)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(Thiophen-3-Yl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (10)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno[2,3-C]Pyridine (10)4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno[3,2-C]Pyridine (9)4,7-Di(Thiophen-2-Yl)Benzo[C][1,2,5]Thiadiazole (9)4,8-Di(Thiophen-2-Yl)Benzo[1,2-B:4,5-B']Dithiophene (8)4-Phenyl-6H-Thieno[3,2-F][1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A][1,4]Diazepine (5)4H-Cyclopenta[2,1-B:3,4-B']Dithiophene (9)4H-Thieno[3,2-B]Pyrrole (6)4H-Thieno[3,4-C]Pyrrole-4,6(5H)-Dione (7)5,6-Dihydro-4H-Cyclopenta[B]Thiophene (7)5-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Isoxazole (5)5-Benzyl-4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno[3,2-C]Pyridine (7)5-Phenylthiophen-2-Amine (5)Benzo[1,2-B:4,5-B']Dithiophene (7)Dibenzo[B,D]Thiophene (22)Dihydrothiophen-3(2H)-One (4)Dithieno[3,2-B:2',3'-D]Thiophene (5)Ethyl Thiophene-2-Carboxylate (19)Ethyl Thiophene-3-Carboxylate (11)Methyl Thiophene-3-Carboxylate (34)N,N-Diphenyl-4-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Aniline (5)Phenyl(Thiophen-2-Yl)Methanone (6)Thieno[2,3-B]Pyridine (22)Thieno[2,3-C]Pyridine (14)Thieno[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (30)Thieno[3,2-B]Pyridine (18)Thieno[3,2-B]Thiophene (19)Thieno[3,2-C]Pyridine (13)Thieno[3,2-D]Pyrimidine (24)Thieno[3,4-B]Thiophene (5)Thiophen-2-Ylboronic Acid (20)Thiophen-2-Ylmethanol (11)Thiophen-3-Amine (18)Thiophen-3-Ol (6)Thiophene-2-Carbaldehyde (43)Thiophene-2-Carbonitrile (23)Thiophene-3-Carbaldehyde (17)Thiophene-3-Carbonitrile (13)Thiophene-3-Carboxamide (5)Thiophene-3-Carboxylic Acid (8)
Triazines (1387)
1,2,4-Triazine (9)1,3,5-Triazin-2-Amine (3)2,4,6-Triphenoxy-1,3,5-Triazine (4)2,4,6-Triphenyl-1,3,5-Triazine (24)2,4-Diphenyl-1,3,5-Triazine (6)2-Chloro-1,3,5-Triazine (10)2-Methoxy-1,3,5-Triazine (10)2-Phenyl-1,3,5-Triazine (6)N2,N4,N6-Triphenyl-1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-Triamine (4)Pyrrolo[2,1-F][1,2,4]Triazine (14)
Triazoles (7749)
(5As,10Br)-2-Phenyl-2,5A,6,10B-Tetrahydro-4H-Indeno[2,1-B][1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-D][1,4]Oxazin-11-Ium (6)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)1-Benzyl-1H-1,2,3-Triazole (8)1-Benzyl-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)1-Methyl-1H-1,2,3-Triazole (9)1-Methyl-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (17)1-Methyl-1H-Benzo[D][1,2,3]Triazole (10)1-Phenethyl-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)1-Phenyl-1H-1,2,3-Triazole (7)1-Phenyl-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (20)1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-Amine (7)1H-1,2,4-Triazol-5-Amine (6)2-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (6)2-Phenyl-2,5,6,7-Tetrahydropyrrolo[2,1-C][1,2,4]Triazol-4-Ium (6)2-Phenyl-2H-1,2,3-Triazole (7)2-Phenyl-2H-Benzo[D][1,2,3]Triazole (8)2H-1,2,3-Triazole (7)4-(4-Cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-Yl)-4H-1,2,4-Triazole (7)4-Phenyl-4H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)4-Phenyl-6H-Thieno[3,2-F][1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A][1,4]Diazepine (5)4H-1,2,4-Triazole (13)5-Bromo-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)5-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D][1,2,3]Triazole (5)5-Fluoro-1H-Benzo[D][1,2,3]Triazole (4)6-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (12)6-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A]Pyridine (8)8-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (6)[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyrazine (9)[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridin-2-Amine (17)[1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A]Pyridin-3-Ylmethanamine (5)Ethyl 1H-1,2,4-Triazole-3-Carboxylate (3)
Organic Building Blocks
Alcohols (45771)
Amino-Propanol (6)Cyclopropylethanol (6)Diethanol (23)Diethanol (23)Dihydroxybenzylidene (4)Dihydroxynaphthalene (7)Dihydroxypropanoate (7)Dihydroxyterephthalic Acid (3)Hydroxyacetamide (1)Hydroxyacetimidamide (3)Hydroxyadamantan (4)Hydroxyadamantan (4)Hydroxyazetidine (7)Hydroxybenzyl (18)Hydroxybenzylidene (5)Hydroxybicyclo (7)Hydroxybutan (4)Hydroxybutan (4)Hydroxybutanoate (36)Hydroxybutanoic (33)Hydroxycarbamimidoyl (2)Hydroxycinnamic Acid (2)Hydroxycyclobutyl (3)Hydroxycyclohexyl (7)Hydroxycyclopentyl (1)Hydroxydiphenylmethyl (2)Hydroxyethoxy (22)Hydroxyethoxy (22)Hydroxyhexanoate (8)Hydroxyhexanoic (6)Hydroxyimino (11)Hydroxyisonicotinaldehyde (7)Hydroxyisonicotinate (5)Hydroxyisonicotinic (5)Hydroxyisonicotinic (5)Hydroxyisonicotinic Acid (4)Hydroxymethyl-Phenyl-Boronic-Acid (31)Hydroxynaphthalene (29)Hydroxynicotinaldehyde (7)Hydroxynicotinate (13)Hydroxynicotinonitrile (6)Hydroxyoctadec (1)Hydroxyoctadec (1)Hydroxyoctadecanoic (7)Hydroxypentanoate (6)Hydroxypropanoic (35)Pentahydroxyhexanal (9)Phenyl-Methanol (3)Propanediol (9)Propanediol (9)Tetrahydroxy (25)Tetrahydroxy (25)Tetrahydroxyhexanal (9)Tetrahydroxypentanal (5)Trihydroxy (246)Trihydroxy (246)(1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Yl)Methanol (7)(1-Phenylcyclopropyl)Methanol (3)(1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Yl)Methanol (14)(1H-Indol-2-Yl)Methanol (8)(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Methanol (10)(2-Bromo-6-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (4)(2-Bromophenyl)Methanol (39)(2-Chlorophenyl)Methanol (39)(2-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (60)(2-Iodophenyl)Methanol (12)(2-Nitrophenyl)Methanol (29)(3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenyl)Methanol (7)(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Methanol (4)(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Methanol (21)(3-Chlorophenyl)Methanol (38)(3-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (58)(3-Iodophenyl)Methanol (13)(3-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (10)(3-Nitrophenyl)Methanol (31)(3-Phenoxyphenyl)Methanol (3)(3-Phenylisoxazol-5-Yl)Methanol (7)(4-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (29)(4-Nitrophenyl)Methanol (17)(6-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (5)(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Methanol (6)1,2-Diphenylethan-1-Ol (8)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Ol (3)1-Phenylethan-1-Ol (102)2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-Phenylethan-1-Ol (27)2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (10)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Ethan-1-Ol (8)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (10)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (10)2-(Piperidin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (8)2-(Piperidin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (5)2-Amino-2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-Ol (7)2-Amino-2-(Anthracen-9-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (4)2-Amino-2-Phenylethan-1-Ol (196)2-Hydroxy-1,2-Diphenylethan-1-One (3)2-Hydroxy-1-Phenylethan-1-One (8)2-Hydroxyethyl Benzoate (3)2-Phenoxyethan-1-Ol (14)2-Phenylethan-1-Ol (77)2-Phenylpropan-2-Ol (21)3-Phenylpropan-1-Ol (24)4-Fluoro-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-5-(9H-Purin-9-Yl)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Ol (4)4-Phenylpiperidin-4-Ol (10)Azetidin-2-Ylmethanol (7)Azetidin-3-Ol (11)Benzyl 3-(Hydroxymethyl)Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (6)Benzyl-2-(Hydroxymethyl)Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (9)Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentan-1-Ylmethanol (3)Cyclobutanol (46)Cyclobutylmethanol (15)Cyclohexanol (72)Cyclohexylmethanol (31)Cyclopentanol (51)Diphenylmethanol (20)Isoxazol-3-Ylmethanol (3)Isoxazol-5-Ylmethanol (5)M-Tolylmethanol (34)Morpholin-2-Ylmethanol (12)Morpholin-3-Ylmethanol (14)Naphthalen-1-Ylmethanol (8)O-Tolylmethanol (35)Oxiran-2-Ylmethanol (3)Piperidin-2-Ylmethanol (11)Piperidin-3-Ol (27)Piperidin-3-Ylmethanol (15)Piperidin-4-Ylmethanol (11)Pyridin-2-Ylmethanol (65)Pyridin-3-Ylmethanol (39)Pyridin-4-Ylmethanol (16)Pyrimidin-2-Ylmethanol (5)Pyrrolidin-2-Ylmethanol (26)Pyrrolidin-3-Ylmethanol (13)Quinazolin-2-Ol (7)Tert-Butyl 3-(Hydroxymethyl)-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (10)Thiazol-2-Ylmethanol (9)Thiophen-2-Ylmethanol (11)Triphenylmethanol (13)
Aldehydes (18914)
Aminonicotinaldehyde (5)Aminonicotinaldehyde (5)Carboxyaldehyde (1094)Dicarbaldehyde (37)Dicarbaldehyde (37)Formylisonicotinate (7)Tetracarbaldehyde (8)Tetracarbaldehyde (8)Tricarbaldehyde (10)1-Methyl-1H-Indole-3-Carbaldehyde (9)1-Naphthaldehyde (23)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbaldehyde (8)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-2-Carbaldehyde (5)1H-Indazole-3-Carbaldehyde (19)1H-Indole-2-Carbaldehyde (20)1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbaldehyde (30)1H-Pyrrole-2-Carbaldehyde (21)1H-Pyrrole-3-Carbaldehyde (9)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-3-Carbaldehyde (14)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-5-Carbaldehyde (5)2,3-Dichlorobenzaldehyde (7)2,3-Difluorobenzaldehyde (18)2,4-Dichlorobenzaldehyde (8)2,4-Difluorobenzaldehyde (19)2,6-Dibromobenzaldehyde (4)2,6-Difluorobenzaldehyde (25)2-(Benzyloxy)Benzaldehyde (13)2-(Phenylethynyl)Benzaldehyde (9)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzaldehyde (7)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzaldehyde (27)2-Bromo-3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (4)2-Bromo-3-Methoxybenzaldehyde (4)2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzaldehyde (15)2-Chloro-3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (4)2-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzaldehyde (7)2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (10)2-Fluoro-3-Methylbenzaldehyde (8)2-Fluorobenzaldehyde (175)2-Hydroxy-3-Iodobenzaldehyde (3)2-Iodobenzaldehyde (17)2-Methyl-1H-Indole-3-Carbaldehyde (3)2-Naphthaldehyde (12)2-Nitrobenzaldehyde (53)2-Oxo-2-Phenylacetaldehyde (12)2-Phenylacetaldehyde (20)3-(Benzyloxy)Benzaldehyde (13)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzaldehyde (10)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzaldehyde (31)3-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzaldehyde (4)3-Bromo-2-Fluorobenzaldehyde (9)3-Bromo-2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (10)3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (7)3-Bromo-4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (9)3-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzaldehyde (9)3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzaldehyde (9)3-Chloro-2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (5)3-Chloro-4-Methoxybenzaldehyde (7)3-Chlorobenzaldehyde (106)3-Fluorobenzaldehyde (137)3-Iodobenzaldehyde (28)3-Methoxy-2-Nitrobenzaldehyde (3)3-Nitrobenzaldehyde (49)3-Phenoxybenzaldehyde (7)4-(1H-Imidazol-1-Yl)Benzaldehyde (7)4-(Benzyloxy)Benzaldehyde (23)4-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Benzaldehyde (5)4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (78)4-Hydroxy-3-Nitrobenzaldehyde (5)4-Morpholinobenzaldehyde (8)4-Nitrobenzaldehyde (18)4-Phenoxybenzaldehyde (12)5-Phenylfuran-2-Carbaldehyde (9)6-Methoxynicotinaldehyde (4)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-Carbaldehyde (20)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Carbaldehyde (31)Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carbaldehyde (7)Benzo[B]Thiophene-3-Carbaldehyde (6)Benzo[D][1,3]Dioxole-5-Carbaldehyde (6)Benzofuran-2-Carbaldehyde (5)Furan-2-Carbaldehyde (22)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-2-Carbaldehyde (8)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-3-Carbaldehyde (9)Isonicotinaldehyde (68)Methyl 3-Formylbenzoate (23)Nicotinaldehyde (153)Picolinaldehyde (98)Pyrazine-2-Carbaldehyde (17)Pyrimidine-5-Carbaldehyde (38)Thiazole-2-Carbaldehyde (9)Thiazole-5-Carbaldehyde (19)Thiophene-2-Carbaldehyde (43)Thiophene-3-Carbaldehyde (17)
Aliphatic Chain Hydrocarbons (12579)
Acetylthio (7)Acetylthio (7)Azanonadecan (7)Azanylylidene (1)Azapentadecan (10)Azapentadecan (10)Azatridecan (4)Butyloctyl (4)Butyloctyl (4)Carbonylbis (2)Carbonylbis (2)Diazirine (13)Diazirine (13)Didodecyl (7)Didodecyl (7)Diethyl (73)Diethyl (73)Dihydroxypropan (6)Diisobutyl (2)Diisopropyl (27)Diisopropyl (27)Dimethoxy (306)Dimethyladamantane (14)Dimethyladamantane (14)Dimethylalkanes (7)Dinonyl (1)Dinonyl (1)Dioctyl (1)Dioxide (451)Dioxide (451)Ethoxy (711)Ethoxyethoxy (5)Ethoxyethoxy (5)Ethoxyethyl (16)Ethoxyethyl (16)Ethoxymethyl (11)Ethoxymethylene (1)Ethoxymethylene (1)Isopropylidenebis (2)Isopropylsulfonyl (10)Isopropylsulfonyl (10)Methoxybut (2)Methoxybut (2)Methoxyethoxy (67)Methoxyethoxy (67)Methoxyethyl (69)Methoxyisonicotinic (11)Methoxyisonicotinic (11)Methoxymethoxy (23)Methoxymethoxy (23)Methoxymethyl (117)Methoxynicotinic (26)Methoxynicotinic (26)Methoxynicotinic Acid (20)Methoxypropan (24)Methoxypropan (24)Methoxypropoxy (8)Methoxypropoxy (8)Methoxypropyl (10)Methoxytetrahydro (14)Methoxytetrahydro (14)Methyladamantan (4)Methylisonicotinic (13)Oxoethoxy (1)Oxopropane (10)Oxopropyl (32)Oxopropyl (32)Pentyloxy (7)Tetramethoxy (6)Trimethoxy (15)Trimethoxy (15)Yldisulfanyl (7)
Aliphatic Cyclic Hydrocarbons (11046)
Aminobicyclo (24)Aminocyclobutanol (5)Aminocyclobutyl (5)Aminocyclohexane (55)Aminocyclohexanol (21)Aminocyclopentanol (17)Aminocyclopentyl (6)Aminocyclopropyl (4)Azabicyclo (292)Azabicyclo (292)Azatricyclo (5)Azatricyclo (5)Azetidine (185)Azetidine (185)Benzylazetidin (9)Bicyclo (61)Bicyclohexyl (6)Bromobicyclo (9)Butylcyclohexyl (9)Butylsulfonyl (6)Chlorocyclopropyl (2)Cyanoazetidine (5)Cyanocyclopropyl (4)Cyclobutanecarbonitrile (2)Cyclobutylacetic (4)Cyclobutylmethyl (4)Cyclobutylmethyl (4)Cyclodextrin (1)Cyclodextrin (1)Cyclohexa (176)Cyclohexa (176)Cyclohexane (127)Cyclohexane (127)Cyclohexanecarboxylic (19)Cyclohexanediamine (8)Cyclohexanone (92)Cyclohexylacetic (2)Cyclohexylamino (9)Cyclohexylbutanoic (4)Cyclohexylcarbamoyl (5)Cyclohexylethanamine (12)Cyclohexylmethoxy (4)Cyclohexylmethoxy (4)Cyclohexylmethyl (7)Cyclohexylmethyl (7)Cyclohexyloxy (10)Cyclohexylpropan (94)Cyclohexylpropanoic (9)Cyclopentadienyl (2)Cyclopentane (169)Cyclopentane (169)Cyclopentanecarboxylic (7)Cyclopentyl (56)Cyclopentyl (56)Cyclopentylacetic (3)Cyclopentylamino (1)Cyclopentylmethyl (4)Cyclopentyloxy (16)Cyclopentyloxy (16)Cyclopentylpropanoic (1)Cyclopropanamine (32)Cyclopropanamine (32)Cyclopropanecarbonitrile (14)Cyclopropanecarbonyl (6)Cyclopropanecarbonyl (6)Cyclopropanecarboxamide (14)Cyclopropanol (4)Cyclopropoxyphenyl (7)Cyclopropyl (355)Cyclopropyl (355)Cyclopropylacetate (6)Cyclopropylacetic (3)Cyclopropylamino (24)Cyclopropylcarbamoyl (5)Cyclopropylethan (5)Cyclopropylethan (5)Cyclopropylethynyl (1)Cyclopropylmethoxy (32)Cyclopropylmethoxy (32)Cyclopropylmethyl (22)Cyclopropylmethyl (22)Cyclopropylpropanoic (5)Cyclopropylsulfonyl (6)Cyclopropylsulfonyl (6)Diazabicyclo (77)Diazabicyclo (77)Dicyclohexyl (6)Dicyclohexyl (6)Dicyclohexylphosphino (18)Dicyclohexylphosphino (18)Difluorocyclobutyl (6)Difluorocyclohexyl (7)Dihydroinden (8)Dihydroindeno (5)Dihydroindeno (5)Dihydropteridin (6)Dimethylbicyclo (5)Dimethylbicyclo (5)Dimethylcyclohex (5)Dimethylcyclohexane (16)Dimethylcyclohexanone (7)Dioxathiolane (1)Dioxathiolane (1)Dioxol (175)Dithiolan (1)Dithiolan (1)Ethylcyclohexyl (4)Ethylcyclohexyl (4)Ethylsulfonyl (42)Fluoroazetidine (1)Fluorobicyclo (4)Hexahydrocyclohepta (6)Hexahydrocyclohepta (6)Hexahydrocyclopenta (4)Hydroxycyclobutanecarboxylic (4)Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic (6)Methanesulfonyl (314)Methanesulfonyl (314)Methoxycyclohexanamine (6)Methylazetidine (30)Methylbicyclo (6)Methylbicyclo (6)Methylcyclobutanamine (5)Methylcyclobutanecarboxylic (5)Methylcyclohexanamine (12)Methylcyclohexane (8)Methylcyclohexane (8)Methylcyclohexanecarboxylic (5)Methylcyclohexanecarboxylic Acid (4)Methylcyclohexanol (21)Methylcyclohexanone (5)Methylcyclohexyl (33)Methylcyclopentane (2)Methylcyclopropanamine (4)Methylcyclopropanamine (4)Methylcyclopropane (16)Methylsulfinyl (24)Methylsulfonimidoyl (6)Methylsulfonimidoyl (6)Methylsulphonyl (10)Octahydrocyclopenta (14)Oxabicyclo (40)Oxabicyclo (40)Oxazepane (13)Oxetanes (228)Oxoazetidine (8)Oxoazetidine (8)Oxobicyclo (11)Oxobicyclo (11)Oxocyclobutyl (2)Oxocyclohex (3)Oxocyclohexane (4)Oxocyclohexane (4)Oxocyclohexanecarboxylic (6)Oxocyclohexyl (3)Oxocyclohexyl (3)Oxocyclopentane (2)Oxocyclopentyl (5)Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl (11)Pentylcyclohexyl (10)Pentylcyclohexyl (10)Phenylcyclopropanamine (8)Propylcyclohexyl (15)Propylcyclohexyl (15)Tetraazacyclododecane (13)Tetraazacyclododecane (13)Tetraazacyclotetradecane (7)Tetraazacyclotetradecane (7)Tetramethylcyclohexane (4)Tetraoxatridecan (3)Tetraoxatridecan (3)Thiazepine (2)Tricyclohexylphosphine (9)Trimethylbicyclo (21)Trimethylcyclohex (20)Trimethylcyclohexane (1)Trimethylcyclohexane (1)(1-Phenylcyclobutyl)Methanamine (9)(1-Phenylcyclopropyl)Methanamine (12)(1-Phenylcyclopropyl)Methanol (3)(3Ar,E)-4-((Z)-2-(2-Methylenecyclohexylidene)Ethylidene)Octahydro-1H-Indene (7)(4-Cyclohexylphenyl)Boronic Acid (7)(4-Pentylcyclohexyl)Benzene (5)(4-Propylcyclohexyl)Benzene (5)(9H-Fluoren-2-Yl)Boronic Acid (6)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (4-Methoxybenzyl)Carbamate (7)(Cyclopropylmethoxy)Benzene (18)1,1-Difluorocyclobutane (14)1,1-Difluorocyclohexane (18)1,1-Difluorocyclopentane (5)1-Bromo-2-Cyclopropylbenzene (3)1-Bromo-3-Cyclopropylbenzene (6)1-Chloro-2-Cyclopropylbenzene (7)1-Cyclohexyl-2-Fluorobenzene (4)1-Cyclopropyl-3-Methylbenzene (3)1-Methylcyclohex-1-Ene (26)1-Phenylcyclobutan-1-Amine (5)1-Phenylcyclobutane-1-Carbonitrile (7)1-Phenylcyclobutane-1-Carboxylic Acid (16)1-Phenylcyclohexane-1-Carboxylic Acid (6)1-Phenylcyclopropan-1-Amine (26)1-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carbonitrile (19)1-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid (23)2-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-2-Phenylacetic Acid (5)2-Bromo-9,9-Diphenyl-9H-Fluorene (5)2-Bromo-9H-Fluorene (15)2-Cyclohexylacetic Acid (14)2-Cyclopropyl-4-Phenylquinoline (12)2-Cyclopropylpyridine (20)2-Cyclopropylpyrimidine (10)2-Iodo-9H-Fluorene (8)2-Methylcyclohexan-1-One (3)2-Phenylcyclopropan-1-Amine (19)3,3-Dimethylcyclohexan-1-One (4)3-Cyclopropylpyridine (28)3-Methylcyclohexan-1-One (9)4-Cyclohexylbenzoic Acid (6)4-Cyclohexylbenzonitrile (10)4-Cyclohexylphenol (7)5-Azaspiro[2.4]Heptane (13)6-Azaspiro[2.5]Octane (10)9,9-Dimethyl-9H-Fluorene (16)Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentan-1-Ylmethanol (3)Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentane-1-Carboxylic Acid (6)Bicyclo[2.2.1]Hept-2-Ene (18)Bicyclo[2.2.1]Heptane (15)Bromocyclohexane (7)Cyclobutanamine (90)Cyclobutanecarboxylic Acid (23)Cyclobutanol (46)Cyclobutylmethanol (15)Cycloheptane (12)Cyclohex-3-Ene-1-Carboxylic Acid (7)Cyclohexanamine (59)Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid (83)Cyclohexanol (72)Cyclohexylmethanol (31)Cyclopentanamine (5)Cyclopentanecarboxylic Acid (26)Cyclopentanol (51)Cyclopropoxybenzene (13)Ethyl 1-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylate (4)Ethyl 2-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Cyclohexanecarboxylate (33)Isopropylcyclohexane (19)Methoxycyclohexane (7)Methyl 1-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylate (10)Methyl 4-Oxocyclohexane-1-Carboxylate (5)Methyl Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentane-1-Carboxylate (10)Methyl Cyclobutanecarboxylate (24)Methyl Cyclohexanecarboxylate (45)Methyl Cyclopentanecarboxylate (18)N-Methylcyclohexanamine (7)Naphthalene-1,4-Dione (23)Spiro[3.3]Heptane (11)Tert-Butyl (1-Phenylcyclopropyl)Carbamate (6)Tert-Butyl (2-Phenylcyclopropyl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentan-1-Ylcarbamate (5)Tert-Butyl Cyclobutylcarbamate (17)Tert-Butyl Cyclohexylcarbamate (9)Tert-Butyl Cyclopentylcarbamate (28)
Alkenyls (16078)
Acrylaldehyde (11)Acryloyl (9)Acryloyl (9)Annulene (2)Cyclohexene (88)Cyclooctene (9)Cyclopentene (3)Diacrylamide (6)Diallyl (5)Diazene (21)Divinyl (1)Divinyl (1)Enamide (6)Enamide (6)Enecarbaldehyde (2)Enoyl (9)Methacrylamide (3)Methacrylamide (3)Methoxycinnamaldehyde (3)Nitroethylene (37)Tetrahydrocyclopenta (19)(1E,4E)-1,5-Diphenylpenta-1,4-Dien-3-One (7)(1E,6E)-1,7-Diphenylhepta-1,6-Diene-3,5-Dione (7)(2,2-Dibromovinyl)Benzene (6)(2-(4-Bromophenyl)Ethene-1,1,2-Triyl)Tribenzene (11)(2-Nitrovinyl)Benzene (28)(Allyloxy)Benzene (19)(E)-5-Benzylidenethiazolidine-2,4-Dione (6)(E)-[3,3'-Biindolinylidene]-2,2'-Dione (5)(E)-N-(3-Oxo-1-Phenyl-3-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Prop-1-En-2-Yl)Benzamide (6)(Z)-3-(Phenyl(Phenylamino)Methylene)Indolin-2-One (5)(Z)-3-Benzylideneindolin-2-One (7)1,2-Diphenylethene (5)1,3,3-Trimethylcyclohex-1-Ene (12)1-Bromo-4-Styrylbenzene (5)1-Methylcyclohex-1-Ene (26)2-Benzalacetophenone (36)2-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (7)2-Methylcyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (5)3-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acrylic Acid (17)3-(3-Chlorophenyl)Acrylic Acid (10)3-Methylene-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (5)3-Methyleneazetidine (8)3-Phenylacrylaldehyde (29)3-Styrylphenol (11)4-(1,2,2-Triphenylvinyl)Benzaldehyde (5)4-(Prop-1-En-2-Yl)Cyclohex-1-Ene (5)5H-Dibenzo[B,F]Azepine (4)Allyl Benzoate (5)Cyclohex-1-En-1-Yl Trifluoromethanesulfonate (3)Cyclohex-1-En-1-Ylboronic Acid (4)Cyclohex-1-Ene-1-Carboxylic Acid (4)Cyclohexa-1,3-Diene (5)Cyclopent-2-En-1-Amine (4)Ethyl Cyclohex-1-Ene-1-Carboxylate (5)Methyl Cinnamate (36)Methyl Cyclohex-3-Ene-1-Carboxylate (3)Methylenecyclobutane (8)Methylenecyclohexane (8)N-Phenylacrylamide (7)Styrene (81)Tert-Butyl-Cyclopent-2-En-1-Ylcarbamate (6)Vinylcyclopropane (8)
Alkynyls (2698)
(Bromoethynyl)Benzene (5)(Prop-2-Yn-1-Yloxy)Benzene (13)1,3,5-Tris(Phenylethynyl)Benzene (6)1,4-Bis(Phenylethynyl)Benzene (7)1,4-Diphenylbuta-1,3-Diyne (9)1-Ethynyl-2-Fluorobenzene (10)1-Methyl-4-(Phenylethynyl)Benzene (7)2-(Phenylethynyl)Benzaldehyde (9)2-Ethynylpyridine (31)2-Ethynylthiophene (8)3-Ethynylpyridine (22)4-(Phenylethynyl)-1,1'-Biphenyl (5)4-(Phenylethynyl)Phenol (7)4-Ethynylpyridine (10)9,10-Bis(Phenylethynyl)Anthracene (5)Ethynylbenzene (145)Trimethyl(Phenylethynyl)Silane (23)
Amides (90371)
Acetamide (651)Acetamide (651)Acetamido (156)Carboxamide (929)Carboxamide (929)Diacetamide (3)Dicarboxamide (19)Diethylacetamide (4)Diethylacetamide (4)Dimethylacetamide (9)Dimethylnicotinamide (7)Dimethylnicotinamide (7)Formamidophenylboronic Acid/Ester (11)Isobutyramide (7)Oxobutanamide (10)Oxobutanamide (10)Pentanamide (18)Pentanamide (18)Propanamide (2)Propanamido (5)Propanamido (5)(3-(Phenylcarbamoyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (3)(4-(Phenylcarbamoyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (11)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (3-Phenylpropyl)Carbamate (24)(S)-N-Phenethyl-3-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Propanamide (5)(S)-N-Phenylpiperidine-2-Carboxamide (1)1-(Pyridin-2-Yl-L2-Azaneyl)Ethan-1-One (12)1-Methylindoline-2,3-Dione (8)1-Phenylurea (11)1H-Pyrazole-5-Carboxamide (3)2,2-Dimethyl-1-(Pyridin-2-Yl-L2-Azaneyl)Propan-1-One (7)2-((Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)Amino)Benzoic Acid (11)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzamide (6)2-Amino-3-Phenylpropanamide (8)2-Amino-N-Phenylbenzamide (21)2-Aminobenzamide (30)2-Bromo-N-Phenylacetamide (5)2-Chloro-N-Phenylacetamide (26)2-Chloro-N-Phenylbenzamide (4)2-Chlorobenzamide (16)2-Fluoro-N-Methylbenzamide (12)2-Fluorobenzamide (32)2-Hydroxy-N-Phenylbenzamide (3)2-Hydroxybenzamide (14)2-Iodobenzamide (4)2-Methoxybenzamide (9)3-Benzamidopropanoic Acid (3)3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzamide (3)3-Fluorobenzamide (26)3-Nitrobenzamide (17)3-Oxo-N-Phenylbutanamide (10)4-Amino-N-Phenylbenzamide (7)4-Benzamidobenzoic Acid (3)4-Fluorobenzamide (19)4-Oxo-4-(Phenylamino)Butanoic Acid (7)Benzoylglycine (15)Benzyl Benzylcarbamate (16)Benzyl Cyclohexylcarbamate (9)Benzyl Phenylcarbamate (15)Ethyl 2-Oxo-2-(Phenylamino)Acetate (8)Isonicotinamide (12)N,N-Diethylbenzamide (17)N,N-Dimethylbenzamide (34)N-((5R,6R)-7-Oxo-4-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[3.2.0]Heptan-6-Yl)-3-Phenylisoxazole-4-Carboxamide (1)N-((6R,7R)-8-Oxo-5-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[4.2.0]Oct-2-En-7-Yl)-2-Phenylacetamide (5)N-(2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethyl)Acetamide (5)N-(2-Benzoylphenyl)-2-Bromoacetamide (3)N-(2-Chlorophenyl)Acetamide (16)N-(2-Iodophenyl)Acetamide (8)N-(2-Nitrophenyl)Acetamide (11)N-(3-Fluorophenyl)Acetamide (14)N-(4-Aminophenyl)Benzamide (2)N-(4-Chlorophenyl)Acetamide (9)N-(4-Chlorophenyl)Benzamide (6)N-(4-Fluorophenyl)Benzamide (3)N-(4-Phenoxyphenyl)Acetamide (4)N-(O-Tolyl)Benzamide (9)N-(P-Tolyl)Benzamide (6)N-(Thiazol-2-Yl)Acetamide (9)N-Isopropylbenzamide (16)N-Methoxy-N-Methylbenzamide (24)N-Methylbenzamide (58)N-Methylpicolinamide (10)N-Phenylacrylamide (7)N-Phenylpivalamide (11)Nicotinamide (64)Phenyl Dimethylcarbamate (5)Phenyl Ethyl(Methyl)Carbamate (5)Picolinamide (26)Piperidine-3-Carboxamide (5)Pyrazine-2-Carboxamide (10)Pyrrolidine-2-Carboxamide (12)Tert-Butyl (1-Phenylethyl)Carbamate (19)Tert-Butyl (4-Fluorophenyl)Carbamate (9)Tert-Butyl Benzylcarbamate (52)Tert-Butyl Methyl(Phenyl)Carbamate (9)Tert-Butyl O-Tolylcarbamate (11)Tert-Butyl Phenethylcarbamate (12)Tert-Butyl-Cyclopent-2-En-1-Ylcarbamate (6)Thiophene-3-Carboxamide (5)
Amines (139951)
Amino-Carboxylate (2)Amino-Propanol (6)Aminoacetamido (4)Aminoacetyl (2)Aminoadamantan (5)Aminoadamantan (5)Aminoazepane (10)Aminobutane (23)Aminobutane (23)Aminobutyl (15)Aminobutyl (15)Aminoethoxy (18)Aminoethoxy (18)Aminoethyl (157)Aminoethyl (157)Aminohexan (6)Aminohexyl (3)Aminohexyl (3)Aminoisonicotinic Acid (12)Aminomethyl (403)Aminomethyl (403)Aminooxy (6)Aminopentyl (10)Aminopentyl (10)Aminopropanamido (1)Aminopropane (20)Aminopropane (20)Aminopropoxy (2)Aminopropoxy (2)Aminotetrahydro (12)Aminotetrahydro (12)Benzylazetidine (4)Bromobenzylamine (6)Bromobenzylcarbamate (28)Butoxycarbonylamino (8)Butylcarbamoyl (5)Carbamothioyl (2)Carbamoyl (114)Chlorobenzylamine (4)Chroman-Amine (1)Diamino (90)Diamino (90)Diaminopteridin (3)Diaminopteridin (3)Dibutylamino (6)Dibutylamino (6)Dichlorobenzylamine (5)Diethylamino (91)Diethylamino (91)Diisopropylamino (1)Dimethyl-Ethylamine (2)Dimethylamino (490)Dimethylamino (490)Dimethylcarbamoyl (14)Dimethylmethanamine (16)Dipropylamino (1)Dipropylamino (1)Ethylamino (37)Ethylamino (37)Fluindamine (32)Hydroxyamino (3)Hydroxyamino (3)Imidazol-Amine (1)Methoxyethanamine (1)Methoxyethanamine (1)Methoxyimino (2)Methylamino (241)Methylamino (241)Methylcarbamoyl (19)Methylcarbamoyl (19)Propanediamine (6)Propylamino (5)Propylamino (5)Pyrrol-Amine (1)Pyrrolopyridine-Methylamine (6)Silanamine (3)Triamine (25)Triamine (25)(1-Phenylcyclobutyl)Methanamine (9)(1-Phenylcyclopropyl)Methanamine (12)(1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Yl)Methanamine (7)(2,3-Dihydrobenzo[B][1,4]Dioxin-2-Yl)Methanamine (3)(2-Aminophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (30)(2-Bromophenyl)Methanamine (12)(2-Chlorophenyl)Methanamine (28)(2-Fluorophenyl)Methanamine (49)(3-Chlorophenyl)Methanamine (19)(3-Fluoropyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(3-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(4-Aminophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (4)(4-Fluorophenyl)Methanamine (27)(6-Methylpyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (6)(Tetrahydrofuran-2-Yl)Methanamine (4)(Tetrahydrofuran-3-Yl)Methanamine (3)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-5-Amine (4)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-6-Amine (3)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-7-Amine (3)1,2-Diphenylethan-1-Amine (15)1,3,4-Thiadiazol-2-Amine (9)1,3,5-Triazin-2-Amine (3)1-(2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-5-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (3)1-(2-Aminophenyl)Ethan-1-One (29)1-(2-Bromophenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (10)1-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1H-Pyrazole (3)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (80)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Propan-1-Amine (8)1-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (6)1-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (25)1-(3-Aminophenyl)Ethan-1-One (18)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N-Methylmethanamine (8)1-(4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (6)1-(Anthracen-9-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (3)1-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (15)1-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (17)1-(Pyridin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (23)1-Aminoanthracene-9,10-Dione (8)1-Benzyl-N-Methylpiperidin-3-Amine (6)1-Benzylpiperidin-4-Amine (8)1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Amine (14)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-3-Amine (3)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-5-Amine (4)1-Phenylcyclobutan-1-Amine (5)1-Phenylcyclopropan-1-Amine (26)1-Phenylethan-1-Amine (436)1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-Amine (7)1H-1,2,4-Triazol-5-Amine (6)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Amine (7)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-5-Amine (4)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-6-Amine (6)1H-Imidazol-2-Amine (6)1H-Indazol-3-Amine (23)1H-Indazol-4-Amine (12)1H-Indazol-5-Amine (3)1H-Indazol-6-Amine (5)1H-Indazol-7-Amine (6)1H-Indol-4-Amine (10)1H-Indol-6-Amine (21)1H-Indol-7-Amine (10)1H-Pyrazol-4-Amine (6)1H-Pyrazol-5-Amine (19)1H-Pyrrol-1-Amine (7)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridin-6-Amine (4)2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-Phenylethan-1-Amine (48)2,3-Dichloroaniline (18)2,3-Difluoroaniline (34)2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran-3-Amine (11)2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran-5-Amine (3)2,4-Dibromoaniline (18)2,4-Dichloropyrimidin-5-Amine (6)2,4-Difluoroaniline (44)2,5-Difluoroaniline (34)2,6-Dibromoaniline (17)2,6-Dichloroaniline (27)2,6-Difluoroaniline (23)2,6-Diiodoaniline (8)2-((2-Nitrophenyl)Amino)Ethan-1-Ol (5)2-((3-Phenylpropyl)Amino)-1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (2)2-(1H-Benzo[D]Imidazol-2-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (6)2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (4)2-(Diethylamino)Ethyl Benzoate (3)2-(Methylsulfonyl)Aniline (3)2-(Phenylamino)Benzoic Acid (11)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (8)2-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (8)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Aniline (18)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (58)2-Amino-2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-Ol (7)2-Amino-2-Phenylethan-1-Ol (196)2-Amino-3,3-Diphenylpropanoic Acid (4)2-Amino-3-Chlorophenol (4)2-Amino-3-Fluorobenzoic Acid (11)2-Amino-6-Bromophenol (3)2-Amino-6-Chlorobenzoic Acid (5)2-Amino-6-Chlorobenzonitrile (3)2-Amino-6-Chlorophenol (5)2-Aminobenzamide (30)2-Aminobenzenesulfonic Acid (9)2-Aminophenol (107)2-Aminopyrimidin-4(3H)-One (11)2-Bromo-3-Chloroaniline (4)2-Bromo-3-Fluoroaniline (13)2-Bromo-3-Methylaniline (6)2-Bromo-4-Methylaniline (14)2-Bromo-6-Methylaniline (11)2-Bromo-N,N-Dimethylaniline (5)2-Bromo-N-Methylaniline (8)2-Chloro-3-Methylaniline (4)2-Chloro-4-Methylaniline (7)2-Chloro-6-Methylaniline (11)2-Chloro-N-Methylaniline (4)2-Chloro-N-Phenylaniline (7)2-Chloroaniline (214)2-Chlorobenzene-1,3-Diamine (3)2-Chlorobenzene-1,4-Diamine (6)2-Chloropyrimidin-4-Amine (22)2-Fluoro-6-Iodoaniline (7)2-Fluoro-N-Phenylaniline (4)2-Fluoroaniline (262)2-Iodo-4-Methylaniline (5)2-Iodo-N,N-Dimethylaniline (3)2-Iodoaniline (87)2-Methoxypyridin-3-Amine (6)2-Methyl-6-Nitroaniline (10)2-Methyl-N-Phenylaniline (6)2-Methylpyridin-4-Amine (7)2-Methylpyrimidin-4-Amine (22)2-Nitro-N-Phenylaniline (3)2-Phenoxyaniline (4)2-Phenylcyclopropan-1-Amine (19)2-Phenylpyrimidin-5-Amine (5)3,4-Dibromoaniline (4)3,4-Dichloroaniline (21)3,4-Difluoroaniline (44)3-(1,3,2-Dioxaborinan-2-Yl)Aniline (3)3-(Benzyloxy)Aniline (12)3-(Methylsulfonyl)Aniline (7)3-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Aniline (3)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Aniline (22)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (102)3-Aminobenzenesulfonic Acid (6)3-Aminodihydrofuran-2(3H)-One (4)3-Bromo-2-Fluoroaniline (15)3-Bromo-4-Chloroaniline (13)3-Bromo-4-Fluoroaniline (22)3-Bromo-4-Methoxyaniline (7)3-Bromo-4-Methylaniline (14)3-Bromoaniline (187)3-Bromobenzene-1,2-Diamine (11)3-Chloro-2-Iodoaniline (3)3-Chloro-2-Methylaniline (11)3-Chloro-4-Fluoroaniline (18)3-Chloro-4-Iodoaniline (3)3-Chloro-4-Methoxyaniline (6)3-Chloro-4-Methylaniline (12)3-Chlorobenzene-1,2-Diamine (6)3-Chloropyrazin-2-Amine (6)3-Fluoro-2-Methylaniline (9)3-Fluoroaniline (289)3-Iodo-2-Methylaniline (4)3-Iodoaniline (32)3-Methoxypyridin-2-Amine (5)3-Methyl-N-Phenylaniline (4)3-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (7)3-Nitroaniline (98)3-Phenoxyaniline (2)3-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-5-Amine (11)3-Phenylisoxazol-5-Amine (8)4,6-Dichloropyrimidin-2-Amine (9)4-(Benzyloxy)Aniline (8)4-(Oxazol-5-Yl)Aniline (3)4-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Aniline (3)4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Aniline (26)4-Amino-2-Chlorobenzonitrile (8)4-Amino-2-Fluorophenol (9)4-Amino-3-Chlorobenzoic Acid (6)4-Amino-3-Chlorophenol (5)4-Amino-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (3)4-Aminopyridazin-3(2H)-One (4)4-Benzylaniline (7)4-Bromo-3-Chloroaniline (21)4-Bromo-3-Fluoroaniline (29)4-Bromo-3-Methylaniline (19)4-Bromo-3-Nitroaniline (8)4-Bromo-N,N-Diphenylaniline (10)4-Bromo-N-Phenylaniline (6)4-Chloro-2-Iodoaniline (9)4-Chloro-3-Fluoroaniline (17)4-Chloro-3-Iodoaniline (3)4-Chloro-3-Methylaniline (11)4-Chloro-N-Phenylaniline (6)4-Chloropyrimidin-2-Amine (23)4-Chloropyrimidin-5-Amine (7)4-Fluoro-N-Phenylaniline (4)4-Fluoroaniline (225)4-Iodo-N,N-Diphenylaniline (3)4-Methoxy-N-Phenylaniline (5)4-Methyl-3-Nitroaniline (8)4-Methylpyrimidin-2-Amine (9)4-Methylthiazol-2-Amine (7)4-Morpholinoaniline (4)4-Nitroaniline (65)4-Phenoxyaniline (6)4-Phenylpyrimidin-2-Amine (15)4-Phenylthiazol-2-Amine (37)5-Bromopyrazin-2-Amine (13)5-Bromothiazol-2-Amine (6)5-Chloropyrazin-2-Amine (9)5-Methoxypyridin-3-Amine (4)5-Methyl-2-Nitroaniline (6)5-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (7)5-Methylpyridin-3-Amine (4)5-Methylthiazol-2-Amine (6)5-Phenylthiophen-2-Amine (5)5H-Dibenzo[B,F]Azepine (4)6-Amino-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (3)6-Bromopyrazin-2-Amine (5)6-Chloropyrazin-2-Amine (11)6-Chloropyridazin-3-Amine (5)6-Chloropyrimidin-4-Amine (8)6-Methoxypyridin-2-Amine (14)6-Methoxypyridin-3-Amine (8)6-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (46)6-Methylpyridin-3-Amine (5)6-Phenoxypyridin-3-Amine (5)7-Methoxy-N-Phenylquinazolin-4-Amine (12)7H-Purin-2-Amine (6)7H-Purin-6-Amine (9)7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidin-2-Amine (5)7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidin-4-Amine (3)9H-Purin-6-Amine (3)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Amine (8)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-Amine (11)[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridin-2-Amine (17)[1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A]Pyridin-3-Ylmethanamine (5)Azetidin-3-Amine (4)Azetidin-3-Ylmethanamine (3)Aziridine (9)Benzo[B]Thiophen-2-Amine (5)Benzo[D]Oxazol-2-Amine (16)Benzo[D]Thiazol-2-Amine (29)Benzo[D]Thiazol-5-Amine (3)Benzo[D]Thiazol-6-Amine (3)Benzyl-3-Aminopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (6)Benzyl-3-Aminopyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (7)Bis(Pyridin-2-Ylmethyl)Amine (6)Chroman-2-Ylmethanamine (3)Chroman-3-Amine (3)Chroman-4-Amine (20)Cyclobutanamine (90)Cyclohexanamine (59)Cyclopent-2-En-1-Amine (4)Cyclopentanamine (5)Cyclopropyl(Phenyl)Methanamine (22)Diphenylmethanamine (26)Ethyl 2-Aminobenzoate (23)Ethyl 3-Aminobenzoate (19)Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate (23)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-3-Amine (7)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-8-Amine (7)Isoquinolin-1-Amine (18)Isoquinolin-3-Amine (13)Isoquinolin-4-Amine (16)Isoquinolin-5-Amine (9)Isoquinolin-8-Amine (6)Isoxazol-5-Amine (15)Methyl 2-Amino-2-Phenylacetate (38)Methyl 2-Aminobenzoate (95)Methyl 3-Amino-3-Phenylpropanoate (27)Methyl 3-Aminobenzoate (88)Methyl 4-Aminobenzoate (71)Methyl L-Phenylalaninate (20)Morpholin-2-Ylmethanamine (8)N,N-Diethylaniline (17)N,N-Dimethyl-2-Phenoxyethan-1-Amine (17)N,N-Dimethylaniline (117)N,N-Dimethylnaphthalen-1-Amine (4)N,N-Dimethylpyridin-2-Amine (10)N,N-Dimethylpyridin-4-Amine (6)N,N-Dimethylpyrimidin-2-Amine (10)N,N-Dimethylpyrrolidin-3-Amine (7)N,N-Diphenyl-4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Aniline (6)N,N-Diphenyl-[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Amine (8)N-(4-Aminophenyl)Benzamide (2)N-(Furan-2-Ylmethyl)Aniline (5)N-(Prop-2-Yn-1-Yl)-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-Amine (3)N-Benzyl-1-Phenylethan-1-Amine (7)N-Benzyl-2-Phenylethan-1-Amine (1)N-Benzylpiperidin-4-Amine (3)N-Cyclopropylpyrimidin-2-Amine (5)N-Methyl-1,2-Diphenylethan-1-Amine (7)N-Methyl-1-Phenylmethanamine (65)N-Methyl-2-Nitroaniline (20)N-Methyl-4-Nitroaniline (6)N-Methylaniline (140)N-Methylcyclohexanamine (7)N-Methylpiperidin-3-Amine (5)N-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (47)N-Methylpyridin-3-Amine (15)N-Methylpyrimidin-2-Amine (10)N-Methylpyrimidin-4-Amine (10)N-Methylpyrrolidin-3-Amine (6)N-Phenyl-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (3)N-Phenyl-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (3)N-Phenylnaphthalen-1-Amine (5)N-Phenylpyridin-2-Amine (9)N-Phenylpyrimidin-2-Amine (5)N-Phenylpyrimidin-4-Amine (7)N1,N1-Diphenylbenzene-1,4-Diamine (2)N1-Phenylbenzene-1,4-Diamine (3)N2,N4,N6-Triphenyl-1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-Triamine (4)N2,N4-Diphenylpyrimidine-2,4-Diamine (5)Naphthalen-2-Amine (12)O-Benzylhydroxylamine (16)Oxazol-2-Amine (8)Phenylmethanamine (315)Piperidin-2-Ylmethanamine (6)Piperidin-3-Amine (17)Piperidin-3-Ylmethanamine (5)Piperidin-4-Amine (14)Piperidin-4-Ylmethanamine (7)Pyrazin-2-Amine (22)Pyrazin-2-Ylmethanamine (12)Pyridazin-3-Amine (18)Pyridazin-4-Amine (10)Pyridin-2-Amine (29)Pyridin-2-Ylmethanamine (38)Pyridin-3-Amine (21)Pyridin-3-Ylmethanamine (29)Pyridin-4-Amine (22)Pyridin-4-Ylmethanamine (12)Pyridine-2,3-Diamine (5)Pyridine-2,6-Diamine (12)Pyrimidin-2-Ylmethanamine (7)Pyrimidin-4-Amine (29)Pyrimidin-5-Amine (6)Pyrimidine-2,4-Diamine (14)Pyrrolidin-2-Ylmethanamine (12)Pyrrolidin-3-Ylmethanamine (6)Quinazolin-2-Amine (13)Quinazolin-4-Amine (8)Quinoxalin-2-Amine (3)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Amine (6)Thiazol-2-Ylmethanamine (5)Thiazol-5-Amine (6)Thiophen-3-Amine (18)Tri([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Yl)Amine (9)
Aryls (187653)
Acetylbenzonitrile (3)Aminobenzyl (7)Benzylamine (21)Benzylamino (47)Benzylhydroxylamine (25)Benzylidene (16)Benzylidene (16)Benzyloxy (1061)Benzylthio (16)Benzylthio (16)Cyanobenzyl (12)Dibenzyl (15)Dibenzylamino (7)Dichlorobenzylidene (8)Difluorobenzyl (17)Dimethoxybenzyl (20)Dimethoxybenzyl (20)Dimethylbenzonitrile (25)Dimethylbenzyl (6)Dimethylbenzyl (6)Dimethylbenzylamine (6)Ethoxybenzyl (8)Ethoxybenzyl (8)Fluorobenzyl (132)Fluorobenzylidene (2)Formylbenzonitrile (35)Iodobenzyl (9)Isopropylbenzonitrile (4)Methoxybenzyl (176)Methoxybenzylamine (7)Methoxybenzylidene (6)Methylbenzonitrile (104)Methylbenzyl (73)Methylbenzyl (73)Methylbenzylamine (8)Methylbenzylidene (1)Methylbenzylidene (1)Nitrobenzyl (33)Nitrobenzylidene (2)Phenoxybenzonitrile (5)Trifluorobenzyl (2)(6-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Methanol (17)(8S,9S,14R)-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-Tetradecahydro-3H-Cyclopenta[A]Phenanthren-3-One (1)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (2-(Tritylthio)Ethyl)Carbamate (10)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl Cyclohexylcarbamate (8)(Benzylsulfonyl)Benzene (11)(Cyclopentyloxy)Benzene (12)1,1-Dimethylcyclopropane (5)1,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-2H-Benzo[B]Azepin-2-One (15)1,3-Diphenylurea (24)1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-Phenylethan-1-One (6)1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-Phenylprop-2-En-1-One (11)1-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)1-(Naphthalen-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (3)1-Benzyl-4-Chlorobenzene (6)1-Benzyl-4-Fluorobenzene (2)1-Bromonaphthalene (4)1-Chloronaphthalene (24)1-Fluoronaphthalene (23)1-Methoxynaphthalene (17)1-Methyl-4-(Phenylethynyl)Benzene (7)1-Methylnaphthalene (10)1-Naphthaldehyde (23)1-Naphthoic Acid (23)1-Nitronaphthalene (3)10H-Phenothiazine (20)2,2',3,3',5,5',6,6'-Octafluoro-1,1'-Biphenyl (4)2,5-Diphenylthiophene (5)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenol (7)2-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,1'-Biphenyl (8)2-Benzylaniline (5)2-Bromo-1,1'-Biphenyl (12)2-Bromonaphthalene (4)2-Chloro-1,1'-Biphenyl (8)2-Chloronaphthalene (6)2-Ethoxynaphthalene (4)2-Fluorocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid (7)2-Hydroxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (3)2-Iodonaphthalene (5)2-Methoxy-1,1'-Biphenyl (7)2-Methoxynaphthalene (22)2-Methoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran (9)2-Methyl-1,1'-Biphenyl (26)2-Methylnaphthalene (13)2-Naphthaldehyde (12)2-Naphthoic Acid (14)2-Naphthonitrile (15)2-Nitronaphthalene (4)2-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran-4-Yl Acetate (6)2-Phenylnaphthalene (12)3,3'-Diphenyl-5,5',6,6',7,7',8,8'-Octahydro-1,1'-Binaphthalene (13)3,3-Diphenyl-3H-Benzo[C][1,2]Oxathiole 1,1-Dioxide (19)3-Bromo-1,1'-Biphenyl (12)3-Chloro-1,1'-Biphenyl (12)3-Fluoro-1,1'-Biphenyl (16)3-Methyl-1,1'-Biphenyl (10)3-Methyl-1,1':4',1''-Terphenyl (3)3-Phenethylphenol (5)3-Phenyl-1,2,4,5-Tetrazine (9)3-Styrylphenol (11)4-(Bromomethyl)-1,1'-Biphenyl (13)4-(Phenyldiazenyl)Benzoic Acid (4)4-(Phenylsulfonyl)Morpholine (14)4-(Tert-Butyl)-1,1'-Biphenyl (5)4-Cyclohexylphenol (7)4-Iodo-1,1'-Biphenyl (9)4-Methoxy-1,1'-Biphenyl (4)9H-Xanthene (7)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Amine (8)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Carbonitrile (12)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Carboxylic Acid (24)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Ol (16)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-Amine (11)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-Carbaldehyde (20)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-Carboxylic Acid (39)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-Ol (9)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Carbaldehyde (31)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Carbonitrile (27)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Ol (28)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Ylboronic Acid (29)Benzyltriphenylphosphonium (14)Cyclopentylbenzene (28)Cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid (11)Cyclopropyl(Phenyl)Methanamine (22)Cyclopropyl(Phenyl)Methanone (13)Diphenyl Phosphonate (11)Diphenylphosphane (25)Diphenylphosphine Oxide (27)Ethane-1,1-Diyldibenzene (3)Ethene-1,1,2-Triyltribenzene (13)Ethyl Cyclopropanecarboxylate (8)Methyl 1-Naphthoate (7)Methyl 2-Naphthoate (11)Methyl [1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Carboxylate (8)Methyl Cyclopropanecarboxylate (8)N,1-Diphenylmethanimine (15)N,N-Dimethylnaphthalen-1-Amine (4)N-((5R,6R)-7-Oxo-4-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[3.2.0]Heptan-6-Yl)-2-Phenylacetamide (5)N-Benzylbenzamide (21)N-Benzylbenzenesulfonamide (17)N-Cyclopropylbenzamide (14)N-Cyclopropylbenzenesulfonamide (10)N-Phenethylbenzamide (9)N-Phenyl-2-Naphthamide (11)Naphthalen-1-Ol (28)Naphthalen-1-Ylboronic Acid (4)Naphthalen-1-Ylmethanol (8)Naphthalen-2-Amine (12)Naphthalen-2-Ol (25)Naphthalen-2-Ylboronic Acid (8)Naphthalene-1,4-Diol (3)Naphthalene-2-Sulfonic Acid (4)Propane-2,2-Diyldibenzene (17)Tert-Butyl Cyclopropylcarbamate (7)Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Ol (12)Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl Acetate (12)Tetraphenylmethane (16)Triphenylene (12)Vinylcyclopropane (8)
Benzene Compounds (19035)
Acetamidophenoxy (1)Acetamidophenyl (5)Acetylbenzoate (7)Acetylphenyl (13)Acetylphenyl (13)Acetylphenylboronic (3)Aminobenzoyl (4)Aminobiphenyl (4)Aminonaphthalene (14)Aminophenoxy (19)Aminophenyl (239)Anisole (4)Anthracenes (142)Benzaldehyde (1601)Benzamidophenyl (1)Benzenedimethanol (4)Benzenethiol (8)Benzhydrylazetidine (10)Benzhydrylazetidine (10)Benzhydryloxy (4)Benzhydryloxy (4)Benziodoxol (2)Benzodioxole (5)Benzoquinone (6)Benzoquinone (6)Benzoylbenzoate (4)Benzoylphenyl (4)Binaphthalene (123)Binaphthalene (123)Biphenyl (1393)Boronophenyl (1)Boronophenyl (1)Bromobenzo (104)Bromobenzoyl (6)Bromodibenzo (9)Bromophenoxy (34)Bromophenyl (989)Butoxyphenyl (8)Butylaniline (7)Butylbenzene (16)Butyldiphenylsilyl (7)Butylphenol (20)Butylphenyl (32)Butylphenyl (32)Carbamoylphenoxy (12)Carbamoylphenyl (8)Carboxyphenyl (17)Carboxyphenyl (17)Chlorobenzenesulfonyl (23)Chlorobenzoyl (9)Chlorodibenzo (18)Chloronaphthalene (36)Chlorophenethyl (7)Chlorophenoxy (44)Chlorophenylacetate (4)Chlorophenylacetate Acid (9)Chlorophenylboronic (5)Cyclopropylaniline (6)Cyclopropylbenzoate (5)Cyclopropylnaphthalen (10)Cyclopropylnaphthalen (10)Cyclopropylphenyl (12)Cyclopropylphenyl (12)Diaminobenzene (7)Dibenzaldehyde (19)Dibenzene (7)Dibenzimidamide (5)Dibenzo (108)Dibenzo (108)Dibenzoate (9)Dibenzonitrile (11)Dibromobenzene (45)Dibromobenzo (14)Dibromodibenzo (8)Dibromonaphthalene (15)Dibromophenanthrene (3)Dibromophenoxy (2)Dibromophenylboronic (3)Dichlorobenzene (38)Dichlorobenzoyl (4)Dichlorophenoxy (16)Dichlorophenyl (345)Dichlorophenylboronic (5)Didehydrodibenz (2)Didehydrodibenz (2)Diethoxyphenyl (10)Diethylaniline (6)Diethylbenzamide (7)Diethylbenzene (6)Diethylbenzene (6)Difluorobenzene (57)Difluorobenzo (12)Difluorobenzoyl (9)Difluorophenoxy (9)Difluorophenyl (403)Difluorophenylboronic (11)Dihydroanthracene (1)Dihydroanthracene (1)Dihydrobenzo (189)Dihydrobenzo (189)Dihydrodibenzo (7)Dihydronaphthalene (104)Dihydronaphthalene (104)Diiodobenzene (12)Diisopropylaniline (5)Diisopropylbenzamide (8)Diisopropylphenyl (40)Diisopropylphenyl (40)Dimesityl (12)Dimesityl (12)Dimethoxyacetophenone (5)Dimethoxyaniline (20)Dimethoxybenzaldehyde (40)Dimethoxybenzamide (6)Dimethoxybenzene (47)Dimethoxybenzo (4)Dimethoxybenzo (4)Dimethoxybenzoate (20)Dimethoxybenzohydrazide (3)Dimethoxybenzonitrile (11)Dimethoxybenzoyl (4)Dimethoxybiphenyl (3)Dimethoxybiphenyl (3)Dimethoxynaphthalene (10)Dimethoxynaphthalene (10)Dimethoxyphenol (22)Dimethoxyphenyl (257)Dimethoxyphenylboronic (17)Dimethoxyphenylboronic (17)Dimethoxystyryl (4)Dimethylaminophenyl (4)Dimethylanthracene (4)Dimethylbenzaldehyde (27)Dimethylbenzamide (37)Dimethylbenzene (334)Dimethylbenzene (334)Dimethylbenzenesulfonamide (16)Dimethylbenzo (21)Dimethylbenzo (21)Dimethylbenzoate (27)Dimethylbenzoyl (3)Dimethylbenzoyl (3)Dimethylnaphthalene (6)Dimethylphenol (36)Dimethylphenoxy (13)Dimethylphenoxy (13)Dimethylphenylboronic (6)Dimethylphenylboronic (6)Dimethylphenylhydrazine (3)Dimethylphenylisothiocyanate (4)Dinaphtho (5)Dinitrobenzene (20)Diphenol (32)Diphenylamino (27)Diphenylaniline (9)Diphenylethane (19)Diphenylethanone (5)Diphenylethene (6)Diphenylethyl (7)Diphenylethyl (7)Diphenylmethyl (8)Diphenylmethyl (8)Diphenylmethylene (6)Diphenylphosphine (204)Diphenylphosphine (204)Diphenylpropane (22)Diphenylsilane (2)Diphenylurea (4)Diphenylurea (4)Ethoxyaniline (10)Ethoxybenzaldehyde (9)Ethoxybenzoate (12)Ethoxybenzonitrile (6)Ethoxyphenoxy (7)Ethoxyphenoxy (7)Ethoxyphenyl (46)Ethoxyphenyl (46)Ethoxyphenylboronic (7)Ethylaniline (8)Ethylaniline (8)Ethylbenzenesulfonamide (338)Ethylbenzo (7)Ethylbenzo (7)Ethylbenzoate (9)Ethylphenol (12)Ethylphenyl (39)Ethylphenyl (39)Ethynylaniline (7)Ethynylbenzaldehyde (17)Ethynylphenyl (35)Fluorobenzeneboronic (24)Fluoronaphthalene (34)Fluorophenoxy (46)Formylbenzoate (39)Formylphenoxy (4)Formylphenoxy (4)Formylphenyl (43)Formylphenyl (43)Formylphenylboronic (9)Formylphenylboronic (9)Hexahydrobenzo (3)Hexahydrobenzo (3)Hexylphenyl (3)Hexylphenyl (3)Homophenylalanine (18)Hydroxybenzenesulfonate (5)Hydroxybenzimidamide (11)Hydroxyisophthalaldehyde (6)Hydroxyphenethyl (2)Hydroxyphenethyl (2)Hydroxyphenyl (461)Hydroxyphenyl (461)Iodobenzo (15)Iodobenzoic (54)Iodobenzoyl (7)Iodobiphenyl (24)Iododibenzo (7)Iodonaphthalene (9)Iodophenoxy (6)Isobutoxyphenyl (15)Isobutoxyphenyl (15)Isobutylbenzene (5)Isobutylbenzene (5)Isobutylphenyl (9)Isophthalate (8)Isophthalonitrile (4)Isopropoxyaniline (10)Isopropoxyaniline (10)Isopropoxybenzaldehyde (7)Isopropoxybenzoate (7)Isopropoxyphenyl (41)Isopropoxyphenyl (41)Isopropylaniline (18)Isopropylbenzaldehyde (6)Isopropylbenzamide (9)Isopropylbenzenesulfonamide (19)Isopropylbenzoate (8)Isopropylphenyl (58)Mercaptobenzo (21)Methanobenzo (15)Methanobenzo (15)Methoxyacetophenone (12)Methoxyaniline (74)Methoxybenzaldehyde (104)Methoxybenzene (1749)Methoxybenzene (1749)Methoxybenzenesulfonamide (6)Methoxybenzenesulfonic (3)Methoxybenzenesulfonyl (13)Methoxybenzenesulfonyl (13)Methoxybenzimidamide (5)Methoxybenzo (52)Methoxybenzo (52)Methoxybenzoate (116)Methoxybenzonitrile (67)Methoxybenzoyl (12)Methoxybenzoyl (12)Methoxycarbonylphenylboronic (5)Methoxynaphthalene (56)Methoxynaphthalene (56)Methoxyphenethyl (1)Methoxyphenethyl (1)Methoxyphenol (72)Methoxyphenoxy (41)Methoxyphenoxy (41)Methoxyphenylacetate (4)Methoxyphenylboronic (24)Methoxyphenylboronic (24)Methoxyphenylhydrazine (4)Methoxystyryl (13)Methylacetophenone (6)Methylaniline (183)Methylanisole (3)Methylanthracene (5)Methylbenzaldehyde (101)Methylbenzamide (90)Methylbenzamido (3)Methylbenzenesulfinamide (4)Methylbenzenesulfonamide (81)Methylbenzenesulfonic (9)Methylbenzenesulfonyl (4)Methylbenzenesulfonyl (4)Methylbenzimidamide (6)Methylbenzoate (193)Methylbenzohydrazide (7)Methylbenzothioamide (6)Methylbenzothioamide (6)Methylbenzotrifluoride (5)Methylbenzoyl (24)Methylbenzoyl (24)Methylnaphthalene (34)Methylnaphthalene (34)Methylphenol (107)Methylphenoxy (18)Methylphenoxy (18)Methylphenyl (529)Methylphenylacetonitrile (45)Methylphenylboronic (24)Methylphenylhydrazine (10)Methylpropiophenone (5)Methylpropiophenone (5)Naphthaldehyde (28)Naphthalene (465)Naphthalene (465)Naphthaleneboronic (15)Naphthalenesulfonic (7)Naphthamide (15)Naphthonitrile (18)Nitrobenzenesulfonyl (8)Nitrobenzo (54)Nitrobenzoyl (13)Nitronaphthalene (24)Nitrophenoxy (43)Nitrophenyl (727)Nitrophenylboronic (14)Nitrotoluene (27)Octylbenzene (11)Octylbenzene (11)Paracyclophane (2)Paracyclophane (2)Pentafluorobenzene (13)Pentylbenzene (5)Pentylbenzene (5)Pentylbenzoate (2)Pentylphenol (4)Pentylphenyl (5)Pentylphenyl (5)Perfluorophenoxy (5)Perfluorophenyl (31)Phenoxyacetate (5)Phenoxyaniline (8)Phenoxybenzaldehyde (5)Phenoxybenzoate (5)Phenoxyethyl (6)Phenoxyethyl (6)Phenoxymethyl (7)Phenoxymethyl (7)Phenoxyphenyl (61)Phenoxyphenyl (61)Phenoxypropan (4)Phenylacetamide (34)Phenylacetonitrile (8)Phenylacetyl (2)Phenylacetyl (2)Phenylacrylamide (3)Phenylalaninol (4)Phenylamino (31)Phenylaniline (19)Phenylanthracene (16)Phenylbenzamide (23)Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (3)Phenylbutanoate (12)Phenylbutoxy (2)Phenylbutoxy (2)Phenylcarbamoyl (4)Phenylcyclohexanone (6)Phenylcyclopropanecarboxylic (6)Phenylcyclopropyl (7)Phenylcyclopropyl (7)Phenyldiazenyl (4)Phenylene (169)Phenylene (169)Phenylenediamine (13)Phenylenedimethanamine (5)Phenylethanamine (12)Phenylethane (14)Phenylethane (14)Phenylethanol (10)Phenylethanone (20)Phenylethoxy (2)Phenylethyl (70)Phenylethyl (70)Phenylethylisocyanate (2)Phenylhex (3)Phenylimino (1)Phenylisocyanate (9)Phenylisoserine (4)Phenylmethanesulfonyl (2)Phenylmethanesulfonyl (2)Phenylmethanone (2)Phenylmethoxy (4)Phenylmethoxy (4)Phenylmethyl (8)Phenylmethyl (8)Phenylnaphthalene (6)Phenylpentan (11)Phenylpentan (11)Phenylpropanamide (15)Phenylpropyl (20)Phenylpyrazolo (8)Phenylsulfinyl (3)Phenylsulfinyl (3)Phenylsulfonyl (88)Phenylsulfonyl (88)Phenylthio (24)Phenylthio (24)Phenylthiophene (23)Phenylthiophene (23)Phenylthiourea (6)Phenylurea (3)Phenylurea (3)Phenylvinyl (9)Phthalate (23)Phthalimide (12)Phthalonitrile (9)Propoxybenzaldehyde (4)Propoxyphenyl (29)Propoxyphenyl (29)Propoxyphenylboronic (79)Propylphenyl (26)Propylphenyl (26)Pyrenes (52)Quaternaphthalene (6)Quaterphenyl (15)Quaterphenyl (15)Styryl (12)Sulfamoylphenyl (3)Sulfophenyl (4)Sulfophenyl (4)Terephthalaldehyde (11)Terephthalate (13)Terphenyl (239)Terphenyl (239)Tetraaniline (6)Tetrabenzaldehyde (7)Tetrafluorobenzene (17)Tetrahydrobenzo (70)Tetrahydrobenzo (70)Tetrahydronaphthalene (149)Tetrahydronaphthalene (149)Tetralone (12)Tetramethylbenzene (9)Tetramethylbenzene (9)Tetramethylbiphenyl (57)Tetramethylbiphenyl (57)Tetraphenyl (11)Tetraphenyl (11)Toluenesulfonyl (68)Tolyl (418)Tolyl (418)Tolylamino (3)Tolylazanediyl (4)Tolylazanediyl (4)Tolylethynyl (3)Tolyloxy (19)Tolyloxy (19)Tolylphosphine (8)Tolylphosphine (8)Tolylthio (3)Tolylthio (3)Trianiline (7)Tribenzaldehyde (5)Tribromobenzene (7)Trichlorobenzene (20)Trichlorophenoxy (3)Trichlorophenylboronic (6)Triethylbenzene (5)Trifluorophenyl (56)Trifluorophenylboronic (154)Triiodobenzene (5)Triisopropylbenzene (9)Triisopropylphenyl (6)Triisopropylphenyl (6)Trimethoxybenzene (43)Trimethoxystyryl (5)Trimethylaniline (18)Trimethylbenzene (28)Trimethylphenol (6)Trimethylphenyl (20)Trimethylphenyl (20)Trimethylpropiophenone (4)Triphenylphosphoranylidene (9)Triphenylphosphoranylidene (9)Triphenylvinyl (11)Trityl (19)Trityl (19)Tritylamino (2)Trityloxy (2)Tritylthio (3)Tritylthio (3)(((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(4-Fluorophenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)(10Ar)-1,2,3,4,4A,9,10,10A-Octahydrophenanthrene (3)(1E,1'E)-N,N'-(Ethane-1,2-Diyl)Bis(1-Phenylmethanimine) (5)(1R,4R)-4-Phenyl-1,1'-Bi(Cyclohexane) (24)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl Benzylcarbamate (22)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (7)(Cyclopentylmethyl)Benzene (5)(R)-3-Benzylpyrrolidine (6)(R)-3-Phenylmorpholine (7)(R)-4-Benzyloxazolidin-2-One (5)(R)-N-(1,2-Diphenylethyl)Benzenesulfonamide (7)(S)-N-(1,2-Diphenylethyl)Benzenesulfonamide (7)1,1':2',1''-Terphenyl (4)1,1':3',1''-Terphenyl (28)1,1':4',1'':4'',1'''-Quaterphenyl (7)1,1,2,2-Tetra([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Yl)Ethene (10)1,1-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene (10)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalen-1-Amine (36)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalen-1-Ol (5)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene-1-Carboxylic Acid (3)1,2,3,5,6,7-Hexahydro-S-Indacene (23)1,2,4-Trimethylbenzene (41)1,2-Dihydroacenaphthylene (6)1,2-Dinitrobenzene (6)1,3,5-Tris(Phenylethynyl)Benzene (6)1,3,6,8-Tetraphenylpyrene (10)1,3-Bis(Benzyloxy)Benzene (8)1,3-Dihydro-2H-Inden-2-One (6)1,3-Diphenoxypropane (6)1,3-Diphenyl-1H-Pyrazole (6)1,3-Diphenylpropane (7)1,3-Diphenylpropane-1,3-Dione (4)1,4-Bis(Phenylethynyl)Benzene (7)1,4-Diphenylbuta-1,3-Diyne (9)1-(2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-5-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (3)1-(Anthracen-9-Yl)Ethan-1-Amine (3)1-Benzylazetidine (6)1-Bromopyrene (4)1-Cyclohexyl-4-(Phenylethynyl)Benzene (10)1-Cyclopropylnaphthalene (6)1-Phenyl-1H-Tetrazole (6)1-Phenylnaphthalene (12)1-Trityl-1H-Pyrazole (5)1H-Indene (19)1H-Indene-1,3(2H)-Dione (5)2,2 ', 3,3' - Tetrahydro-1,1 '- Spiro [Indene] (5)2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-1H-Benzo[C]Azepine (7)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-Amine (52)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-Ol (13)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-4-Amine (6)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-4-Ol (6)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene-1-Carboxylic Acid (5)2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene-4-Carbonitrile (4)2,4-Diphenyl-1,3,5-Triazine (6)2,5-Diphenyl-1,3,4-Oxadiazole (6)2,7-Bis(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-9H-Fluorene (7)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (24)2-(2-Fluorophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (21)2-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (29)2-(3-Bromophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (14)2-(3-Fluorophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (19)2-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (30)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Aniline (17)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzaldehyde (20)2-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (15)2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (16)2-Amino-2-(Anthracen-9-Yl)Ethan-1-Ol (4)2-Methyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (9)2-Phenyl-1,3,5-Triazine (6)2-Phenyl-1,3-Dioxane (7)2-Phenyl-2H-1,2,3-Triazole (7)2-Phenylisoindoline-1,3-Dione (7)2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Thiazin-3(4H)-One (6)3,3-Dimethyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (5)3,4-Dihydro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Dioxepine (7)3,5,6,7-Tetrahydro-S-Indacen-1(2H)-One (5)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(2-Bromophenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(2-Chlorophenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(3-Fluorophenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Propanoic Acid (4)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(3-Nitrophenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(4-Nitrophenyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(O-Tolyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-((((9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-3-(P-Tolyl)Propanoic Acid (3)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Aniline (25)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzaldehyde (19)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzoic Acid (12)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenol (13)3-Methyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (4)3-Phenyl-1H-Pyrrole (5)3-Phenylazetidine (5)3-Phenyloxazolidin-2-One (4)3-Phenylpiperidine (6)4',5'-Diphenyl-1,1':2',1''-Terphenyl (7)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (19)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(3-Nitrophenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (24)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(M-Tolyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (21)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(O-Tolyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (24)4,5-Diphenyloxazole (7)4,7-Diphenylbenzo[C][1,2,5]Thiadiazole (6)4-(4-Cyclopropylnaphthalen-1-Yl)-4H-1,2,4-Triazole (7)4-(Phenylethynyl)-1,1'-Biphenyl (5)4-Bromo-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (5)4-Bromo-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (10)4-Chloro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (8)4-Chloro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (5)4-Cyclohexyl-1,1'-Biphenyl (18)4-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (6)4-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (14)4-Methoxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (6)4-Methyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (8)4-Methyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (3)4-Phenyl-1,1'-Bi(Cyclohexane) (8)4-Phenyl-4H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)5''-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Yl)-1,1':4',1'':3'',1''':4''',1''''-Quinquephenyl (5)5',5''-Diphenyl-1,1':3',1'':3'',1'''-Quaterphenyl (8)5,5',6,6',7,7',8,8'-Octahydro-1,1'-Binaphthalene (6)5,6,7,8-Tetrahydronaphthalen-2-Ol (5)5-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene (6)5-Bromo-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (8)5-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (3)5-Methoxy-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene (3)5-Methoxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (2)5-Methyl-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (6)5-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (6)5-Phenylcyclohexane-1,3-Dione (6)6,7,8,9-Tetrahydro-5H-Benzo[7]Annulen-5-One (6)6-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene (9)6-Bromo-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (8)6-Bromo-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (3)6-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene (3)6-Chloro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (5)6-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene (6)6-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (4)6-Methoxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (6)6-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (5)6-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronaphthalene (5)6-Methyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (3)6-Methyl-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (2)7-Bromo-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (13)7-Chloro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (9)7-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (8)7-Hydroxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (6)7-Methoxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (6)7-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (6)7-Methyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (7)9,10-Bis(Phenylethynyl)Anthracene (5)9,10-Diphenylanthracene (16)9-Methylanthracene (4)9-Phenylxanthylium (7)9H-Fluoren-9-One (17)[1,1'-Binaphthalen]-2-Amine (3)[1,1':4',1''-Terphenyl]-4,4''-Dicarbaldehyde (9)Benzenesulfinic Acid (6)Benzil (17)Benzo-18-Crown-6 (7)Benzo[Lmn][3,8]Phenanthroline-1,3,6,8(2H,7H)-Tetraone (10)Benzyl ((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Glycinate (8)Benzyl (4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenyl)Carbamate (5)Benzyl (S)-Pyrrolidin-3-Ylcarbamate (7)Benzyl 3-Phenylpropanoate (8)Benzyl Piperidin-4-Ylcarbamate (7)Bicyclo[4.2.0]Octa-1,3,5-Triene (13)Cumene (181)Dibenzyl Phosphonate (6)Diphenylmethanimine (9)Ethane-1,1,2-Triyltribenzene (5)Ethylbenzene (198)Mesitylene (71)Methyl 2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzoate (14)Methyl 3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzoate (11)N,2-Diphenylacetamide (7)N,N,N-Trimethyl-1-Phenylmethanaminium (6)N,N-Diphenyl-[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Amine (8)N-Benzyl-2-Phenylethan-1-Amine (1)N-Benzylcyclopropanamine (6)N-Phenylcinnamamide (16)N1,N1,N4,N4-Tetraphenylbenzene-1,4-Diamine (6)N4,N4,N4',N4'-Tetraphenyl-[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4,4'-Diamine (7)Phenanthrene (23)Phenanthrene-9,10-Dione (8)Phenethyldiphenylphosphane (6)Phenothiazin-5-Ium (6)Phenyl (1R,4R)-[1,1'-Bi(Cyclohexane)]-4-Carboxylate (6)Phenyl 4-Cyclohexylbenzoate (8)Tert-Butyl (2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butylbenzene (251)Triphenyl Phosphate (6)
Benzyl Bromides (1065)
1-(Bromomethyl)-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (13)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Chlorobenzene (28)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Fluorobenzene (50)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (17)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-Chlorobenzene (27)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-Fluorobenzene (47)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-Methoxybenzene (19)1-Bromo-2-(Bromomethyl)Benzene (34)2-(2-(Bromomethyl)Phenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (9)2-(Bromomethyl)-1,3-Difluorobenzene (12)2-(Bromomethyl)Benzonitrile (15)Methyl 2-(Bromomethyl)Benzoate (33)
Bromides (52859)
Bromoacetyl (14)Bromoaniline (2)Bromoanthracene (5)Bromoanthracene (5)Bromobenzaldehyde (15)Bromobenzamide (7)Bromobenzimidamide (6)Bromobenzyl (36)Bromobut (2)Bromobut (2)Bromobutoxy (4)Bromobutoxy (4)Bromobutyl (6)Bromobutyl (6)Bromochroman (26)Bromochroman (26)Bromocyclopropanecarboxylate (1)Bromoethoxy (22)Bromoethoxy (22)Bromoethyl (86)Bromoethyl (86)Bromoethynyl (6)Bromohexyl (11)Bromohexyl (11)Bromomethyl (760)Bromonicotinaldehyde (5)Bromonicotinamide (5)Bromooctyl (3)Bromopentyl (8)Bromopentyl (8)Bromopropane (10)Bromopropane (10)Bromopropoxy (6)Bromopropoxy (6)Bromopropyl (25)Bromopropyl (25)Bromothiochroman (4)Bromothiochroman (4)Bromovinyl (2)Dibromo (698)Dibromo (698)Dibromoanthracene (3)Dibromoanthracene (3)Dibromobenzaldehyde (8)Dibromobenzonitrile (8)Dibromomethyl (6)Dibromomethyl (6)Dibromopropoxy (1)Dibromopropoxy (1)Tetrabromo (10)Tetrabromo (10)Tribromo (9)Tribromo (9)(1-Bromoethyl)Benzene (11)(2,2-Dibromovinyl)Benzene (6)(2-(4-Bromophenyl)Ethene-1,1,2-Triyl)Tribenzene (11)(2-Bromo-6-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (4)(2-Bromoethyl)Benzene (33)(2-Bromophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (3)(2-Bromophenyl)Boronic Acid (39)(2-Bromophenyl)Hydrazine (8)(2-Bromophenyl)Methanamine (12)(2-Bromophenyl)Methanol (39)(3-Bromo-2-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (7)(3-Bromo-2-Methoxyphenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(3-Bromophenyl)Boronic Acid (65)(3-Bromopropyl)Benzene (10)(3-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (7)(4-Bromophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (9)(5-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(5-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Methanol (5)(Bromoethynyl)Benzene (5)(Dibromomethyl)Benzene (6)1,2,3-Tribromobenzene (5)1,2,4-Tribromobenzene (13)1,2-Dibromo-3-Chlorobenzene (3)1,2-Dibromo-3-Fluorobenzene (9)1,2-Dibromo-3-Methylbenzene (9)1,2-Dibromo-4-Fluorobenzene (11)1,2-Dibromobenzene (64)1,3-Dibromo-2,4-Difluorobenzene (5)1,3-Dibromo-2,4-Dimethylbenzene (3)1,3-Dibromo-2-Chlorobenzene (8)1,3-Dibromo-2-Fluorobenzene (15)1,3-Dibromo-2-Iodobenzene (4)1,3-Dibromo-2-Methoxybenzene (11)1,3-Dibromo-2-Methylbenzene (14)1,3-Dibromo-2-Nitrobenzene (4)1,4-Dibromo-2-Iodobenzene (3)1-(2-Bromophenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (10)1-(2-Bromophenyl)Ethan-1-One (27)1-(5-Bromopyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine (6)1-(Azetidin-1-Yl)-2-Bromoethan-1-One (3)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Bromobenzene (12)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Bromobenzene (12)1-(Benzyloxy)-4-Bromobenzene (8)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Iodobenzene (9)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Methoxybenzene (14)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Methylbenzene (14)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Nitrobenzene (23)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-Methylbenzene (11)1-Benzyl-3-Bromobenzene (7)1-Benzyl-4-Bromo-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-Bromo-2,3-Dichlorobenzene (18)1-Bromo-2,3-Difluorobenzene (67)1-Bromo-2,3-Dimethoxybenzene (8)1-Bromo-2,3-Dimethylbenzene (23)1-Bromo-2,4-Difluorobenzene (59)1-Bromo-2-(Bromomethyl)Benzene (34)1-Bromo-2-(Difluoromethyl)Benzene (5)1-Bromo-2-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzene (4)1-Bromo-2-(Tert-Butyl)Benzene (7)1-Bromo-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (22)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-3-Fluorobenzene (20)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzene (6)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-3-Methylbenzene (9)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-4-Nitrobenzene (5)1-Bromo-2-Cyclopropylbenzene (3)1-Bromo-2-Ethoxybenzene (16)1-Bromo-2-Ethylbenzene (13)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (4)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-Methoxybenzene (7)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-Methylbenzene (11)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (11)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (13)1-Bromo-2-Iodobenzene (65)1-Bromo-2-Isopropylbenzene (10)1-Bromo-2-Phenoxybenzene (3)1-Bromo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (100)1-Bromo-3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzene (9)1-Bromo-3-Chloro-2-Methylbenzene (6)1-Bromo-3-Cyclopropylbenzene (6)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Iodobenzene (4)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Methoxybenzene (12)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Methylbenzene (17)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (10)1-Bromo-3-Iodobenzene (70)1-Bromo-3-Methoxybenzene (187)1-Bromo-3-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene (3)1-Bromo-3-Nitrobenzene (235)1-Bromo-3-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Bromo-4-(Phenylsulfonyl)Benzene (7)1-Bromo-4-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzene (22)1-Bromo-4-Fluoro-2-Methoxybenzene (11)1-Bromo-4-Fluoro-2-Methylbenzene (18)1-Bromo-4-Iodobenzene (67)1-Bromo-4-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Bromo-4-Styrylbenzene (5)1-Bromobicyclo[1.1.1]Pentane (3)1-Bromoisoquinoline (20)1-Bromonaphthalene (4)2,3-Dibromopyridine (21)2,4-Dibromo-1-Chlorobenzene (8)2,4-Dibromo-1-Fluorobenzene (18)2,4-Dibromo-1-Methoxybenzene (6)2,4-Dibromoaniline (18)2,4-Dibromophenol (16)2,4-Dibromopyridine (5)2,4-Dibromothiazole (5)2,5-Dibromopyrazine (4)2,5-Dibromopyridine (26)2,5-Dibromothiazole (5)2,5-Dibromothiophene (18)2,6-Dibromo-3-Fluoropyridine (3)2,6-Dibromoaniline (17)2,6-Dibromobenzaldehyde (4)2,6-Dibromobenzonitrile (4)2,6-Dibromophenol (21)2,6-Dibromopyrazine (9)2,6-Dibromopyridin-4-Amine (3)2,6-Dibromopyridine (28)2-(2-Bromophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)2-(2-Bromophenyl)Acetic Acid (23)2-(2-Bromophenyl)Acetonitrile (10)2-(4-Bromophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (8)2-(Bromomethyl)Furan (3)2-(Bromomethyl)Pyridine (27)2-Amino-3-Bromobenzoic Acid (8)2-Amino-3-Bromobenzonitrile (7)2-Amino-3-Bromophenol (3)2-Amino-6-Bromophenol (3)2-Bromo-1,1'-Biphenyl (12)2-Bromo-1,3,4-Thiadiazole (11)2-Bromo-1,3,4-Trifluorobenzene (16)2-Bromo-1,3,4-Trimethylbenzene (4)2-Bromo-1,3-Dichlorobenzene (12)2-Bromo-1,3-Difluorobenzene (43)2-Bromo-1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (7)2-Bromo-1,3-Dimethylbenzene (35)2-Bromo-1,4-Dichlorobenzene (12)2-Bromo-1,4-Difluorobenzene (64)2-Bromo-1,4-Dimethoxybenzene (11)2-Bromo-1,4-Dimethylbenzene (22)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-3-Fluorobenzene (9)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzene (20)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-4-Methylbenzene (6)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-4-Nitrobenzene (9)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (9)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (4)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-Methoxybenzene (12)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-Methylbenzene (17)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (23)2-Bromo-1-Methoxy-3-Methylbenzene (3)2-Bromo-1-Methoxy-4-Methylbenzene (7)2-Bromo-1-Methyl-4-Nitrobenzene (12)2-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (4)2-Bromo-1H-Imidazole (13)2-Bromo-1H-Pyrrole (11)2-Bromo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (4)2-Bromo-3-Chloroaniline (4)2-Bromo-3-Chloropyridine (25)2-Bromo-3-Fluoroaniline (13)2-Bromo-3-Fluoropyridine (26)2-Bromo-3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (4)2-Bromo-3-Methoxybenzaldehyde (4)2-Bromo-3-Methoxypyridine (7)2-Bromo-3-Methylaniline (6)2-Bromo-3-Methylphenol (4)2-Bromo-3-Methylpyrazine (5)2-Bromo-3-Methylpyridine (25)2-Bromo-3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (4)2-Bromo-3-Nitropyridine (5)2-Bromo-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (9)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Fluorobenzene (16)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Methoxybenzene (7)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Methylbenzene (11)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Nitrobenzene (5)2-Bromo-4-Chloroaniline (15)2-Bromo-4-Chlorophenol (11)2-Bromo-4-Chloropyridine (7)2-Bromo-4-Fluoro-1-Methoxybenzene (12)2-Bromo-4-Fluoro-1-Methylbenzene (21)2-Bromo-4-Fluoro-1-Nitrobenzene (23)2-Bromo-4-Fluoroaniline (28)2-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (7)2-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (8)2-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzonitrile (7)2-Bromo-4-Fluorophenol (10)2-Bromo-4-Methoxy-1-Nitrobenzene (6)2-Bromo-4-Methoxyaniline (6)2-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzaldehyde (8)2-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (4)2-Bromo-4-Methylaniline (14)2-Bromo-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (5)2-Bromo-4-Methylpyridine (6)2-Bromo-4-Methylthiazole (7)2-Bromo-4-Nitroaniline (12)2-Bromo-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-Bromo-5-Chloropyrazine (6)2-Bromo-5-Chloropyridine (22)2-Bromo-5-Fluoroaniline (18)2-Bromo-5-Fluorobenzaldehyde (7)2-Bromo-5-Fluorobenzoic Acid (11)2-Bromo-5-Fluoropyridine (33)2-Bromo-5-Methoxybenzaldehyde (6)2-Bromo-5-Methoxypyridine (11)2-Bromo-5-Methylpyridine (19)2-Bromo-5-Methylthiazole (7)2-Bromo-5-Nitropyridine (11)2-Bromo-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (5)2-Bromo-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-Bromo-6-Chloroaniline (10)2-Bromo-6-Chlorophenol (5)2-Bromo-6-Chloropyrazine (5)2-Bromo-6-Chloropyridine (23)2-Bromo-6-Fluoroaniline (14)2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzaldehyde (15)2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzoic Acid (11)2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzonitrile (7)2-Bromo-6-Fluorophenol (9)2-Bromo-6-Fluoropyridine (21)2-Bromo-6-Iodoaniline (4)2-Bromo-6-Methoxyaniline (5)2-Bromo-6-Methoxyphenol (5)2-Bromo-6-Methoxypyridine (15)2-Bromo-6-Methylaniline (11)2-Bromo-6-Methylbenzoic Acid (5)2-Bromo-6-Methylphenol (7)2-Bromo-6-Methylpyrazine (5)2-Bromo-6-Methylpyridine (17)2-Bromo-6-Nitroaniline (14)2-Bromo-6-Nitrophenol (9)2-Bromo-6-Phenylpyridine (4)2-Bromo-9,9-Diphenyl-9H-Fluorene (5)2-Bromo-9H-Fluorene (15)2-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (6)2-Bromo-N,N-Dimethylaniline (5)2-Bromo-N-Methylaniline (8)2-Bromo-N-Phenylacetamide (5)2-Bromobenzene-1,3-Diol (7)2-Bromobenzene-1,4-Diol (4)2-Bromobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (8)2-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (28)2-Bromodibenzo[B,D]Furan (6)2-Bromofuran (21)2-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (5)2-Bromonaphthalene (4)2-Bromonicotinic Acid (5)2-Bromooxazole (7)2-Bromopyrazine (15)2-Bromopyridin-3-Amine (10)2-Bromopyridin-3-Ol (7)2-Bromopyridine (10)2-Bromopyridine 1-Oxide (6)2-Bromopyrimidine (22)2-Bromoquinazoline (4)3,4-Dibromoaniline (4)3,4-Dibromophenol (3)3,5-Dibromopyridine (12)3-(Bromomethyl)Pyridine (18)3-Bromo-1,1'-Biphenyl (12)3-Bromo-1,5-Naphthyridine (8)3-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (16)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrole (16)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (7)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (6)3-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzaldehyde (4)3-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzoic Acid (7)3-Bromo-2-Chloropyridin-4-Amine (3)3-Bromo-2-Chloropyridine (20)3-Bromo-2-Fluoroaniline (15)3-Bromo-2-Fluorobenzaldehyde (9)3-Bromo-2-Fluorobenzoic Acid (10)3-Bromo-2-Fluorobenzonitrile (10)3-Bromo-2-Fluorophenol (5)3-Bromo-2-Fluoropyridine (21)3-Bromo-2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (10)3-Bromo-2-Hydroxybenzoic Acid (4)3-Bromo-2-Hydroxybenzonitrile (3)3-Bromo-2-Methoxypyridine (20)3-Bromo-2-Methylpyridine (27)3-Bromo-4-Chloroaniline (13)3-Bromo-4-Chlorobenzoic Acid (6)3-Bromo-4-Chlorophenol (5)3-Bromo-4-Fluoroaniline (22)3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (7)3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzamide (3)3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (10)3-Bromo-4-Fluorophenol (11)3-Bromo-4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (9)3-Bromo-4-Hydroxybenzoic Acid (3)3-Bromo-4-Methoxyaniline (7)3-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzaldehyde (9)3-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (7)3-Bromo-4-Methylaniline (14)3-Bromo-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (9)3-Bromo-4-Methylpyridine (13)3-Bromo-5'-Phenyl-1,1':3',1''-Terphenyl (4)3-Bromo-5-Chloropyridine (14)3-Bromo-5-Fluoropyridine (18)3-Bromo-5-Methylpyridine (14)3-Bromo-5-Nitropyridine (10)3-Bromoaniline (187)3-Bromoazetidine (3)3-Bromobenzene-1,2-Diamine (11)3-Bromobenzene-1,2-Diol (8)3-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (5)3-Bromobenzoic Acid (159)3-Bromobenzonitrile (110)3-Bromofuran (13)3-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (26)3-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrimidine (6)3-Bromoisoquinoline (10)3-Bromoisoxazole (7)3-Bromopicolinic Acid (9)3-Bromopicolinonitrile (13)3-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (11)3-Bromopyridazine (25)3-Bromopyridin-2-Amine (30)3-Bromopyridin-2-Ol (17)3-Bromopyridine 1-Oxide (8)3-Bromopyrrolidine (6)3-Bromothiophene (6)4-(Bromomethyl)-1,1'-Biphenyl (13)4-(Bromomethyl)Pyridine (8)4-Bromo-1,5-Naphthyridine (5)4-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (14)4-Bromo-1-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole (9)4-Bromo-1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole (11)4-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (14)4-Bromo-1H-Indole (25)4-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (4)4-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (9)4-Bromo-2-Chloro-1-Iodobenzene (4)4-Bromo-2-Chloropyridine (29)4-Bromo-2-Fluoro-1-Iodobenzene (8)4-Bromo-2-Fluoropyridine (4)4-Bromo-2-Iodoaniline (8)4-Bromo-2-Methoxypyridine (4)4-Bromo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (7)4-Bromo-3-Chloroaniline (21)4-Bromo-3-Fluoroaniline (29)4-Bromo-3-Methylaniline (19)4-Bromo-3-Methylpyridine (5)4-Bromo-3-Nitroaniline (8)4-Bromo-N,N-Diphenylaniline (10)4-Bromo-N-Phenylaniline (6)4-Bromo-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (23)4-Bromobenzo[C][1,2,5]Thiadiazole (14)4-Bromobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (6)4-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (9)4-Bromobenzofuran (3)4-Bromoindoline (4)4-Bromoisoindolin-1-One (3)4-Bromoisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (3)4-Bromoisoquinoline (33)4-Bromopyridazine (5)4-Bromopyridine (31)4-Bromopyrimidine (24)4-Bromothiazole (10)5-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)5-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Indole (4)5-Bromo-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)5-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D][1,2,3]Triazole (5)5-Bromo-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (13)5-Bromo-1H-Indazole (14)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrazole (11)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (11)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-C]Pyridine (5)5-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)5-Bromo-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (8)5-Bromo-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (6)5-Bromo-2-Chloro-4-Methylpyridine (5)5-Bromo-2-Chloropyridine (40)5-Bromo-2-Chloropyrimidine (6)5-Bromo-2-Fluoropyridine (22)5-Bromo-2-Methoxypyridine (29)5-Bromo-2-Methylpyridine (23)5-Bromo-2-Methylpyrimidine (5)5-Bromo-2-Phenylpyridine (3)5-Bromo-4-Methylpyridin-2-Amine (5)5-Bromo-6-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (3)5-Bromo-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (3)5-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (3)5-Bromobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (12)5-Bromobenzo[D]Oxazole (3)5-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (6)5-Bromoindoline (8)5-Bromoisoindolin-1-One (8)5-Bromoisoquinoline (17)5-Bromonicotinaldehyde (12)5-Bromonicotinic Acid (6)5-Bromonicotinonitrile (6)5-Bromopicolinic Acid (11)5-Bromopicolinonitrile (13)5-Bromopyrazin-2-Ol (5)5-Bromopyridin-2-Amine (35)5-Bromopyridin-2-Ol (18)5-Bromopyridin-3-Amine (10)5-Bromopyridin-3-Ol (6)5-Bromoquinoxaline (6)5-Bromothiazole (8)6-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)6-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (6)6-Bromo-1-Methyl-1H-Indole (3)6-Bromo-1H-Indazole (23)6-Bromo-1H-Indole (15)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-B]Pyridine (4)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (6)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (7)6-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (5)6-Bromo-3,4-Dihydro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazine (5)6-Bromo-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (6)6-Bromo-3,4-Dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-One (4)6-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (12)6-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3-A]Pyridine (8)6-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (4)6-Bromobenzo[D]Oxazole (3)6-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (7)6-Bromochroman-4-One (6)6-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyrimidine (5)6-Bromoindoline-2,3-Dione (4)6-Bromoisoindolin-1-One (4)6-Bromoisoquinoline (9)6-Bromonicotinaldehyde (11)6-Bromonicotinic Acid (9)6-Bromonicotinonitrile (7)6-Bromopicolinic Acid (5)6-Bromopyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (7)6-Bromopyridin-2-Amine (8)6-Bromopyridin-3-Amine (12)6-Bromopyridin-3-Ol (13)6-Bromoquinazoline (7)6-Bromoquinoxaline (9)7-Bromo-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (4)7-Bromo-1H-Indazole (18)7-Bromo-1H-Indole (28)7-Bromo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (4)7-Bromo-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (6)7-Bromo-3,4-Dihydro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazine (7)7-Bromo-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (6)7-Bromo-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (8)7-Bromobenzo[B]Thiophene (5)7-Bromobenzo[D]Thiazole (8)7-Bromobenzofuran (6)7-Bromochromane (7)7-Bromoindoline (3)7-Bromoisoquinoline (6)8-Bromo-[1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-A]Pyridine (6)8-Bromochromane (6)8-Bromoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (15)8-Bromoisoquinoline (17)8-Bromoquinazoline (8)9-Bromoanthracene (5)Bromocyclohexane (7)Ethyl 2-Bromo-2-Phenylacetate (6)Methyl 2-(2-Bromophenyl)Acetate (8)Methyl 2-Bromo-2-Phenylacetate (7)Methyl 2-Bromo-3-Nitrobenzoate (3)Methyl 2-Bromo-5-Fluorobenzoate (8)Methyl 2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzoate (7)Methyl 2-Bromo-6-Methylbenzoate (8)Methyl 2-Bromobenzoate (69)Methyl 3-(Bromomethyl)Benzoate (16)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Chlorobenzoate (6)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzoate (7)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzoate (10)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Methylbenzoate (9)Methyl 3-Bromobenzoate (153)Methyl 3-Bromopicolinate (9)Methyl 4-Amino-3-Bromobenzoate (8)Methyl 5-Amino-2-Bromobenzoate (6)Methyl 6-Bromonicotinate (6)N-(2-Benzoylphenyl)-2-Bromoacetamide (3)Tert-Butyl 2-(Bromomethyl)Morpholine-4-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl 3-Bromo-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (9)Tert-Butyl 3-Bromopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (4)
Carboxylic Acids (58191)
Aceticacid (1249)Acetylbenzoic Acid (3)Acrylic (95)Aminobenzoic (7)Aminobutanoic (8)Aminoheptanoic (6)Aminohexanoic (10)Aminonicotinic Acid (4)Aminopentanoic (8)Aminophenylacetic Acid (22)Aminopropanoic (11)Aminoundecanoic Acid (4)Benzenedicarboxylic (6)Benzenedicarboxylic Acid (6)Benzylpropanoic Acid (75)Benzylsuccinic Acid (6)Boronobenzoic (4)Bromobutanoic (5)Bromododecanoate (3)Bromoisonicotinic Acid (4)Bromonicotinic (8)Bromonicotinic Acid (9)Bromophenylacetic Acid (15)Bromovalerate (4)Butanoic (124)Chlorobenzoic (35)Chloromandelic Acid (3)Chromene-Carboxylic Acid (1)Cyanonicotinic (5)Cyanonicotinic Acid (3)Diacetic (19)Diacetic (19)Diaminobenzoic (7)Diaminobutanoic (5)Diaminohexanoic (4)Dibenzoic (40)Dibromobenzoic (10)Dibromobenzoic Acid (10)Dibromonicotinic Acid (7)Dicarboxylic (183)Dicarboxylic (183)Dichlorobenzoic (21)Dichlorobenzoic Acid (22)Dichloroisonicotinic (6)Dichloroisonicotinic Acid (6)Dichlorophenylacetic Acid (4)Dienoate (14)Dienoic (10)Difluorobenzoic (54)Difluorobutanoic (3)Difluoroisonicotinic Acid (7)Difluorophenylacetic (7)Difluorophenylacetic Acid (7)Diiodobenzoic (5)Diisophthalic (17)Diisophthalic Acid (9)Diisopropylbenzoic Acid (4)Dimethoxybenzoic (33)Dimethoxyphenylacetic Acid (3)Dimethylbenzoic (32)Dimethylbutanoic (13)Dimethylbutanoic (13)Dimethylpropanoic (5)Diphenylpropanoic (8)Diyldimethanol (17)Enedioic (8)Enoic (127)Ethoxybenzoic (9)Ethylbenzoic (11)Ethylbenzoic Acid (12)Ethynylbenzoic (6)Ethynylbenzoic Acid (5)Fluoroisophthalic Acid (4)Fluorophenylacetic (10)Fluorophenylacetic Acid (11)Fluorophthalic (5)Fluorophthalic Acid (3)Fluoropicolinic (12)Formylbenzoic (22)Formylbenzoic Acid (19)Guanidinopentanoic (8)Heptanoic (6)Heptanoic (6)Hexacarboxylic Acid (5)Hexanoic (25)Hexanoic (25)Hydrazinylbenzoic (6)Hydrazinylbenzoic Acid (5)Hydroxynicotinic (15)Indolecarboxylic (2)Isophthalic (29)Isophthalic Acid (15)Isopropoxybenzoic (8)Isopropoxybenzoic Acid (7)Isopropylbenzoic (13)Isopropylnicotinic Acid (4)Malonate (39)Mercaptobenzoic (6)Mercaptobenzoic Acid (4)Mercaptopropanoic (11)Methoxybenzoic (142)Methoxybutanoic (4)Methoxybutanoic (4)Methoxyisophthalic Acid (5)Methoxyphenylacetic (10)Methoxyphenylacetic Acid (11)Methoxypropanoic (7)Methoxypropanoic (7)Methylbenzoic (175)Methylbutanoic (32)Methylbutanoic (32)Methylcinnamic Acid (9)Methylhexanoic (8)Methylhexanoic (8)Methylisophthalic Acid (17)Methylnicotinic (46)Methyloctanoic (6)Methylpentanoic (108)Methylpentanoic (108)Methylpropanoic (57)Naphthoic (64)Nitrobenzoic (161)Nitroisonicotinic Acid (5)Nitroisophthalic Acid (3)Nitronicotinic (10)Nitropicolinic (11)Octanoic (6)Octanoic (6)Oxoacetic (22)Oxobutanoic (57)Oxobutanoic (57)Oxodecanoic (5)Oxodecanoic (5)Oxododecanoic (9)Oxododecanoic (9)Oxoheptanoic (5)Oxoheptanoic (5)Oxoheptanoic Acid (4)Oxohexadecanoic (13)Oxohexadecanoic (13)Oxohexanoic (10)Oxohexanoic (10)Oxooctadecanoic (7)Oxooctadecanoic (7)Oxopentanoic (37)Oxopentanoic (37)Oxopropanoic (8)Pentanedioic (18)Pentanedioic (18)Pentanoic (27)Phenoxybenzoic (5)Phenylacetic (35)Phenylbutanoic (47)Phenylpentanoic (11)Phenylpropanoic (45)Propanoic (1167)Propenoic (6)Pyridazinecarboxylic (1)Succinic (13)Sulfamoylbenzoic (15)Sulfobenzoic (5)Terephthalic (7)Tetraacetic (5)Tetrabenzoic (13)Tetrabenzoic Acid (14)Tetracarboxylic (13)Tribenzoic (15)Tribenzoic Acid (14)Tricarboxylic (18)Trichlorobenzoic (5)Trichlorobenzoic Acid (4)Trifluorobenzoic (12)Trifluorobenzoic Acid (11)Trifluorobutanoic (3)Trifluoromethylbenzoic (5)Trifluoromethylbenzoic Acid (4)Trifluoropentanoic (4)Trifluorophenylacetic Acid (16)Trifluoropropanoic (4)Triiodobenzoic (4)Trimethylbenzoic Acid (4)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline-1-Carboxylic Acid (19)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-Carboxylic Acid (12)1,5-Naphthyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (6)1-((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Piperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (5)1-((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Piperidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (3)1-((Benzyloxy)Carbonyl)Pyrrolidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (6)1-Methyl-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylic Acid (8)1-Naphthoic Acid (23)1-Phenyl-1H-Imidazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (5)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (10)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (19)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (3)1-Phenylcyclobutane-1-Carboxylic Acid (16)1-Phenylcyclohexane-1-Carboxylic Acid (6)1-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid (23)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-2-Carboxylic Acid (7)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (6)1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Imidazole-2-Carboxylic Acid (7)1H-Imidazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Indazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (27)1H-Indazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (9)1H-Indazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Indazole-7-Carboxylic Acid (6)1H-Indole-3-Carboxylic Acid (32)1H-Indole-4-Carboxylic Acid (10)1H-Indole-5-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Indole-6-Carboxylic Acid (5)1H-Indole-7-Carboxylic Acid (7)1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (9)1H-Pyrazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (10)1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylic Acid (30)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (5)1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (6)2,3-Difluorobenzoic Acid (35)2,3-Dihydrobenzo[B][1,4]Dioxine-2-Carboxylic Acid (3)2,3-Dihydrobenzo[B][1,4]Dioxine-6-Carboxylic Acid (3)2,4-Difluorobenzoic Acid (29)2,5-Dichlorobenzoic Acid (13)2,5-Difluorobenzoic Acid (32)2,6-Dichlorobenzoic Acid (13)2,6-Difluorobenzoic Acid (33)2-(1,3-Dioxoisoindolin-2-Yl)Propanoic Acid (3)2-(1H-Indol-1-Yl)Acetic Acid (5)2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (28)2-(2-Bromophenyl)Acetic Acid (23)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Acetic Acid (24)2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (43)2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (8)2-(2-Methoxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (16)2-(2-Methyl-1H-Indol-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (5)2-(2-Nitrophenyl)Acetic Acid (20)2-(2-Oxo-2H-Chromen-4-Yl)Acetic Acid (4)2-(3-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (50)2-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (7)2-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (23)2-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Acetic Acid (3)2-(4-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (30)2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (19)2-(4-Nitrophenyl)Acetic Acid (9)2-(Benzofuran-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (3)2-(M-Tolyl)Acetic Acid (16)2-(Morpholin-2-Yl)Acetic Acid (5)2-(O-Tolyl)Acetic Acid (17)2-(P-Tolyl)Acetic Acid (9)2-(Phenylamino)Benzoic Acid (11)2-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (14)2-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Benzoic Acid (3)2-(Pyrrolidin-2-Yl)Acetic Acid (8)2-(Pyrrolidin-3-Yl)Acetic Acid (6)2-(Thiazol-4-Yl)Acetic Acid (9)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzoic Acid (8)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoic Acid (33)2-Amino-2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (11)2-Amino-3,3-Diphenylpropanoic Acid (4)2-Amino-3-(2-Fluorophenyl)Propanoic Acid (16)2-Amino-3-Bromobenzoic Acid (8)2-Amino-3-Chlorobenzoic Acid (7)2-Amino-6-Chlorobenzoic Acid (5)2-Benzoylbenzoic Acid (10)2-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (8)2-Bromo-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (5)2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzoic Acid (11)2-Bromo-6-Methylbenzoic Acid (5)2-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzoic Acid (6)2-Chloro-3-Methylbenzoic Acid (4)2-Chloro-3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (4)2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (9)2-Chloro-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (3)2-Chloro-6-Fluorobenzoic Acid (8)2-Chlorobenzoic Acid (130)2-Cyclohexylacetic Acid (14)2-Fluoro-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (7)2-Fluoro-5-Methoxybenzoic Acid (9)2-Fluorobenzoic Acid (220)2-Fluorocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid (7)2-Iodobenzoic Acid (47)2-Methoxyisonicotinic Acid (13)2-Methyl-2-Phenylpropanoic Acid (20)2-Methyl-3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (7)2-Naphthoic Acid (14)2-Nitrobenzoic Acid (65)2-Oxo-2-Phenylacetic Acid (17)2-Oxo-2H-Chromene-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)2-Phenoxypropanoic Acid (13)3-((Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)Amino)-4-(2-Fluorophenyl)Butanoic Acid (9)3-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Propanoic Acid (4)3-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acrylic Acid (17)3-(3-Chlorophenyl)Acrylic Acid (10)3-(3-Chlorophenyl)Propanoic Acid (11)3-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Propanoic Acid (9)3-(Benzyloxy)Benzoic Acid (5)3-(Chlorosulfonyl)Benzoic Acid (15)3-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzoic Acid (6)3-(Phenyldiazenyl)Benzoic Acid (7)3-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Benzoic Acid (3)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzoic Acid (19)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoic Acid (52)3-Benzamidopropanoic Acid (3)3-Bromo-2-Chlorobenzoic Acid (7)3-Bromo-2-Fluorobenzoic Acid (10)3-Bromo-2-Hydroxybenzoic Acid (4)3-Bromo-4-Chlorobenzoic Acid (6)3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (10)3-Bromo-4-Hydroxybenzoic Acid (3)3-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (7)3-Bromo-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (9)3-Bromobenzoic Acid (159)3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzoic Acid (9)3-Chloro-2-Methoxybenzoic Acid (4)3-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (8)3-Chloro-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (5)3-Chlorobenzoic Acid (144)3-Fluoro-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (6)3-Fluorobenzoic Acid (206)3-Fluoropicolinic Acid (6)3-Iodobenzoic Acid (55)3-Methoxy-4-Nitrobenzoic Acid (4)3-Methylpicolinic Acid (13)3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (109)3-Phenoxybenzoic Acid (6)3-Phenoxypropanoic Acid (14)4-(1H-Pyrazol-1-Yl)Benzoic Acid (3)4-(Benzyloxy)Benzoic Acid (5)4-(Phenyldiazenyl)Benzoic Acid (4)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Nicotinic Acid (3)4-Amino-3-Chlorobenzoic Acid (6)4-Benzamidobenzoic Acid (3)4-Cyclohexylbenzoic Acid (6)4-Fluoro-3-Iodobenzoic Acid (5)4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (114)4-Methylnicotinic Acid (5)4-Morpholinobenzoic Acid (5)4-Nitrobenzoic Acid (35)4-Oxo-1,4-Dihydroquinoline-3-Carboxylic Acid (3)4-Oxo-4-(Phenylamino)Butanoic Acid (7)4-Oxo-4-Phenylbutanoic Acid (16)4-Oxopiperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (3)4-Phenoxybenzoic Acid (4)4-Phenylbutanoic Acid (19)5'-(4-Carboxyphenyl)-[1,1':3',1''-Terphenyl]-4,4''-Dicarboxylic Acid (7)5-Oxotetrahydrofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)5-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (15)5-Phenylfuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)5-Phenylisoxazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (15)6,6-Dimethylmorpholine-3-Carboxylic Acid (5)6-Methoxypicolinic Acid (9)6-Methylnicotinic Acid (6)6-Methylpicolinic Acid (12)6-Oxopiperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (3)6-Phenylpicolinic Acid (3)7-Fluoro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylic Acid (5)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Carboxylic Acid (24)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-3-Carboxylic Acid (39)Azetidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carboxylic Acid (32)Benzo[D]Thiazole-6-Carboxylic Acid (5)Benzofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (21)Benzofuran-3-Carboxylic Acid (6)Benzoic Acid (3519)Benzoylglycine (15)Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentane-1-Carboxylic Acid (6)Chromane-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)Chromane-3-Carboxylic Acid (4)Cyclobutanecarboxylic Acid (23)Cyclohex-1-Ene-1-Carboxylic Acid (4)Cyclohex-3-Ene-1-Carboxylic Acid (7)Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid (83)Cyclopentanecarboxylic Acid (26)Cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid (11)Ethyl 5-Oxopyrrolidine-2-Carboxylate (3)Furan-2-Carboxylic Acid (31)Furan-3-Carboxylic Acid (11)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-2-Carboxylic Acid (21)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-5-Carboxylic Acid (3)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-7-Carboxylic Acid (5)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-8-Carboxylic Acid (6)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyrimidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (5)Indoline-2-Carboxylic Acid (3)Isonicotinic Acid (23)Isoquinoline-1-Carboxylic Acid (10)Isoquinoline-3-Carboxylic Acid (7)Isoquinoline-4-Carboxylic Acid (12)Isoquinoline-5-Carboxylic Acid (5)Isoquinoline-6-Carboxylic Acid (3)Isoxazole-3-Carboxylic Acid (8)Isoxazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (7)Methyl Benzofuran-2-Carboxylate (6)Methyl Isoquinoline-3-Carboxylate (3)Morpholine-2-Carboxylic Acid (12)Morpholine-3-Carboxylic Acid (10)Nicotinic Acid (53)Oxazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (4)Picolinic Acid (22)Piperidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (26)Piperidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)Piperidine-4-Carboxylic Acid (11)Proline (13)Pyrazine-2-Carboxylic Acid (34)Pyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (7)Pyridazine-3-Carboxylic Acid (7)Pyridine-2,6-Dicarboxylic Acid (9)Pyrimidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (11)Pyrimidine-4-Carboxylic Acid (17)Pyrimidine-5-Carboxylic Acid (7)Pyrrolidine-3-Carboxylic Acid (14)Tetrahydrofuran-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Carboxylic Acid (4)Thiazole-2-Carboxylic Acid (9)Thiazole-4-Carboxylic Acid (5)Thiazole-5-Carboxylic Acid (10)Thiophene-3-Carboxylic Acid (8)Tryptophan (21)
Chlorides (77875)
Chloroacetamide (17)Chloroacetyl (12)Chloroaniline (18)Chlorobenzaldehyde (18)Chlorobenzamide (12)Chlorobutyl (6)Chlorobutyl (6)Chlorocarbonyl (7)Chloroethoxy (10)Chloroethoxy (10)Chloroethyl (89)Chloromethyl (479)Chloropicolinaldehyde (8)Chloropicolinamide (5)Chloropropane (18)Chloropropane (18)Chloropropoxy (2)Chloropropoxy (2)Chloropropyl (23)Dichloride (28)Dichloroaniline (9)Dichloroanthracene (3)Dichlorobenzaldehyde (13)Dichlorobenzamide (8)Dichloroisonicotinaldehyde (4)Dichloromethyl (3)Dichloromethyl (3)Dichloronicotinaldehyde (6)Dichloronicotinic (6)Dichloronicotinic (6)Dichloronicotinic Acid (5)Dichloropalladium (4)Dichloropalladium (4)Tetrachloro (2)Tetrachloro (2)Trichloro (36)Trichloro (36)Trichloroacetimidate (5)Trichloroaniline (6)Trichlorobenzaldehyde (4)Trichloromethyl (11)Trichloromethyl (11)(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (11)(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(2-Chloroethoxy)Benzene (5)(2-Chlorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (19)(2-Chlorophenyl)Hydrazine (16)(2-Chlorophenyl)Methanamine (28)(2-Chlorophenyl)Methanol (39)(2-Chloropyridin-4-Yl)Boronic Acid (6)(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (10)(3-Chloro-4-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (8)(3-Chlorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (19)(3-Chlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (121)(3-Chlorophenyl)Hydrazine (12)(3-Chlorophenyl)Methanamine (19)(3-Chlorophenyl)Methanol (38)(3-Chloropyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (6)(4-Chlorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (10)(5-Chloropyridin-2-Yl)Methanamine (5)(Chloromethanetriyl)Tribenzene (7)(Chloromethylene)Dibenzene (5)1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorobenzene (8)1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene (26)1,2-Dibromo-3-Chlorobenzene (3)1,2-Dichloro-3-Fluorobenzene (13)1,2-Dichloro-3-Methoxybenzene (7)1,2-Dichloro-3-Methylbenzene (8)1,2-Dichloro-4-Fluorobenzene (15)1,2-Dichloro-4-Methoxybenzene (11)1,2-Dichloro-4-Nitrobenzene (16)1,3-Dibromo-2-Chlorobenzene (8)1,3-Dichloro-2-Fluorobenzene (23)1,3-Dichloro-2-Iodobenzene (5)1,3-Dichloro-2-Methoxybenzene (9)1,3-Dichloro-2-Nitrobenzene (5)1,3-Dichloroisoquinoline (14)1,4-Dichloro-2-Fluorobenzene (11)1,4-Dichloro-2-Methoxybenzene (8)1-(2-Chlorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (40)1-(2-Chlorophenyl)Piperazine (4)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-1H-Pyrazole (3)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N-Methylmethanamine (8)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (38)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (3)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Chlorobenzene (16)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Chlorobenzene (6)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Chlorobenzene (28)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-Chlorobenzene (27)1-(Chloromethyl)-2-Methylbenzene (7)1-Benzyl-2-Chlorobenzene (9)1-Benzyl-3-Chlorobenzene (3)1-Benzyl-4-Chlorobenzene (6)1-Bromo-2,3-Dichlorobenzene (18)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-3-Methylbenzene (9)1-Bromo-3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzene (9)1-Bromo-3-Chloro-2-Methylbenzene (6)1-Bromo-4-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzene (22)1-Chloro-2,3-Difluorobenzene (27)1-Chloro-2,4-Difluorobenzene (35)1-Chloro-2,4-Dimethoxybenzene (7)1-Chloro-2-(Chloromethyl)Benzene (12)1-Chloro-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (20)1-Chloro-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (81)1-Chloro-2-Cyclopropylbenzene (7)1-Chloro-2-Ethoxybenzene (14)1-Chloro-2-Fluoro-3-Iodobenzene (5)1-Chloro-2-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (9)1-Chloro-2-Iodobenzene (65)1-Chloro-2-Isocyanatobenzene (6)1-Chloro-2-Isothiocyanatobenzene (7)1-Chloro-2-Methyl-3-Nitrobenzene (6)1-Chloro-2-Nitrobenzene (138)1-Chloro-2-Phenoxybenzene (10)1-Chloro-2-Propoxybenzene (5)1-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylbenzene (8)1-Chloro-3-(Chloromethyl)Benzene (7)1-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (18)1-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (101)1-Chloro-3-Fluoro-2-Methylbenzene (10)1-Chloro-3-Fluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (6)1-Chloro-3-Iodo-2-Methylbenzene (3)1-Chloro-3-Iodobenzene (77)1-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzene (126)1-Chloro-3-Nitrobenzene (161)1-Chloro-3-Phenoxybenzene (5)1-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (8)1-Chloro-4-Iodobenzene (49)1-Chloro-4-Methoxybenzene (98)1-Chloro-4-Phenoxybenzene (13)1-Chloroanthracene-9,10-Dione (6)1-Chloroisoquinoline (20)1-Chloronaphthalene (24)2,3,5-Trichloropyridine (13)2,3,6-Trichloropyridine (16)2,3-Dichloroaniline (18)2,3-Dichlorobenzaldehyde (7)2,3-Dichlorophenol (9)2,3-Dichloropyridine (38)2,4,5-Trichloropyrimidine (6)2,4,6-Trichloropyridine (5)2,4,6-Trichloropyrimidine (14)2,4-Dibromo-1-Chlorobenzene (8)2,4-Dichloro-1-Fluorobenzene (27)2,4-Dichloro-1-Methoxybenzene (18)2,4-Dichloro-1-Nitrobenzene (19)2,4-Dichloro-6-Methylpyridine (8)2,4-Dichloro-6-Methylpyrimidine (7)2,4-Dichlorobenzaldehyde (8)2,4-Dichlorobenzonitrile (4)2,4-Dichloropyridine (50)2,4-Dichloroquinazoline (19)2,4-Dichlorothiazole (4)2,5-Dichlorophenol (7)2,5-Dichloropyrazine (4)2,5-Dichloropyridine (32)2,6-Dichloro-3-Fluoropyridine (10)2,6-Dichloro-3-Methylpyridine (5)2,6-Dichloro-3-Nitropyridine (6)2,6-Dichloro-4-Methylpyridine (5)2,6-Dichloroaniline (27)2,6-Dichlorobenzoic Acid (13)2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile (8)2,6-Dichloronicotinonitrile (8)2,6-Dichlorophenol (16)2,6-Dichloropyrazine (14)2,6-Dichloropyridin-3-Amine (11)2,6-Dichloropyridine (49)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Acetic Acid (24)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Acetonitrile (16)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Ethan-1-Ol (8)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Pyridine (3)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (17)2-(3-Chlorophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (8)2-(3-Chlorophenyl)Acetonitrile (16)2-(4-Chlorophenoxy)Acetic Acid (3)2-(Chloromethyl)-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (9)2-(Chloromethyl)-3-Methylpyridine (12)2-(Chloromethyl)Furan (3)2-(Chloromethyl)Pyridine (12)2-(Chloromethyl)Pyridine 1-Oxide (4)2-(Chloromethyl)Pyrimidine (5)2-(Chloromethyl)Thiazole (5)2-Amino-3-Chlorobenzoic Acid (7)2-Amino-3-Chlorobenzonitrile (3)2-Amino-6-Chlorophenol (5)2-Bromo-1,3-Dichlorobenzene (12)2-Bromo-1,4-Dichlorobenzene (12)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-4-Methylbenzene (6)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Iodobenzene (6)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Methoxybenzene (7)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Methylbenzene (11)2-Bromo-4-Chloroaniline (15)2-Bromo-4-Chlorophenol (11)2-Bromo-6-Chloroaniline (10)2-Bromo-6-Chlorophenol (5)2-Chloro-1,1'-Biphenyl (8)2-Chloro-1,3,5-Triazine (10)2-Chloro-1,3-Difluorobenzene (27)2-Chloro-1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (3)2-Chloro-1,3-Dinitrobenzene (2)2-Chloro-1,4-Difluorobenzene (25)2-Chloro-1,4-Dimethoxybenzene (4)2-Chloro-1-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (16)2-Chloro-1-Methyl-3-Nitrobenzene (4)2-Chloro-1-Phenylethan-1-One (20)2-Chloro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (17)2-Chloro-3,6-Dimethylpyridine (4)2-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (3)2-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (12)2-Chloro-3-Fluoropyridin-4-Amine (3)2-Chloro-3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (4)2-Chloro-3-Methoxypyridine (12)2-Chloro-3-Methylaniline (4)2-Chloro-3-Methylbenzoic Acid (4)2-Chloro-3-Methylbenzonitrile (5)2-Chloro-3-Methylpyrazine (7)2-Chloro-3-Methylpyridine (17)2-Chloro-3-Nitropyridine (10)2-Chloro-4,6-Dimethylpyridine (7)2-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (9)2-Chloro-4-Ethoxypyridine (5)2-Chloro-4-Fluoro-1-Nitrobenzene (13)2-Chloro-4-Fluoroaniline (19)2-Chloro-4-Fluoropyridine (10)2-Chloro-4-Methoxypyridine (22)2-Chloro-4-Methyl-1-Nitrobenzene (6)2-Chloro-4-Methylaniline (7)2-Chloro-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (3)2-Chloro-4-Methylpyridine (31)2-Chloro-4-Methylpyrimidine (16)2-Chloro-4-Methylthiazole (5)2-Chloro-4-Phenylpyrimidine (7)2-Chloro-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (4)2-Chloro-5-Fluoropyridin-4-Amine (3)2-Chloro-5-Fluoropyridine (16)2-Chloro-5-Methoxyaniline (8)2-Chloro-5-Methylpyridine (11)2-Chloro-5-Methylpyrimidine (5)2-Chloro-5-Methylthiazole (5)2-Chloro-5-Nitropyridine (8)2-Chloro-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (4)2-Chloro-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (16)2-Chloro-6-Fluoroaniline (8)2-Chloro-6-Fluorophenol (5)2-Chloro-6-Fluoropyridine (14)2-Chloro-6-Iodophenol (3)2-Chloro-6-Methoxyaniline (3)2-Chloro-6-Methoxyphenol (4)2-Chloro-6-Methoxypyridine (24)2-Chloro-6-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine (4)2-Chloro-6-Methylaniline (11)2-Chloro-6-Methylnicotinonitrile (10)2-Chloro-6-Methylphenol (5)2-Chloro-6-Methylpyrazine (12)2-Chloro-6-Methylpyridine (49)2-Chloro-6-Nitroaniline (11)2-Chloro-7H-Purine (3)2-Chloro-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (13)2-Chloro-9H-Purine (5)2-Chloro-N-Phenylacetamide (26)2-Chloro-N-Phenylaniline (7)2-Chloroaniline (214)2-Chlorobenzamide (16)2-Chlorobenzene-1,3-Diamine (3)2-Chlorobenzene-1,3-Diol (4)2-Chlorobenzene-1,4-Diamine (6)2-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (24)2-Chlorobenzenethiol (7)2-Chlorobenzo[D]Oxazole (11)2-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (21)2-Chlorobenzoic Acid (130)2-Chlorobenzonitrile (99)2-Chlorobenzoyl Chloride (13)2-Chlorocyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (4)2-Chlorofuran (3)2-Chloroisonicotinaldehyde (19)2-Chloroisonicotinic Acid (17)2-Chloroisonicotinonitrile (7)2-Chloronaphthalene (6)2-Chloronicotinic Acid (7)2-Chloronicotinonitrile (9)2-Chlorooxazole (7)2-Chlorophenol (163)2-Chloropyrazine (24)2-Chloropyridin-3-Amine (11)2-Chloropyridin-3-Ol (9)2-Chloropyridin-4-Amine (28)2-Chloropyridine 1-Oxide (10)2-Chloroquinoxaline (39)2-Chlorothiazole (32)2-Chlorothiophene (20)3,4-Dichloroaniline (21)3,5-Dichloropyridine (16)3,6-Dichloropyridazine (20)3-(3-Chlorophenyl)Propanoic Acid (11)3-(Chloromethyl)Pyridine (22)3-Chloro-1,1'-Biphenyl (12)3-Chloro-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (7)3-Chloro-1-Phenylpropan-1-One (10)3-Chloro-1H-Indazole (13)3-Chloro-2-Fluoroaniline (9)3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzaldehyde (9)3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzoic Acid (9)3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzonitrile (7)3-Chloro-2-Fluoropyridine (13)3-Chloro-2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (5)3-Chloro-2-Methoxypyridine (16)3-Chloro-2-Methylaniline (11)3-Chloro-2-Methylpyridine (4)3-Chloro-2-Nitroaniline (5)3-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (5)3-Chloro-4-Fluoroaniline (18)3-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (8)3-Chloro-4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (7)3-Chloro-4-Methylaniline (12)3-Chloro-4-Methylpyridazine (7)3-Chloro-4-Nitroaniline (5)3-Chloro-5-Fluoropyridine (10)3-Chloro-5-Methylpyridine (7)3-Chloro-5-Nitropyridine (5)3-Chloro-9H-Carbazole (3)3-Chlorobenzaldehyde (106)3-Chlorobenzene-1,2-Diamine (6)3-Chlorobenzene-1,2-Diol (6)3-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (21)3-Chlorobenzo[B]Thiophene (6)3-Chlorobenzoic Acid (144)3-Chlorobenzonitrile (100)3-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)3-Chloroisoquinoline (20)3-Chlorophenol (112)3-Chloropicolinic Acid (9)3-Chloropicolinonitrile (6)3-Chloropyridazine (44)3-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (17)3-Chloropyridin-2-Ol (10)3-Chlorothiophene (17)4,5-Dichloropyrimidine (7)4,6-Dichloro-2-Methylpyrimidine (7)4,6-Dichloropyridin-2-Amine (6)4,6-Dichloropyridin-3-Amine (4)4,6-Dichloropyrimidine (14)4-Chloro-1,5-Naphthyridine (6)4-Chloro-1-Phenylbutan-1-One (8)4-Chloro-1H-Indazole (18)4-Chloro-1H-Indole (21)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazole (10)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (5)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidine (5)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-C]Pyridine (7)4-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (10)4-Chloro-2,6-Dimethylpyridine (4)4-Chloro-2-Methoxypyridine (6)4-Chloro-2-Phenylpyrimidine (5)4-Chloro-3-Fluoroaniline (17)4-Chloro-3-Methylaniline (11)4-Chloro-3-Methylpyridine (7)4-Chloro-5-Methylpyrimidine (8)4-Chloro-N-Phenylaniline (6)4-Chlorobenzene-1,3-Diol (6)4-Chlorobenzenesulfonic Acid (4)4-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (12)4-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (7)4-Chloroindoline-2,3-Dione (6)4-Chloroisoquinoline (11)4-Chloronicotinic Acid (4)4-Chloropyridazine (16)4-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (6)4-Chloropyridine (31)4-Chloroquinazoline (39)5,6-Dichloro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (4)5,6-Dichloropyridin-2-Amine (4)5-Bromo-4-Chloropyrimidine (4)5-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)5-Chloro-1H-Imidazole (2)5-Chloro-1H-Indazole (9)5-Chloro-1H-Indole (64)5-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylic Acid (6)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrazole (8)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-B]Pyridine (6)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)5-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (6)5-Chloro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (5)5-Chloro-2-Fluoropyridine (13)5-Chloro-2-Methoxypyridine (10)5-Chloro-2-Methylpyridine (10)5-Chlorobenzo[B]Thiophene (4)5-Chlorobenzo[D]Oxazole (5)5-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (5)5-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)5-Chloroindolin-2-One (3)5-Chloroisoquinoline (6)5-Chloropicolinic Acid (7)5-Chloropicolinonitrile (6)5-Chloropyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (24)5-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (26)5-Chloropyridin-2-Ol (15)5-Chloropyridin-3-Amine (7)5-Chloropyrimidine (8)5-Chloroquinazoline (4)6-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)6-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)6-Chloro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (25)6-Chloro-1H-Indazole (14)6-Chloro-1H-Indole (19)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrazolo[4,3-C]Pyridine (8)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (13)6-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-C]Pyridine (13)6-Chloro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (3)6-Chloro-3,4-Dihydro-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazine (5)6-Chloro-3-Nitropyridin-2-Amine (4)6-Chloro-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Amine (3)6-Chlorobenzo[D]Oxazole (4)6-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (6)6-Chlorochroman-4-One (6)6-Chlorochromane (6)6-Chloroindoline (3)6-Chloroindoline-2,3-Dione (5)6-Chloronicotinaldehyde (24)6-Chloronicotinic Acid (4)6-Chloropicolinic Acid (12)6-Chloropicolinonitrile (9)6-Chloropyridazin-3(2H)-One (5)6-Chloropyridin-2-Amine (21)6-Chloropyridin-2-Ol (9)6-Chloropyridin-3-Amine (4)6-Chloropyridine-3-Sulfonyl Chloride (5)6-Chloroquinoxaline (3)7-Chloro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (5)7-Chloro-1H-Indazole (7)7-Chloro-1H-Indole (29)7-Chloro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-C]Pyridine (5)7-Chloro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (3)7-Chloro-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (6)7-Chlorobenzo[D]Thiazole (6)7-Chlorochromane (5)7-Chloroisoquinoline (6)7-Chloropyrazolo[1,5-A]Pyrimidine (8)8-Chlorochromane (5)8-Chloroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (7)8-Chloroisoquinoline (7)8-Chloroquinazoline (5)Ethyl 4,6-Dichloronicotinate (4)Ethyl 5-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 6-Chloropicolinate (7)Ethyl 7-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 2,6-Dichlorobenzoate (7)Methyl 2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzoate (5)Methyl 2-Chloro-6-Fluorobenzoate (7)Methyl 2-Chlorobenzoate (79)Methyl 2-Chloroisonicotinate (11)Methyl 2-Chloronicotinate (6)Methyl 3-Chlorobenzoate (88)Methyl 3-Chloropicolinate (9)Methyl 6-Chloropicolinate (11)N-(2-Chlorophenyl)Acetamide (16)N-(3-Chlorophenyl)Benzenesulfonamide (6)N-(3-Chlorophenyl)Quinazolin-4-Amine (9)N-(4-Chlorophenyl)Acetamide (9)Phenyl Carbonochloridate (5)Pyridine-2-Sulfonyl Chloride (9)Pyridine-3-Sulfonyl Chloride (25)Tert-Butyl (2-Chloropyridin-4-Yl)Carbamate (4)
Esters (51168)
Acetoxymethyl (85)Acetoxyphenyl (1)Acetyloxy (53)Acrylate (118)Acryloyloxy (3)Adipate (17)Adipate (17)Amino-Carboxylate (2)Aminobenzoate (18)Aminobenzylcarbamate (8)Aminobutanoate (14)Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic Acid (4)Aminocyclohexanecarboxylic (16)Aminocyclohexanecarboxylic Acid (10)Aminocyclopentanecarboxylic (13)Aminoheptanoate (9)Aminohexanoate (6)Aminoisonicotinate (4)Aminoisophthalate (5)Aminonicotinate (7)Aminopentanedioate (15)Aminopentanoate (7)Aminopropanoate (16)Benzoyloxy (14)Benzylcarbamate (8)Bromobenzoate (26)Bromobutanoate (9)Bromocyclopropanecarboxylate (1)Bromodecanoate (20)Bromoisonicotinate (8)Bromoisophthalate (3)Bromonicotinate (13)Bromopropanoate (9)Bromoundecanoate (3)Butoxycarbonyl (1675)Butoxycarbonyl (1675)Carbamate (1539)Chlorobenzoate (49)Chloroformate (4)Chloropicolinate (30)Chloropropanoate (5)Cyanoacrylate (6)Decanedioate (9)Decanedioate (9)Decanoate (7)Decanoate (7)Diacetate (56)Diacetoxy (1)Diacrylate (15)Diaminobenzoate (7)Dibromobenzoate (4)Dicarbamate (14)Dichlorobenzoate (24)Dichloroisonicotinate (9)Dimethacrylate (1)Dimethylbutanoate (14)Dimethylcarbamate (3)Dimethylnicotinate (10)Dimethylnicotinate (10)Dipropanoate (6)Dipropanoate (6)Diyldicarbamate (5)Dodecanoate (11)Enecarboxylate (9)Enoate (116)Ethoxycarbonyl (70)Ethylbutanoate (6)Ethynylbenzoate (7)Ethynylbenzylcarbamate (3)Glutarate (3)Glutarate (3)Hexanoate (14)Hexanoate (14)Indoline-Carboxylate (1)Iodoacrylate (6)Iodobutanoate (4)Iodopropanoate (1)Isobutyrate (18)Isobutyrate (18)Methacrylate (87)Methacryloyloxy (7)Methoxycarbonyl (169)Methoxycarbonyl (169)Methoxyisonicotinate (11)Methoxyisonicotinate (11)Methoxynicotinate (24)Methoxynicotinate (24)Methoxypropanoate (5)Methoxypropanoate (5)Methylacrylate (13)Methylbutanoate (38)Methylmalonate (6)Methylnicotinate (57)Methylpentanoate (17)Methylpropanoate (47)Nitropicolinate (13)Nonanedioate (4)Nonanedioate (4)Oxoacetate (21)Oxoacetate (21)Oxobutanoate (56)Oxobutanoate (56)Oxoheptanoate (8)Oxoheptanoate (8)Oxohexanoate (14)Oxohexanoate (14)Oxopentanoate (31)Oxopropanoate (39)Oxopropanoate (39)Pentanoate (13)Pentanoate (13)Phenylacrylate (5)Phenylpropanoate (42)Propanoate (296)Propylpentanoate (5)Propylpentanoate (5)Succinate (23)Succinate (23)Sulfamoylbenzoate (6)Tetraacetate (7)Tetraacetate (7)Tetradecanoate (10)Tetradecanoate (10)Thiophenecarboxylate (2)Tosylcarbamate (4)Tosyloxy (12)Triacetate (12)Triacetate (12)Vinylbenzoate (3)Vinylcyclopropanecarboxylic Acid (3)(2R,3S)-2-((Benzoyloxy)Methyl)Tetrahydrofuran-3-Yl Benzoate (8)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (3-Phenylpropyl)Carbamate (24)1,3-Dioxoisoindolin-2-Yl 2-Phenylacetate (5)1-Benzyl 2-Methyl Pyrrolidine-1,2-Dicarboxylate (7)1-Benzyl 3-Methyl Piperidine-1,3-Dicarboxylate (3)1-Benzyl 4-(Tert-Butyl) Piperazine-1,4-Dicarboxylate (10)1H-Indol-3-Yl Acetate (4)2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-Yl Benzoate (8)2-((Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)Amino)Benzoic Acid (11)2-(Diethylamino)Ethyl Benzoate (3)2-Ethylhexyl Benzoate (13)2-Hydroxyethyl Benzoate (3)2-Phenoxyacetyl Chloride (3)4-Cyanophenyl Benzoate (11)Allyl Benzoate (5)Azetidin-3-Yl Acetate (3)Benzoic Anhydride (6)Benzyl Acetate (11)Benzyl Benzoate (12)Benzyl Benzylcarbamate (16)Benzyl Cyclohexylcarbamate (9)Benzyl Morpholine-4-Carboxylate (5)Benzyl Phenylcarbamate (15)Benzyl Piperidine-1-Carboxylate (50)Butyl Benzoate (10)Dimethyl Isophthalate (32)Dimethyl Phthalate (14)Dimethyl Pyridine-2,6-Dicarboxylate (7)Ethane-1,2-Diyl Dibenzoate (11)Ethyl 1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-3-Carboxylate (4)Ethyl 1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylate (13)Ethyl 1-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylate (4)Ethyl 1H-1,2,4-Triazole-3-Carboxylate (3)Ethyl 1H-Imidazole-2-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl 1H-Indole-3-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl 1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylate (11)Ethyl 1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylate (24)Ethyl 1H-Pyrrole-3-Carboxylate (8)Ethyl 2-(Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-3-Yl)Acetate (3)Ethyl 2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Acetate (15)Ethyl 2-Aminobenzoate (23)Ethyl 2-Aminothiazole-4-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl 2-Aminothiazole-5-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 2-Bromo-2-Phenylacetate (6)Ethyl 2-Fluorobenzoate (37)Ethyl 2-Hydroxybenzoate (18)Ethyl 2-Iodobenzoate (4)Ethyl 2-Methylbenzoate (26)Ethyl 2-Methylnicotinate (6)Ethyl 2-Nitrobenzoate (9)Ethyl 2-Oxo-2-(Phenylamino)Acetate (8)Ethyl 2-Oxo-2-Phenylacetate (18)Ethyl 2-Oxo-2H-Chromene-3-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 2-Phenoxyacetate (10)Ethyl 2-Phenylacetate (60)Ethyl 2-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzoate (6)Ethyl 3-Aminobenzoate (19)Ethyl 3-Fluorobenzoate (34)Ethyl 3-Hydroxybenzoate (12)Ethyl 3-Iodobenzoate (11)Ethyl 3-Nitrobenzoate (22)Ethyl 3-Oxo-3-Phenylpropanoate (41)Ethyl 3-Phenylpropanoate (17)Ethyl 4-Aminobenzoate (23)Ethyl 4-Chloropyrimidine-5-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 5-Fluoro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl 6-Chloro-1H-Indole-2-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carboxylate (9)Ethyl Cinnamate (26)Ethyl Cyclohex-1-Ene-1-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Cyclohexanecarboxylate (33)Ethyl Cyclopropanecarboxylate (8)Ethyl Furan-2-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-2-Carboxylate (25)Ethyl Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (13)Ethyl Isonicotinate (12)Ethyl Isoxazole-3-Carboxylate (8)Ethyl Isoxazole-4-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Morpholine-2-Carboxylate (4)Ethyl Nicotinate (25)Ethyl Oxazole-4-Carboxylate (8)Ethyl Oxazole-5-Carboxylate (3)Ethyl Oxirane-2-Carboxylate (4)Ethyl Picolinate (41)Ethyl Piperidine-2-Carboxylate (9)Ethyl Piperidine-3-Carboxylate (14)Ethyl Piperidine-4-Carboxylate (10)Ethyl Pyrazine-2-Carboxylate (10)Ethyl Pyridazine-3-Carboxylate (6)Ethyl Pyrimidine-4-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl Pyrimidine-5-Carboxylate (5)Ethyl Quinazoline-2-Carboxylate (4)Ethyl Thiazole-2-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl Thiazole-4-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl Thiazole-5-Carboxylate (7)Ethyl Thiophene-2-Carboxylate (19)Ethyl Thiophene-3-Carboxylate (11)Hexyl Benzoate (5)Isobutyl Benzoate (10)Isopropyl Benzoate (10)Methyl 1-Naphthoate (7)Methyl 1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 1H-Imidazole-2-Carboxylate (4)Methyl 1H-Imidazole-5-Carboxylate (8)Methyl 1H-Indazole-3-Carboxylate (23)Methyl 1H-Indazole-4-Carboxylate (10)Methyl 1H-Indazole-5-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 1H-Indazole-6-Carboxylate (9)Methyl 1H-Indazole-7-Carboxylate (8)Methyl 1H-Indole-3-Carboxylate (21)Methyl 1H-Indole-4-Carboxylate (9)Methyl 1H-Indole-5-Carboxylate (7)Methyl 1H-Indole-6-Carboxylate (9)Methyl 1H-Indole-7-Carboxylate (7)Methyl 1H-Pyrazole-4-Carboxylate (10)Methyl 1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylate (30)Methyl 1H-Pyrrole-3-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-3-Carboxylate (4)Methyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-6-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 2,6-Dichlorobenzoate (7)Methyl 2,6-Difluorobenzoate (17)Methyl 2-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Acetate (3)Methyl 2-(2-Bromophenyl)Acetate (8)Methyl 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)Acetate (10)Methyl 2-(Bromomethyl)Benzoate (33)Methyl 2-(Chlorosulfonyl)Benzoate (7)Methyl 2-(Morpholin-3-Yl)Acetate (3)Methyl 2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Acetate (9)Methyl 2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoate (14)Methyl 2-Amino-2-Phenylacetate (38)Methyl 2-Aminobenzoate (95)Methyl 2-Aminothiazole-4-Carboxylate (6)Methyl 2-Bromo-2-Phenylacetate (7)Methyl 2-Bromo-3-Nitrobenzoate (3)Methyl 2-Bromo-5-Fluorobenzoate (8)Methyl 2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzoate (7)Methyl 2-Bromo-6-Methylbenzoate (8)Methyl 2-Bromobenzoate (69)Methyl 2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzoate (5)Methyl 2-Chloro-6-Fluorobenzoate (7)Methyl 2-Chlorobenzoate (79)Methyl 2-Cyanobenzoate (22)Methyl 2-Fluorobenzoate (132)Methyl 2-Hydroxybenzoate (74)Methyl 2-Iodobenzoate (28)Methyl 2-Methoxybenzoate (70)Methyl 2-Methyl-2H-Indazole-3-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 2-Methylbenzoate (101)Methyl 2-Naphthoate (11)Methyl 2-Nitrobenzoate (54)Methyl 2-Phenoxyacetate (12)Methyl 2-Phenoxybenzoate (4)Methyl 2-Phenylacetate (114)Methyl 3-(Benzyloxy)Benzoate (5)Methyl 3-(Bromomethyl)Benzoate (16)Methyl 3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoate (22)Methyl 3-Amino-3-Phenylpropanoate (27)Methyl 3-Aminobenzoate (88)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Chlorobenzoate (6)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzoate (7)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzoate (10)Methyl 3-Bromo-4-Methylbenzoate (9)Methyl 3-Bromobenzoate (153)Methyl 3-Bromopyrazine-2-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 3-Chlorobenzoate (88)Methyl 3-Cyanobenzoate (29)Methyl 3-Fluorobenzoate (136)Methyl 3-Formylbenzoate (23)Methyl 3-Hydroxybenzoate (58)Methyl 3-Iodo-4-Methylbenzoate (6)Methyl 3-Iodobenzoate (47)Methyl 3-Methoxybenzoate (70)Methyl 3-Methylbenzoate (75)Methyl 3-Nitrobenzoate (109)Methyl 3-Oxo-3-Phenylpropanoate (16)Methyl 3-Phenylpropanoate (28)Methyl 4-Amino-3-Bromobenzoate (8)Methyl 4-Amino-3-Iodobenzoate (7)Methyl 4-Amino-3-Nitrobenzoate (9)Methyl 4-Aminobenzoate (71)Methyl 4-Fluorobenzoate (75)Methyl 4-Nitrobenzoate (29)Methyl 4-Oxocyclohexane-1-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 4-Oxopiperidine-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 4-Phenoxybenzoate (3)Methyl 5-Amino-2-Bromobenzoate (6)Methyl 5-Hydroxypicolinate (5)Methyl 5-Oxopyrrolidine-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl 5-Phenylisoxazole-3-Carboxylate (6)Methyl 6-Bromopyrazine-2-Carboxylate (7)Methyl 6-Chloropyrazine-2-Carboxylate (5)Methyl 6-Methoxynicotinate (4)Methyl [1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Carboxylate (8)Methyl Azetidine-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carboxylate (27)Methyl Benzo[D]Oxazole-2-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Benzo[D]Thiazole-6-Carboxylate (5)Methyl Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentane-1-Carboxylate (10)Methyl Cinnamate (36)Methyl Cyclobutanecarboxylate (24)Methyl Cyclohex-3-Ene-1-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Cyclohexanecarboxylate (45)Methyl Cyclopentanecarboxylate (18)Methyl Cyclopropanecarboxylate (8)Methyl Furan-2-Carboxylate (20)Methyl Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-8-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Indoline-6-Carboxylate (3)Methyl Isonicotinate (16)Methyl Isoquinoline-4-Carboxylate (6)Methyl L-Phenylalaninate (20)Methyl Morpholine-2-Carboxylate (4)Methyl Morpholine-3-Carboxylate (10)Methyl Nicotinate (52)Methyl Oxazole-4-Carboxylate (9)Methyl Piperidine-2-Carboxylate (12)Methyl Piperidine-3-Carboxylate (19)Methyl Prolinate (43)Methyl Pyrazine-2-Carboxylate (19)Methyl Pyridazine-3-Carboxylate (7)Methyl Pyrimidine-2-Carboxylate (10)Methyl Pyrimidine-4-Carboxylate (11)Methyl Pyrimidine-5-Carboxylate (5)Methyl Pyrrolidine-3-Carboxylate (9)Methyl Thiazole-2-Carboxylate (6)Methyl Thiazole-4-Carboxylate (6)Methyl Thiophene-3-Carboxylate (34)Phenyl (1R,4R)-[1,1'-Bi(Cyclohexane)]-4-Carboxylate (6)Phenyl Dimethylcarbamate (5)Phenyl Ethyl(Methyl)Carbamate (5)Propyl Benzoate (11)Tert-Butyl (1-Phenylethyl)Carbamate (19)Tert-Butyl (2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (2-Phenylcyclopropyl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (3-Oxocyclohexyl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (Morpholin-2-Ylmethyl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (Tetrahydrofuran-3-Yl)Carbamate (4)Tert-Butyl 1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole-1-Carboxylate (5)Tert-Butyl 1H-Imidazole-1-Carboxylate (6)Tert-Butyl 1H-Indazole-1-Carboxylate (29)Tert-Butyl 1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (18)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrrole-1-Carboxylate (8)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrrole-2-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl 1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine-1-Carboxylate (9)Tert-Butyl 3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-Carboxylate (19)Tert-Butyl 3-((Methylsulfonyl)Oxy)Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (5)Tert-Butyl 3-Oxopiperazine-1-Carboxylate (7)Tert-Butyl 4-Phenylpiperazine-1-Carboxylate (23)Tert-Butyl 4-Phenylpiperidine-1-Carboxylate (16)Tert-Butyl Azetidine-1-Carboxylate (64)Tert-Butyl Benzoate (66)Tert-Butyl Benzylcarbamate (52)Tert-Butyl Bicyclo[1.1.1]Pentan-1-Ylcarbamate (5)Tert-Butyl Cyclopentylcarbamate (28)Tert-Butyl Isoindoline-2-Carboxylate (13)Tert-Butyl Methyl(Phenyl)Carbamate (9)Tert-Butyl Morpholine-4-Carboxylate (23)Tert-Butyl O-Tolylcarbamate (11)Tert-Butyl Phenethylcarbamate (12)Tert-Butyl Piperazine-1-Carboxylate (30)Tert-Butyl Pyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (21)
Ethers (82526)
Butoxy-Phenyl-Boronic Acid/Ester (76)Diethoxy (14)Diethoxy (14)Diethoxyethyl (9)Diethoxyethyl (9)Diethoxymethyl (8)Diethoxymethyl (8)Dimethoxyethyl (8)Dimethoxypropane (11)Dimethoxypropane (11)Dioxane (153)Dioxepine (7)Dioxepine (7)Disulfide (38)Methoxyphenylboronic-Acid (32)(1S,4Ar,7Ar)-1-(((S)-Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Oxy)-1,4A,5,7A-Tetrahydrocyclopenta[C]Pyran (4)(2,2,2-Trifluoroethoxy)Benzene (18)(2-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (23)(2-(Phenoxymethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (3)(2-Chloro-3-Methoxyphenyl)Boronic Acid (5)(2-Chloroethoxy)Benzene (5)(2-Methoxyethoxy)Benzene (32)(3-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (9)(3-(Phenoxymethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (3)(3-Chloro-2-Methoxyphenyl)Boronic Acid (4)(3-Phenoxyphenyl)Methanol (3)(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (26)(4-(Phenoxymethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(4-Methoxyphenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (7)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (2-(Benzyloxy)Ethyl)Carbamate (6)(9H-Fluoren-9-Yl)Methyl (4-Methoxybenzyl)Carbamate (7)(Allyloxy)Benzene (19)(Ethoxymethyl)Benzene (7)(Hexyloxy)Benzene (7)(Methoxymethyl)Benzene (30)(Prop-2-Yn-1-Yloxy)Benzene (13)(R)-2-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran (7)(S)-7-(((S)-Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran-2-Yl)Oxy)-7,8,9,10-Tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-Dione (5)1,2-Bis(Benzyloxy)Benzene (11)1,2-Dichloro-3-Methoxybenzene (7)1,2-Dichloro-4-Methoxybenzene (11)1,2-Difluoro-3-Methoxybenzene (28)1,2-Difluoro-4-Methoxybenzene (19)1,2-Dimethoxybenzene (223)1,2-Diphenoxyethane (11)1,3-Bis(Benzyloxy)Benzene (8)1,3-Dibromo-2-Methoxybenzene (11)1,3-Dichloro-2-Methoxybenzene (9)1,3-Diiodo-2-Phenoxybenzene (3)1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (235)1,3-Diphenoxybenzene (8)1,4-Dichloro-2-Methoxybenzene (8)1,4-Dimethoxybenzene (66)1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (33)1-(3-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-One (3)1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (38)1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Piperazine (4)1-(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(4-Methoxybenzyl)-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Bromobenzene (12)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Chlorobenzene (16)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Fluorobenzene (10)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Methoxybenzene (19)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Methylbenzene (12)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Nitrobenzene (3)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Bromobenzene (12)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Chlorobenzene (6)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Fluorobenzene (14)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Methylbenzene (8)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Nitrobenzene (10)1-(Benzyloxy)-4-Bromobenzene (8)1-(Benzyloxy)-4-Iodobenzene (3)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Methoxybenzene (14)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-Methoxybenzene (19)1-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Fluorobenzene (11)1-Benzyl-4-Methoxybenzene (8)1-Bromo-2,3-Dimethoxybenzene (8)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzene (6)1-Bromo-2-Ethoxybenzene (16)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-Methoxybenzene (7)1-Bromo-2-Phenoxybenzene (3)1-Bromo-3-Methoxybenzene (187)1-Bromo-3-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Bromo-4-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Chloro-2,4-Dimethoxybenzene (7)1-Chloro-2-Ethoxybenzene (14)1-Chloro-2-Phenoxybenzene (10)1-Chloro-2-Propoxybenzene (5)1-Chloro-3-Fluoro-2-Methoxybenzene (4)1-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzene (126)1-Chloro-3-Phenoxybenzene (5)1-Chloro-4-Methoxybenzene (98)1-Chloro-4-Phenoxybenzene (13)1-Cyclopropyl-3-(4-(Quinolin-4-Yloxy)Phenyl)Urea (6)1-Ethoxy-2,3-Difluorobenzene (9)1-Ethoxy-2-Fluorobenzene (37)1-Ethoxy-3-Nitrobenzene (7)1-Fluoro-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (20)1-Fluoro-2-Isopropoxybenzene (18)1-Fluoro-2-Phenoxybenzene (11)1-Fluoro-3-Methoxybenzene (213)1-Fluoro-3-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Fluoro-4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (14)1-Fluoro-4-Methoxybenzene (125)1-Fluoro-4-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Iodo-2-Methoxybenzene (50)1-Iodo-3-Methoxybenzene (48)1-Iodo-4-Methoxybenzene (34)1-Iodo-4-Phenoxybenzene (4)1-Methoxy-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (21)1-Methoxy-3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (9)1-Methoxy-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (40)1-Methoxy-3-Nitrobenzene (108)1-Methoxy-4-(Phenoxymethyl)Benzene (3)1-Methoxy-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (18)1-Methoxy-4-Nitrobenzene (90)1-Methoxynaphthalene (17)1-Methyl-3-Phenoxybenzene (9)1-Nitro-2-Phenoxybenzene (4)1-Nitro-4-Phenoxybenzene (5)1-Phenoxy-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (2)1-Phenoxy-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (2)1-Phenyl-3-(4-(Pyridin-4-Yloxy)Phenyl)Urea (8)2,3,5,6,8,9,11,12-Octahydrobenzo[B][1,4,7,10,13]Pentaoxacyclopentadecine (8)2,3-Dimethoxypyridine (7)2,4,6-Triphenoxy-1,3,5-Triazine (4)2,4-Dibromo-1-Methoxybenzene (6)2,4-Dichloro-1-Methoxybenzene (18)2,4-Difluoro-1-Methoxybenzene (25)2,4-Dimethoxy-1-Nitrobenzene (5)2,4-Dimethoxypyrimidine (13)2,6-Dimethoxypyridine (11)2-(2-Methoxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (16)2-(3-Isopropoxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)2-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (23)2-(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Acetonitrile (3)2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (19)2-(Benzyloxy)Benzaldehyde (13)2-(Benzyloxy)Naphthalene (5)2-(Benzyloxy)Phenol (5)2-(Methoxymethyl)Morpholine (4)2-(Methoxymethyl)Pyrrolidine (6)2-(Phenoxymethyl)Oxirane (13)2-(Phenoxymethyl)Pyridine (5)2-(Phenoxymethyl)Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran (5)2-Bromo-1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (7)2-Bromo-1,4-Dimethoxybenzene (11)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-Methoxybenzene (12)2-Bromo-1-Methoxy-3-Methylbenzene (3)2-Bromo-1-Methoxy-4-Methylbenzene (7)2-Bromo-3-Methoxypyrazine (5)2-Bromo-4-Methoxy-1-Nitrobenzene (6)2-Bromo-4-Methoxyaniline (6)2-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzaldehyde (8)2-Bromo-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (4)2-Bromo-5-Methoxybenzaldehyde (6)2-Bromo-6-Methoxyaniline (5)2-Bromo-6-Methoxyphenol (5)2-Chloro-1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (3)2-Chloro-1,4-Dimethoxybenzene (4)2-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzaldehyde (7)2-Chloro-3-Methoxybenzoic Acid (6)2-Chloro-4-Fluoro-1-Methoxybenzene (10)2-Chloro-4-Methoxypyrimidine (14)2-Chloro-5-Methoxyaniline (8)2-Chloro-6-Methoxyaniline (3)2-Chloro-6-Methoxyphenol (4)2-Ethoxynaphthalene (4)2-Ethoxypyridine (20)2-Ethoxypyrimidine (7)2-Fluoro-1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (8)2-Fluoro-1-Methoxy-4-Nitrobenzene (8)2-Fluoro-4-Methoxyaniline (6)2-Fluoro-5-Methoxybenzoic Acid (9)2-Fluoro-5-Methoxypyridine (4)2-Fluoro-6-Methoxypyridine (6)2-Isopropoxypyridine (16)2-Methoxy-1,1'-Biphenyl (7)2-Methoxy-1,3,5-Triazine (10)2-Methoxy-4-Methylpyridine (5)2-Methoxy-5-Methylpyridine (5)2-Methoxy-6-Methylpyridine (14)2-Methoxy-6-Nitrophenol (5)2-Methoxybenzamide (9)2-Methoxybenzenesulfonyl Chloride (15)2-Methoxynaphthalene (22)2-Methoxyphenol (197)2-Methoxypyrazine (45)2-Methoxypyridine (436)2-Methoxypyrimidin-4-Amine (6)2-Methoxypyrimidine (59)2-Methoxythiophene (7)2-Methyl-N-Phenylaniline (6)2-Phenoxyacetonitrile (11)2-Phenoxyaniline (4)2-Phenoxybenzonitrile (5)2-Phenoxyethan-1-Ol (14)2-Phenoxypropanoic Acid (13)2-Phenoxypyrimidine (8)2-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran (6)2-Phenoxythiazole (5)2-Propoxypyridine (9)3,5-Dimethoxypyridine (4)3-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Propanoic Acid (9)3-(Benzyloxy)Aniline (12)3-(Benzyloxy)Benzaldehyde (13)3-(Benzyloxy)Benzoic Acid (5)3-(Benzyloxy)Phenol (5)3-(Methoxymethyl)Morpholine (4)3-Chloro-2-Methoxybenzoic Acid (4)3-Chloro-4-Methoxyaniline (6)3-Chloro-4-Methoxybenzaldehyde (7)3-Chloro-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (5)3-Ethoxypyridine (12)3-Fluoro-2-Methoxypyridine (14)3-Fluoro-4-Methoxybenzoic Acid (6)3-Methoxypiperidine (7)3-Methoxypyridazine (17)3-Methoxypyridine (52)3-Methoxythiophene (9)3-Phenoxyaniline (2)3-Phenoxybenzaldehyde (7)3-Phenoxybenzoic Acid (6)3-Phenoxybenzonitrile (5)3-Phenoxypropanoic Acid (14)3-Phenoxypyrrolidine (5)4-(3-Phenoxypropyl)Morpholine (7)4-(Benzyloxy)Aniline (8)4-(Benzyloxy)Benzaldehyde (23)4-(Benzyloxy)Benzoic Acid (5)4-(Benzyloxy)Phenol (2)4-(Difluoromethoxy)Aniline (6)4-(Dimethoxymethyl)Pyrimidine (5)4-(Phenylethynyl)Phenol (7)4-Chloro-2-Methoxypyrimidine (12)4-Chloro-5-Methoxypyrimidine (7)4-Chloro-6-Methoxypyrimidine (5)4-Ethoxypyridine (7)4-Ethoxypyrimidine (6)4-Methoxy-1,1'-Biphenyl (4)4-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (7)4-Methoxy-1H-Indole (11)4-Methoxy-2-Methylpyrimidine (8)4-Methoxy-N-Phenylaniline (5)4-Methoxy-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (3)4-Methoxybenzenesulfonamide (5)4-Methoxypyridazine (8)4-Methoxypyridine (136)4-Methoxypyrimidin-2-Amine (6)4-Methoxypyrimidine (102)4-Phenoxyaniline (6)4-Phenoxybenzaldehyde (12)4-Phenoxybenzoic Acid (4)4-Phenoxypyridine (7)4-Phenoxypyrimidine (5)4-Phenoxyquinoline (5)4-Phenoxytetrahydro-2H-Pyran (5)5-(Benzyloxy)Pyrimidine (5)5-Fluoro-2-Methoxypyridine (15)5-Methoxy-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (2)5-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (5)5-Methoxy-1H-Indole (11)5-Methoxy-2-Methyl-1H-Indole (5)5-Methoxy-2-Nitroaniline (7)5-Methoxyindoline (4)5-Methoxyisobenzofuran-1(3H)-One (5)5-Methoxyisoquinoline (6)6-Methoxy-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)6-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (14)6-Methoxy-1H-Indole (12)6-Methoxy-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (3)6-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (3)6-Methoxybenzo[D]Thiazole (6)6-Methoxybenzofuran (4)6-Methoxychromane (5)6-Methoxyisoindolin-1-One (3)6-Methoxyquinoxaline (6)7-(Benzyloxy)Quinoline (6)7-Methoxy-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (6)7-Methoxy-1H-Indazole (5)7-Methoxy-1H-Indole (8)7-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-One (3)7-Methoxyisoquinoline (5)8-Methoxyisoquinoline (7)8-Methoxyquinazoline (3)Butoxybenzene (51)Ethoxybenzene (285)Ethyl 2-Phenoxyacetate (10)Isobutoxybenzene (22)Isopropoxybenzene (85)Methoxycyclohexane (7)Methyl 2-Methoxybenzoate (70)Methyl 2-Phenoxyacetate (12)Methyl 2-Phenoxybenzoate (4)Methyl 3-(Benzyloxy)Benzoate (5)Methyl 3-Methoxybenzoate (70)Methyl 4-Phenoxybenzoate (3)N,N-Dimethyl-2-Phenoxyethan-1-Amine (17)N-(2-Phenoxyphenyl)Methanesulfonamide (4)N-(4-Phenoxyphenyl)Acetamide (4)N-Phenyl-N-(4-(Quinolin-4-Yloxy)Phenyl)Cyclopropane-1,1-Dicarboxamide (5)Phenethoxybenzene (23)Propoxybenzene (63)Tert-Butoxybenzene (19)Tert-Butyl 3-Methoxypyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (6)Tert-Butyl 4-Phenoxypiperidine-1-Carboxylate (12)Tert-Butyl 5-Methoxy-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (6)
Fluorinated Building Blocks (99063)
Dichlorofluorobenzene (23)Difluoro (901)Difluoroaniline (37)Difluorobenzaldehyde (33)Difluorobenzamide (6)Difluorobenzenesulfonamide (5)Difluorobenzoate (59)Difluoroethyl (27)Difluoroethyl (27)Difluoromethoxy (200)Difluoromethoxy (200)Difluoropropan (7)Difluoropropan (7)Fluindamine (32)Fluoroacetanilide (5)Fluoroacetophenone (8)Fluoroaniline (65)Fluoroanisole (9)Fluorobenzaldehyde (69)Fluorobenzamide (28)Fluorobenzenesulfonamide (7)Fluorobenzenethiol (6)Fluorobenzylamine (10)Fluorobromobenzene (3)Fluorocinnamic (10)Fluorocinnamic (10)Fluorocinnamic Acid (9)Fluorocyclopropanecarboxylic (9)Fluoroethoxy (4)Fluoroethyl (8)Fluoroethyl (8)Fluoroindan (3)Fluoroindan (3)Fluoroisonicotinaldehyde (7)Fluoroisonicotinate (8)Fluoroisonicotinic (13)Fluoroisonicotinic Acid (13)Fluoromethyl (15)Fluoromethyl (15)Fluoronicotinaldehyde (20)Fluoronicotinamide (3)Fluoronicotinic (19)Fluoronicotinic (19)Fluoronicotinic Acid (14)Fluorophenylisocyanate (3)Fluoropropan (15)Fluoropropan (15)Fluorostyryl (7)Fluorosulfonyl (12)Fluorosulfonyl (12)Hexafluoro (9)Hexafluoro (9)Hexafluoropropan (4)Hexafluoropropan (4)Nonafluoro (2)Nonafluoro (2)Octafluoro (2)Octafluoro (2)Pentafluoro (4)Pentafluorobenzoate (4)Tetrafluoro (12)Tetrafluoro (12)Tetrafluoroaniline (7)Tetrafluoroethoxy (3)Tetrafluoroethoxy (3)Trifluoro (271)Trifluoro (271)Trifluoroacetamide (8)Trifluoroacetyl (13)Trifluoroaniline (11)Trifluorobenzaldehyde (9)Trifluorobenzoate (14)Trifluorobut (36)Trifluorobut (36)Trifluoroethan (2)Trifluoroethan (2)Trifluoroethanamine (23)Trifluoroethanol (6)Trifluoroethoxy (60)Trifluoroethoxy (60)Trifluoroethyl (63)Trifluoromethanesulfonamide (4)Trifluoromethanesulfonyl (22)Trifluoromethoxy (480)Trifluoromethoxy (480)Trifluoromethylthio (5)Trifluoromethylthio (5)Trifluoropropane (36)Trifluoropropanoate (5)Trifluoropropyl (9)(2,3-Difluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (33)(2,6-Difluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (28)(2-Chloro-6-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (9)(2-Fluorobenzyl)Hydrazine (6)(2-Fluorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (15)(2-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (229)(2-Fluorophenyl)Hydrazine (22)(2-Fluorophenyl)Methanamine (49)(2-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (60)(3-Fluorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (5)(3-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (169)(3-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (58)(4-Fluorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (8)(4-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (93)(4-Fluorophenyl)Methanamine (27)(4-Fluorophenyl)Methanol (29)1,1-Difluorocyclobutane (14)1,1-Difluorocyclohexane (18)1,2,3,4,5-Pentafluorobenzene (51)1,2,3,4-Tetrafluorobenzene (73)1,2,3-Trifluorobenzene (156)1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene (210)1,2-Dibromo-3-Fluorobenzene (9)1,2-Dibromo-4-Fluorobenzene (11)1,2-Dichloro-3-Fluorobenzene (13)1,2-Dichloro-4-Fluorobenzene (15)1,2-Difluoro-3-Iodobenzene (13)1,2-Difluoro-3-Methoxybenzene (28)1,2-Difluoro-3-Methylbenzene (23)1,2-Difluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (23)1,2-Difluoro-4-Methoxybenzene (19)1,2-Difluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (43)1,2-Difluorobenzene (658)1,3-Dibromo-2,4-Difluorobenzene (5)1,3-Dibromo-2-Fluorobenzene (15)1,3-Dichloro-2-Fluorobenzene (23)1,3-Difluoro-2-Iodobenzene (12)1,3-Difluoro-2-Methylbenzene (18)1,3-Difluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (16)1,4-Dichloro-2-Fluorobenzene (11)1,4-Difluoro-2-Iodobenzene (8)1,4-Difluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (28)1,4-Difluorobenzene (361)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (80)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (58)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Piperazine (8)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Propan-1-Amine (8)1-(3-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (63)1-(4-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (36)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Fluorobenzene (10)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Fluorobenzene (14)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Fluorobenzene (50)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-Fluorobenzene (47)1-(Chloromethyl)-2-Fluorobenzene (8)1-(Chloromethyl)-3-Fluorobenzene (11)1-Benzyl-4-Fluorobenzene (2)1-Bromo-2,3-Difluorobenzene (67)1-Bromo-2,4-Difluorobenzene (59)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-3-Fluorobenzene (20)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-Methylbenzene (11)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Methoxybenzene (12)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Methylbenzene (17)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (10)1-Bromo-4-Fluoro-2-Methoxybenzene (11)1-Bromo-4-Fluoro-2-Methylbenzene (18)1-Chloro-2,3-Difluorobenzene (27)1-Chloro-2,4-Difluorobenzene (35)1-Chloro-3-Fluoro-2-Methoxybenzene (4)1-Chloro-3-Fluoro-2-Methylbenzene (10)1-Cyclohexyl-2-Fluorobenzene (4)1-Ethoxy-2,3-Difluorobenzene (9)1-Ethoxy-2-Fluorobenzene (37)1-Ethynyl-2-Fluorobenzene (10)1-Fluoro-2,3-Dimethylbenzene (8)1-Fluoro-2-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzene (5)1-Fluoro-2-Iodo-4-Methylbenzene (3)1-Fluoro-2-Iodobenzene (102)1-Fluoro-2-Isopropoxybenzene (18)1-Fluoro-2-Methylbenzene (255)1-Fluoro-2-Phenoxybenzene (11)1-Fluoro-3,5-Dimethylbenzene (12)1-Fluoro-3-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzene (10)1-Fluoro-3-Iodo-2-Methylbenzene (3)1-Fluoro-3-Iodobenzene (94)1-Fluoro-3-Methoxybenzene (213)1-Fluoro-3-Methylbenzene (255)1-Fluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (216)1-Fluoro-3-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Fluoro-4-Iodobenzene (65)1-Fluoro-4-Methoxybenzene (125)1-Fluoro-4-Methylbenzene (140)1-Fluoro-4-Phenoxybenzene (8)1-Fluorobicyclo[1.1.1]Pentane (4)1-Fluoronaphthalene (23)2'-Fluoro-1,1':4',1''-Terphenyl (6)2,2',3,3',5,5',6,6'-Octafluoro-1,1'-Biphenyl (4)2,3-Difluoroaniline (34)2,3-Difluorobenzaldehyde (18)2,3-Difluorobenzoic Acid (35)2,3-Difluorobenzonitrile (29)2,3-Difluorophenol (36)2,3-Difluoropyridine (13)2,4-Dibromo-1-Fluorobenzene (18)2,4-Dichloro-1-Fluorobenzene (27)2,4-Difluoro-1-Iodobenzene (14)2,4-Difluoro-1-Methoxybenzene (25)2,4-Difluoro-1-Nitrobenzene (46)2,4-Difluoroaniline (44)2,4-Difluorobenzaldehyde (19)2,4-Difluorobenzoic Acid (29)2,4-Difluorobenzonitrile (21)2,4-Difluorophenol (21)2,5-Difluoroaniline (34)2,5-Difluorobenzoic Acid (32)2,5-Difluoropyridine (8)2,6-Difluoroaniline (23)2,6-Difluorobenzaldehyde (25)2,6-Difluorobenzoic Acid (33)2,6-Difluorobenzonitrile (28)2,6-Difluorophenol (24)2,6-Difluoropyridine (29)2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (43)2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acetonitrile (30)2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (16)2-(3-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (50)2-(3-Fluorophenyl)Pyrrolidine (5)2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1H-Indole (4)2-(4-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (30)2-(Bromomethyl)-1,3-Difluorobenzene (12)2-Amino-2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acetic Acid (11)2-Amino-3-(2-Fluorophenyl)Propanoic Acid (16)2-Amino-3-Fluorobenzoic Acid (11)2-Bromo-1,3,4-Trifluorobenzene (16)2-Bromo-1,3-Difluorobenzene (43)2-Bromo-1,4-Difluorobenzene (64)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-3-Fluorobenzene (9)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzene (20)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-Methylbenzene (17)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Fluorobenzene (16)2-Bromo-4-Fluoro-1-Methoxybenzene (12)2-Bromo-4-Fluoro-1-Methylbenzene (21)2-Bromo-4-Fluoroaniline (28)2-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (7)2-Bromo-4-Fluorobenzonitrile (7)2-Bromo-4-Fluorophenol (10)2-Bromo-5-Fluoroaniline (18)2-Bromo-5-Fluorobenzaldehyde (7)2-Bromo-5-Fluorobenzoic Acid (11)2-Bromo-6-Fluoroaniline (14)2-Bromo-6-Fluorophenol (9)2-Chloro-1,3-Difluorobenzene (27)2-Chloro-1,4-Difluorobenzene (25)2-Chloro-3-Fluoropyridine (20)2-Chloro-4-Fluoro-1-Methoxybenzene (10)2-Chloro-4-Fluoroaniline (19)2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (10)2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (9)2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzonitrile (9)2-Chloro-4-Fluorophenol (9)2-Chloro-5-Fluoropyrimidine (6)2-Chloro-6-Fluoroaniline (8)2-Chloro-6-Fluorobenzoic Acid (8)2-Chloro-6-Fluorobenzonitrile (5)2-Chloro-6-Fluorophenol (5)2-Fluoro-1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (8)2-Fluoro-1,3-Dimethylbenzene (14)2-Fluoro-1-Iodo-4-Methylbenzene (5)2-Fluoro-3-Methylbenzaldehyde (8)2-Fluoro-3-Methylpyridine (14)2-Fluoro-4-Methoxyaniline (6)2-Fluoro-4-Methyl-1-Nitrobenzene (13)2-Fluoro-4-Methylbenzoic Acid (7)2-Fluoro-4-Methylpyridine (6)2-Fluoro-5-Methylpyridine (6)2-Fluoro-6-Methylpyridine (20)2-Fluoro-N-Methylbenzamide (12)2-Fluoro-N-Phenylaniline (4)2-Fluoro-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (6)2-Fluoroaniline (262)2-Fluorobenzaldehyde (175)2-Fluorobenzamide (32)2-Fluorobenzenesulfonamide (12)2-Fluorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (31)2-Fluorobenzoic Acid (220)2-Fluoropyridine (15)2-Fluoropyrimidine (9)3,3-Difluoropiperidine (29)3,3-Difluoropyrrolidine (29)3,4-Difluoroaniline (44)3,4-Difluorophenol (19)3,5-Difluoropyridine (12)3-((Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)Amino)-4-(2-Fluorophenyl)Butanoic Acid (9)3-Chloro-2-Fluoroaniline (9)3-Fluoro-1,1'-Biphenyl (16)3-Fluoro-2-Iodoaniline (8)3-Fluoro-2-Methylaniline (9)3-Fluoro-2-Methylpyridine (15)3-Fluoro-4-Nitroaniline (7)3-Fluoroaniline (289)3-Fluorobenzaldehyde (137)3-Fluorobenzamide (26)3-Fluorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (22)3-Fluorobenzoic Acid (206)3-Fluorophenol (180)3-Fluoropiperidine (26)3-Fluoropyridin-2-Amine (12)3-Fluoropyridin-4-Amine (4)3-Fluorothiophene (6)4,4-Difluoropiperidine (5)4-(2-Fluorophenyl)Morpholine (8)4-(4-Fluorophenyl)Thiazole (9)4-Chloro-5-Fluoro-2-Methylpyrimidine (5)4-Fluoro-1-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene (12)4-Fluoro-1H-Indazole (22)4-Fluoro-1H-Indole (24)4-Fluoro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (6)4-Fluoro-2-Iodoaniline (7)4-Fluoro-2-Nitroaniline (14)4-Fluoroaniline (225)4-Fluorobenzaldehyde (78)4-Fluorobenzamide (19)4-Fluorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (26)4-Fluorobenzo[D]Thiazole (6)4-Fluorobenzoic Acid (114)4-Fluorobenzonitrile (89)4-Fluoroisoquinoline (6)4-Fluorophenol (111)4-Fluoropyrimidine (8)5-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)5-Fluoro-1H-Benzo[D][1,2,3]Triazole (4)5-Fluoro-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (12)5-Fluoro-1H-Indole (50)5-Fluoro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (9)5-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Indene (3)5-Fluoro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (5)5-Fluoro-2-Methylpyridine (8)5-Fluoro-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (5)5-Fluorochromane (6)5-Fluoroindoline (3)5-Fluoroisoindolin-1-One (3)5-Fluoropyridin-2-Amine (15)5-Fluoropyrimidine (11)6-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)6-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)6-Fluoro-1H-Indazole (15)6-Fluoro-1H-Indole (17)6-Fluoro-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (3)6-Fluorobenzo[D]Thiazole (5)6-Fluorochromane (6)6-Fluoropyridin-2-Amine (8)6-Fluoropyridin-3-Amine (4)7-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)7-Fluoro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline (3)7-Fluoro-1H-Indazole (12)7-Fluoro-1H-Indole (24)7-Fluorobenzo[D]Thiazole (9)7-Fluoroindoline-2,3-Dione (6)7-Fluoroisoquinoline (3)8-Fluoro-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (5)8-Fluorochromane (5)8-Fluoroimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (3)8-Fluoroisoquinoline (10)8-Fluoroquinazoline (4)Benzenesulfonyl Fluoride (51)Ethyl 2-Fluorobenzoate (37)Ethyl 3-Fluorobenzoate (34)Fluorobenzene (9967)Methyl 2,6-Difluorobenzoate (17)Methyl 2-Fluorobenzoate (132)Methyl 3-Fluorobenzoate (136)Methyl 4-Fluorobenzoate (75)Methyl 6-Fluoronicotinate (4)N-(3-Fluorophenyl)Acetamide (14)N-(4-Fluorophenyl)Benzamide (3)Pentafluoro(Phenyl)-L6-Sulfane (19)Phenyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate (27)Tert-Butyl (4-Fluorophenyl)Carbamate (9)Trifluoro(Phenyl)Borate (80)
Hydrazines (6277)
Dichlorophenylhydrazine (3)Hydrazinecarbothioamide (2)Hydrazinecarboxamide (1)Hydrazinylbenzoate (6)(2-Bromophenyl)Hydrazine (8)(2-Chlorophenyl)Hydrazine (16)(2-Fluorobenzyl)Hydrazine (6)(2-Fluorophenyl)Hydrazine (22)(3-Chlorophenyl)Hydrazine (12)2-Hydrazineylpyridine (32)2-Hydrazineylpyrimidine (6)3-Hydrazineylpyridine (8)4-Hydrazineylpiperidine (5)Isonicotinohydrazide (6)Phenylhydrazine (153)Picolinohydrazide (5)
Iodides (14083)
Diiodo (19)Diiodobenzoate (5)Iodoaniline (60)Iodoanisole (5)Iodobenzaldehyde (38)Iodobenzamide (6)Iodobutane (1)Iodobutane (1)Iodoethoxy (6)Iodoethoxy (6)Iodoethyl (5)Iodoethyl (5)Iodomethyl (26)Iodomethyl (26)Iodonicotinaldehyde (6)Iodonicotinic (14)Iodonicotinic (14)Iodopropyl (4)Iodopropyl (4)(2-Iodophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (4)(2-Iodophenyl)Methanol (12)(3-Iodophenyl)Boronic Acid (5)(3-Iodophenyl)Methanol (13)1,2-Benziodoxol-3-(1H)-One (6)1,2-Difluoro-3-Iodobenzene (13)1,2-Diiodobenzene (10)1,3-Dibromo-2-Iodobenzene (4)1,3-Dichloro-2-Iodobenzene (5)1,3-Difluoro-2-Iodobenzene (12)1,3-Diiodo-2-Phenoxybenzene (3)1,3-Diiodobenzene (59)1,4-Dibromo-2-Iodobenzene (3)1,4-Difluoro-2-Iodobenzene (8)1-(2-Iodophenyl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(3-Iodophenyl)Ethan-1-One (7)1-(Benzyloxy)-4-Iodobenzene (3)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Iodobenzene (9)1-Benzyl-4-Iodo-1H-Pyrazole (5)1-Bromo-2-Iodobenzene (65)1-Bromo-3-Fluoro-2-Iodobenzene (4)1-Bromo-3-Iodobenzene (70)1-Bromo-4-Iodobenzene (67)1-Chloro-2-Fluoro-3-Iodobenzene (5)1-Chloro-2-Iodobenzene (65)1-Chloro-3-Iodo-2-Methylbenzene (3)1-Chloro-3-Iodobenzene (77)1-Chloro-4-Iodobenzene (49)1-Ethyl-2-Iodobenzene (6)1-Fluoro-2-Iodo-4-Methylbenzene (3)1-Fluoro-2-Iodobenzene (102)1-Fluoro-3-Iodo-2-Methylbenzene (3)1-Fluoro-3-Iodobenzene (94)1-Fluoro-4-Iodobenzene (65)1-Iodo-2,3-Dimethylbenzene (8)1-Iodo-2,4-Dimethylbenzene (9)1-Iodo-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (6)1-Iodo-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (13)1-Iodo-2-Isopropylbenzene (4)1-Iodo-2-Methoxybenzene (50)1-Iodo-2-Methylbenzene (91)1-Iodo-2-Nitrobenzene (36)1-Iodo-3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (6)1-Iodo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (30)1-Iodo-3-Methoxybenzene (48)1-Iodo-3-Methylbenzene (60)1-Iodo-3-Nitrobenzene (45)1-Iodo-4-Methoxybenzene (34)1-Iodo-4-Phenoxybenzene (4)2,4-Difluoro-1-Iodobenzene (14)2,6-Dichloro-4-Iodopyridine (4)2,6-Diiodoaniline (8)2,6-Diiodophenol (16)2-Bromo-3-Iodopyridine (6)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Iodobenzene (6)2-Bromo-6-Iodoaniline (4)2-Bromo-6-Iodopyridine (5)2-Chloro-3-Iodopyridin-4-Amine (3)2-Chloro-3-Iodopyridine (13)2-Chloro-4-Iodopyridine (19)2-Chloro-5-Iodopyridine (18)2-Chloro-6-Iodophenol (3)2-Chloro-6-Iodopyridine (9)2-Fluoro-1-Iodo-4-Methylbenzene (5)2-Fluoro-3-Iodopyridine (8)2-Fluoro-6-Iodoaniline (7)2-Hydroxy-3-Iodobenzaldehyde (3)2-Iodo-1,3-Dimethylbenzene (15)2-Iodo-1,4-Dimethylbenzene (5)2-Iodo-1-Methyl-4-Nitrobenzene (3)2-Iodo-4-Methylaniline (5)2-Iodo-6-Methylpyridine (5)2-Iodo-6-Nitroaniline (3)2-Iodo-9H-Fluorene (8)2-Iodo-N,N-Dimethylaniline (3)2-Iodoaniline (87)2-Iodobenzaldehyde (17)2-Iodobenzamide (4)2-Iodobenzene-1,3-Diol (3)2-Iodobenzoic Acid (47)2-Iodobenzonitrile (26)2-Iodonaphthalene (5)2-Iodophenol (63)2-Iodopyrazine (25)2-Iodopyridine (27)2-Iodopyrimidine (8)2-Iodothiophene (14)3-Chloro-2-Iodoaniline (3)3-Chloro-4-Iodoaniline (3)3-Fluoro-2-Iodoaniline (8)3-Iodo-1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazole (6)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (11)3-Iodo-1H-Pyrrolo[3,2-B]Pyridine (6)3-Iodo-2-Methylaniline (4)3-Iodoaniline (32)3-Iodobenzaldehyde (28)3-Iodobenzoic Acid (55)3-Iodobenzonitrile (27)3-Iodoimidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine (10)3-Iodophenol (21)3-Iodopyridazine (5)3-Iodopyridin-2-Amine (12)3-Iodopyridin-2-Ol (4)3-Iodopyridin-4-Amine (6)3-Iodopyridin-4-Ol (4)3-Iodopyridine (37)3-Iodotetrahydrofuran (3)4-Bromo-2-Chloro-1-Iodobenzene (4)4-Bromo-2-Fluoro-1-Iodobenzene (8)4-Bromo-2-Iodoaniline (8)4-Chloro-2-Iodoaniline (9)4-Chloro-3-Iodoaniline (3)4-Chloro-5-Iodopyrimidine (6)4-Fluoro-2-Iodoaniline (7)4-Fluoro-3-Iodobenzoic Acid (5)4-Iodo-1,1'-Biphenyl (9)4-Iodo-1H-Pyrazole (9)4-Iodo-N,N-Diphenylaniline (3)4-Iodopyridine (17)4-Iodopyrimidine (9)5-Bromo-2-Iodopyridine (5)5-Iodo-1H-Imidazole (4)5-Iodo-1H-Pyrazole (4)5-Iodo-7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-D]Pyrimidine (4)5-Iodopyridin-2-Amine (17)5-Iodopyridin-2-Ol (8)5-Iodopyrimidine (5)6-Chloro-5-Iodopyridin-2-Amine (3)Ethyl 2-Iodobenzoate (4)Ethyl 3-Iodobenzoate (11)Methyl 2-Iodobenzoate (28)Methyl 3-Iodo-4-Methylbenzoate (6)Methyl 3-Iodobenzoate (47)Methyl 4-Amino-3-Iodobenzoate (7)N-(2-Iodophenyl)Acetamide (8)Phenyl(O-Tolyl)Iodonium (14)Tert-Butyl 3-Iodo-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (7)
Ketones (40074)
Acetylacetonate (26)Bromoethanone (4)Butanedione (6)Butanedione (6)Butanone (10)Butanone (10)Carbonyl-Phenyl-Boronic Acid/Ester (184)Chloroethanone (2)Dicarbonyl (2)Dicarbonyl (2)Dichloroacetophenone (5)Dienone (2)Diethanone (5)Diethanone (5)Dione (1793)Dioxobutanoate (2)Enone (21)Ethanone (1026)Heptanedionato (7)Heptanedionato (7)Hydroxyethanone (3)Methyl-Pyrazolone (87)Oxoacetaldehyde (4)Oxoazepane (3)Oxoazepane (3)Oxochroman (5)Oxotetrahydro (11)Pyrimidinone (3)Tetraone (48)Tetraone (48)Trifluoroacetophenone (9)Trifluoroethanone (15)(1E,4E)-1,5-Diphenylpenta-1,4-Dien-3-One (7)(1E,6E)-1,7-Diphenylhepta-1,6-Diene-3,5-Dione (7)(2-Aminophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (30)(2-Bromophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (3)(2-Chlorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (19)(2-Fluorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (15)(2-Hydroxyphenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (24)(2-Iodophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (4)(3-Chlorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (19)(3-Fluorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (5)(3-Nitrophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (5)(4-Aminophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (4)(4-Bromophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (9)(4-Chlorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (10)(4-Fluorophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (8)(4-Hydroxyphenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (3)(4-Methoxyphenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (7)(4-Nitrophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (3)(R)-5-Thia-1-Azabicyclo[4.2.0]Oct-2-En-8-One (8)1,3-Dioxoisoindolin-2-Yl 2-Phenylacetate (5)1,3-Diphenylpropan-1-One (9)1,4-Diazepan-5-One (9)1,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-3(2H)-One (5)1-(1H-Indazol-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (7)1-(1H-Indol-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-(1H-Indol-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (6)1-(1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-(2-Aminophenyl)Ethan-1-One (29)1-(2-Bromophenyl)Ethan-1-One (27)1-(2-Chlorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (40)1-(2-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (58)1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-Phenylethan-1-One (6)1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-Phenylprop-2-En-1-One (11)1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (73)1-(2-Iodophenyl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (33)1-(2-Nitrophenyl)Ethan-1-One (24)1-(3-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-One (3)1-(3-Aminophenyl)Ethan-1-One (18)1-(3-Chlorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (38)1-(3-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (63)1-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (19)1-(3-Iodophenyl)Ethan-1-One (7)1-(3-Methoxy-2-Nitrophenyl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (38)1-(3-Nitrophenyl)Ethan-1-One (25)1-(3-Nitrophenyl)Propan-1-One (4)1-(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(4-Fluorophenyl)Ethan-1-One (36)1-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)1-(Benzofuran-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (3)1-(Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (3)1-(M-Tolyl)Ethan-1-One (37)1-(Naphthalen-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (3)1-(O-Tolyl)Ethan-1-One (26)1-(Piperidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (13)1-(Pyrazin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)1-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (36)1-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Ethan-1-One (29)1-(Pyridin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-One (14)1-(Pyrimidin-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)1-(Pyrimidin-4-Yl)Ethan-1-One (6)1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-(Thiazol-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-(Thiophen-2-Yl)Ethan-1-One (17)1-Aminoanthracene-9,10-Dione (8)1-Benzylindoline-2,3-Dione (5)1-Benzylpiperidin-3-One (5)1-Chloroanthracene-9,10-Dione (6)1-Hydroxyanthracene-9,10-Dione (11)1-Methylpiperazin-2-One (6)1-Methylpyrrolidin-2-One (13)1-Phenylbutan-1-One (13)1-Phenylpentan-1-One (12)1-Phenylpiperidin-2-One (8)1-Phenylpropan-2-One (36)2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-Phenylethan-1-One (51)2,2-Dimethyl-1-Phenylpropan-1-One (8)2,2-Dimethyl-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (3)2,3,4,9-Tetrahydro-1H-Carbazol-1-One (7)2,3-Dihydrofuran-3-One (9)2,3-Dihydropyridin-2-One (5)2,5-Dichlorobenzoic Acid (13)2-Amino-1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Ethan-1-One (5)2-Benzalacetophenone (36)2-Benzoylbenzoic Acid (10)2-Chloro-1-Phenylethan-1-One (20)2-Chlorocyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (4)2-Chloroquinazolin-4(3H)-One (4)2-Hydroxy-1,2-Diphenylethan-1-One (3)2-Hydroxy-1-Phenylethan-1-One (8)2-Hydroxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (3)2-Hydroxyquinolin-4(1H)-One (3)2-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (7)2-Methyl-1-Phenylpropan-1-One (20)2-Methyl-2H-Benzo[B][1,4]Oxazin-3(4H)-One (3)2-Methyl-3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (6)2-Methylcyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione (5)2-Methylcyclohexan-1-One (3)2-Methylisoindolin-1-One (7)2-Methylisoindoline-1,3-Dione (5)2-Methylpyridazin-3(2H)-One (7)2-Oxo-2-Phenylacetaldehyde (12)2-Oxo-2-Phenylacetic Acid (17)3,3-Difluoropiperidin-4-One (3)3,3-Dimethylcyclohexan-1-One (4)3,3-Dimethylpiperidin-4-One (3)3,4-Dihydroquinoxalin-2(1H)-One (7)3-Acetyl-2H-Chromen-2-One (3)3-Aminopyrrolidin-2-One (5)3-Bromo-1H-Pyrrole-2,5-Dione (3)3-Chloro-1-Phenylpropan-1-One (10)3-Fluoropiperidin-4-One (3)3-Hydroxy-2-Phenyl-4H-Chromen-4-One (21)3-Hydroxypyrrolidin-2-One (4)3-Methylcyclohexan-1-One (9)3-Methylene-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (5)3-Methylpiperazin-2-One (7)3-Methylpyrimidin-4(3H)-One (6)3-Oxo-3-Phenylpropanenitrile (21)3-Oxo-N-Phenylbutanamide (10)3-Phenyl-1-(Pyrrolidin-1-Yl)Propan-1-One (5)3-Phenyl-2-Thioxoimidazolidin-4-One (6)3-Phenylacrylaldehyde (29)3-Phenylimidazolidine-2,4-Dione (4)4,4,4-Trifluoro-1-Phenylbutane-1,3-Dione (10)4-(1,2,2-Triphenylvinyl)Benzaldehyde (5)4-(Hydroxymethyl)Pyrrolidin-2-One (4)4-Benzylmorpholin-3-One (6)4-Bromoisoindolin-1-One (3)4-Bromopyridazin-3(2H)-One (3)4-Chloro-1-Phenylbutan-1-One (8)4-Chloropyridazin-3(2H)-One (4)4-Fluoroindoline-2,3-Dione (3)4-Hydroxy-2H-Chromen-2-One (10)4-Hydroxydihydrofuran-2(3H)-One (14)4-Hydroxypiperidin-2-One (3)4-Hydroxypyrrolidin-2-One (7)4-Methyl-2H-Chromen-2-One (27)4-Methylisobenzofuran-1(3H)-One (3)4-Oxo-4-Phenylbutanoic Acid (16)4-Phenylbutan-2-One (14)4-Phenylcyclohexan-1-One (11)4-Phenylmorpholin-3-One (6)4-Phenylpyrrolidin-2-One (7)5,6-Dihydrobenzo[D]Thiazol-7(4H)-One (5)5-(Aminomethyl)Pyrrolidin-2-One (3)5-(Hydroxymethyl)Pyrrolidin-2-One (7)5-Bromoisoindolin-1-One (8)5-Bromoisoindoline-1,3-Dione (3)5-Bromopyrimidin-4(3H)-One (3)5-Chloroisoindoline-1,3-Dione (3)5-Chloropyrimidin-4(3H)-One (4)5-Chloropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (3)5-Fluoro-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (5)5-Fluorochroman-4-One (3)5-Fluoroindolin-2-One (4)5-Fluoroisoindolin-1-One (3)5-Fluoropyrimidin-4(3H)-One (3)5-Fluoropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-Dione (3)5-Hydroxy-2-Phenyl-4H-Chromen-4-One (36)5-Hydroxypiperidin-2-One (3)5-Methoxy-2-Phenyl-4H-Chromen-4-One (10)5-Methyl-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (6)5-Methylindolin-2-One (3)5-Oxopyrrolidine-2-Carboxylic Acid (4)6-Bromoisoindolin-1-One (4)6-Fluorochroman-4-One (5)6-Fluoroindoline-2,3-Dione (3)6-Fluoroisobenzofuran-1(3H)-One (3)6-Hydroxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (3)6-Methoxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (6)6-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (5)6-Methoxyisoindolin-1-One (3)6-Methyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (3)7,8-Dihydroquinolin-5(6H)-One (5)7-(Diethylamino)-2H-Chromen-2-One (9)7-Bromo-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (8)7-Bromochroman-4-One (4)7-Bromoindoline-2,3-Dione (3)7-Bromoquinazolin-4(3H)-One (4)7-Chloro-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (6)7-Fluorochroman-4-One (5)7-Fluoroindolin-2-One (3)7-Fluoroquinazolin-4(3H)-One (4)7-Hydroxy-2H-Chromen-2-One (23)7-Methoxy-2H-Chromen-2-One (12)7-Methoxy-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (6)7-Methoxychroman-4-One (3)7-Methylindoline-2,3-Dione (7)8-Bromochroman-4-One (4)8-Fluoro-3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-One (5)8-Fluoroisoquinolin-1(2H)-One (3)8-Methylchroman-4-One (4)Acetophenone (1120)Azepan-2-One (18)Benzo[Cd]Indol-2(1H)-One (5)Benzofuran-2(3H)-One (7)Chroman-2-One (5)Cyclobutanone (24)Cyclohex-2-En-1-One (27)Cyclohexane-1,3-Dione (12)Cyclopent-2-En-1-One (21)Cyclopentane-1,3-Dione (6)Dihydro-2H-Pyran-2,6(3H)-Dione (5)Dihydrofuran-2,5-Dione (12)Dihydrofuran-3(2H)-One (7)Dihydrothiophen-3(2H)-One (4)Ethene-1,1-Diyldibenzene (10)Ethyl 2-Oxo-2-Phenylacetate (18)Ethyl 3-Oxo-3-Phenylpropanoate (41)Furan-2(5H)-One (26)Isoquinolin-1-Ol (9)Methyl 3-Oxo-3-Phenylpropanoate (16)Morpholin-3-One (11)Phenyl(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Methanone (3)Phenyl(M-Tolyl)Methanone (3)Phenyl(P-Tolyl)Methanone (4)Phenyl(Pyridin-3-Yl)Methanone (9)Phenyl(Thiophen-2-Yl)Methanone (6)Piperidine-2,4-Dione (5)Propiophenone (59)Pyrimidine-4,6(1H,5H)-Dione (3)Tert-Butyl (2-Oxopiperidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (4)Tert-Butyl (2-Oxopyrrolidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (3-Oxocyclohexyl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (5-Oxopyrrolidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl (6-Oxopiperidin-3-Yl)Carbamate (3)Tert-Butyl 2-Oxopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (3)Tert-Butyl 2-Oxopyrrolidine-1-Carboxylate (15)Tert-Butyl 4-Oxopiperidine-1-Carboxylate (16)Tetrahydropyrimidin-2(1H)-One (6)
Nitriles (28529)
Acetonitrile (255)Acrylonitrile (8)Aminobutanenitrile (5)Aminocyclohexanecarbonitrile (6)Bromobenzonitrile (15)Bromonicotinonitrile (9)Bromophenylacetonitrile (2)Butanenitrile (2)Butanenitrile (2)Chlorobenzonitrile (27)Chloroisonicotinonitrile (4)Chloronicotinonitrile (40)Cyanide (434)Cyanide (434)Cyanoacetamide (4)Cyanoacetate (14)Cyanobenzaldehyde (4)Cyanobenzoate (27)Cyanobenzoic (20)Cyanoethyl (15)Cyanoethyl (15)Cyanoisonicotinate (4)Cyanomethyl (42)Cyanomethyl (42)Cyanonicotinate (8)Cyanophenoxy (8)Cyanophenyl (64)Cyanophenylboronic (5)Cyanopropan (4)Cyanopropan (4)Diacetonitrile (1)Diaminobenzonitrile (8)Dibromoisonicotinonitrile (3)Dicarbonitrile (45)Dicarbonitrile (45)Dichlorobenzonitrile (12)Dichloroisonicotinonitrile (4)Difluorobenzonitrile (41)Fluorobenzonitrile (85)Fluoroisonicotinonitrile (5)Fluoronicotinonitrile (14)Fluorophenylacetonitrile (8)Fluoropicolinonitrile (13)Formylnicotinonitrile (5)Formylnicotinonitrile (5)Hydrazinylbenzonitrile (6)Iodobenzonitrile (44)Iodonicotinonitrile (8)Malononitrile (43)Malononitrile (43)Methoxyisonicotinonitrile (7)Methoxyisonicotinonitrile (7)Methoxynicotinonitrile (18)Methoxynicotinonitrile (18)Methylnicotinonitrile (57)Methylnicotinonitrile (57)Methylpropanenitrile (9)Methylpropanenitrile (9)Nitropicolinonitrile (10)Oxopropanenitrile (8)Phenylacrylonitrile (21)Propanenitrile (41)Propanenitrile (41)Pyrazino-Nitrile (50)Tetrafluorobenzonitrile (5)Thiocyanatoaniline (3)Tricarbonitrile (5)Tricarbonitrile (5)Trifluorobenzonitrile (7)Trifluoromethylbenzonitrile (5)1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbonitrile (17)1-Phenylcyclobutane-1-Carbonitrile (7)1-Phenylcyclopropane-1-Carbonitrile (19)1H-Imidazole-4-Carbonitrile (2)1H-Indazole-3-Carbonitrile (9)1H-Indole-2-Carbonitrile (9)1H-Indole-3-Carbonitrile (17)1H-Indole-5-Carbonitrile (5)1H-Indole-6-Carbonitrile (4)1H-Indole-7-Carbonitrile (6)1H-Pyrazole-4-Carbonitrile (5)1H-Pyrrole-2-Carbonitrile (7)1H-Pyrrole-3-Carbonitrile (9)2,3-Difluorobenzonitrile (29)2,4-Dichlorobenzonitrile (4)2,4-Difluorobenzonitrile (21)2,6-Dibromobenzonitrile (4)2,6-Dichlorobenzonitrile (8)2,6-Difluorobenzonitrile (28)2-(1,3,2-Dioxaborinan-2-Yl)Benzonitrile (4)2-(2-Bromophenyl)Acetonitrile (10)2-(2-Chlorophenyl)Acetonitrile (16)2-(2-Fluorophenyl)Acetonitrile (30)2-(3-Chlorophenyl)Acetonitrile (16)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzonitrile (14)2-(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Acetonitrile (3)2-(Bromomethyl)Benzonitrile (15)2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Benzonitrile (6)2-(Pyridin-2-Yl)Acetonitrile (8)2-(Pyridin-3-Yl)Acetonitrile (6)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzonitrile (7)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzonitrile (35)2-Amino-3-Bromobenzonitrile (7)2-Amino-3-Chlorobenzonitrile (3)2-Amino-6-Chlorobenzonitrile (3)2-Aminonicotinonitrile (6)2-Bromo-6-Fluorobenzonitrile (7)2-Chloro-3-Methylbenzonitrile (5)2-Chloro-4-Fluorobenzonitrile (9)2-Chloro-6-Fluorobenzonitrile (5)2-Chloro-N-Methylaniline (4)2-Chlorobenzonitrile (99)2-Hydroxybenzonitrile (45)2-Iodobenzonitrile (26)2-Naphthonitrile (15)2-Nitrobenzonitrile (37)2-Oxo-2H-Chromene-3-Carbonitrile (4)2-Phenoxyacetonitrile (11)2-Phenoxybenzonitrile (5)2-Phenylacetonitrile (172)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzonitrile (25)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzonitrile (11)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzonitrile (47)3-Bromo-2-Fluorobenzonitrile (10)3-Bromo-2-Hydroxybenzonitrile (3)3-Bromobenzonitrile (110)3-Chloro-2-Fluorobenzonitrile (7)3-Chlorobenzonitrile (100)3-Chloropyrazine-2-Carbonitrile (6)3-Fluoropicolinonitrile (5)3-Hydroxybenzonitrile (40)3-Iodobenzonitrile (27)3-Nitrobenzonitrile (59)3-Oxo-3-Phenylpropanenitrile (21)3-Phenoxybenzonitrile (5)4-Amino-2-Chlorobenzonitrile (8)4-Chloropyrimidine-5-Carbonitrile (6)4-Cyanophenyl Benzoate (11)4-Cyclohexylbenzonitrile (10)4-Fluorobenzonitrile (89)4-Nitrobenzonitrile (25)5-Fluoropicolinonitrile (5)6-Methylnicotinonitrile (7)6-Methylpicolinonitrile (10)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Carbonitrile (12)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Carbonitrile (27)Benzo[B]Thiophene-2-Carbonitrile (3)Benzo[D]Thiazole-2-Carbonitrile (11)Benzonitrile (1312)Furan-2-Carbonitrile (8)Imidazo[1,2-A]Pyridine-6-Carbonitrile (3)Isonicotinonitrile (16)Isoquinoline-1-Carbonitrile (7)Methyl 2-Cyanobenzoate (22)Methyl 3-Cyanobenzoate (29)Morpholine-2-Carbonitrile (4)Nicotinonitrile (82)Pyrazine-2-Carbonitrile (15)Pyrimidine-2-Carbonitrile (14)Pyrimidine-4-Carbonitrile (9)Pyrimidine-5-Carbonitrile (6)Pyrrolidine-2-Carbonitrile (9)Pyrrolidine-3-Carbonitrile (6)Thiazole-5-Carbonitrile (7)Thiophene-2-Carbonitrile (23)Thiophene-3-Carbonitrile (13)
Nitroes (23714)
Difluoronitrobenzene (9)Dinitro (7)Dinitroaniline (5)Nitroacetophenone (7)Nitroaniline (211)Nitrobenzaldehyde (100)Nitrobenzamide (35)Nitrobenzenesulfonamide (26)Nitrobenzonitrile (106)Nitrobenzotrifluoride (16)Nitroisophthalate (4)(2-Nitrophenyl)Boronic Acid (13)(2-Nitrophenyl)Methanol (29)(2-Nitrovinyl)Benzene (28)(3-Nitrophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (5)(3-Nitrophenyl)Boronic Acid (32)(3-Nitrophenyl)Methanol (31)(4-Nitrophenyl)(Phenyl)Methanone (3)(4-Nitrophenyl)Methanol (17)1,2-Dichloro-4-Nitrobenzene (16)1,2-Difluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (23)1,2-Difluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (43)1,2-Dimethyl-3-Nitrobenzene (6)1,2-Dinitrobenzene (6)1,3-Dibromo-2-Nitrobenzene (4)1,3-Dichloro-2-Nitrobenzene (5)1,3-Difluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (16)1,3-Dimethyl-2-Nitrobenzene (9)1,3-Dinitrobenzene (31)1,4-Difluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (28)1,4-Dimethyl-2-Nitrobenzene (10)1-(2-Nitrophenyl)Ethan-1-One (24)1-(3-Methoxy-2-Nitrophenyl)Ethan-1-One (4)1-(3-Nitrophenyl)Ethan-1-One (25)1-(3-Nitrophenyl)Propan-1-One (4)1-(Benzyloxy)-2-Nitrobenzene (3)1-(Benzyloxy)-3-Nitrobenzene (10)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-Nitrobenzene (23)1-(Methylsulfonyl)-3-Nitrobenzene (7)1-(Tert-Butyl)-2-Nitrobenzene (4)1-(Tert-Butyl)-3-Nitrobenzene (7)1-Bromo-2-Chloro-4-Nitrobenzene (5)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (11)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (13)1-Bromo-3-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene (3)1-Bromo-3-Nitrobenzene (235)1-Chloro-2-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (9)1-Chloro-2-Methyl-3-Nitrobenzene (6)1-Chloro-2-Nitrobenzene (138)1-Chloro-3-Fluoro-2-Nitrobenzene (6)1-Chloro-3-Nitrobenzene (161)1-Ethoxy-3-Nitrobenzene (7)1-Fluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (216)1-Iodo-2-Nitrobenzene (36)1-Iodo-3-Nitrobenzene (45)1-Methoxy-3-Nitrobenzene (108)1-Methoxy-4-Nitrobenzene (90)1-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene (176)1-Methyl-3-Nitrobenzene (147)1-Methyl-4-Nitrobenzene (82)1-Nitro-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (8)1-Nitro-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (32)1-Nitro-2-Phenoxybenzene (4)1-Nitro-3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (9)1-Nitro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (82)1-Nitro-4-Phenoxybenzene (5)1-Nitronaphthalene (3)2,4-Dichloro-1-Nitrobenzene (19)2,4-Difluoro-1-Nitrobenzene (46)2,4-Dimethoxy-1-Nitrobenzene (5)2,4-Dimethyl-1-Nitrobenzene (15)2-((2-Nitrophenyl)Amino)Ethan-1-Ol (5)2-(2-Nitrophenyl)Acetic Acid (20)2-(4-Nitrophenyl)Acetic Acid (9)2-Bromo-1-Chloro-4-Nitrobenzene (9)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-3-Nitrobenzene (9)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (23)2-Bromo-1-Methyl-4-Nitrobenzene (12)2-Bromo-3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (4)2-Bromo-4-Chloro-1-Nitrobenzene (5)2-Bromo-4-Fluoro-1-Nitrobenzene (23)2-Bromo-4-Nitroaniline (12)2-Bromo-6-Nitroaniline (14)2-Bromo-6-Nitrophenol (9)2-Chloro-1,3-Dinitrobenzene (2)2-Chloro-1-Fluoro-4-Nitrobenzene (16)2-Chloro-1-Methyl-3-Nitrobenzene (4)2-Chloro-3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (4)2-Chloro-4-Fluoro-1-Nitrobenzene (13)2-Chloro-4-Methyl-1-Nitrobenzene (6)2-Chloro-4-Nitrophenol (5)2-Chloro-5-Nitropyrimidine (5)2-Chloro-6-Nitroaniline (11)2-Chloro-6-Nitrophenol (7)2-Fluoro-1-Methoxy-4-Nitrobenzene (8)2-Fluoro-4-Methyl-1-Nitrobenzene (13)2-Iodo-1-Methyl-4-Nitrobenzene (3)2-Iodo-6-Nitroaniline (3)2-Methoxy-5-Nitropyridine (8)2-Methoxy-6-Nitrophenol (5)2-Methyl-3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (7)2-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine (9)2-Methyl-6-Nitroaniline (10)2-Nitro-1H-Pyrrole (5)2-Nitro-N-Phenylaniline (3)2-Nitrobenzaldehyde (53)2-Nitrobenzoic Acid (65)2-Nitrobenzonitrile (37)2-Nitrofuran (9)2-Nitronaphthalene (4)2-Nitropyridine (40)2-Nitrothiophene (20)3-Chloro-2-Nitroaniline (5)3-Chloro-4-Nitroaniline (5)3-Fluoro-4-Nitroaniline (7)3-Methoxy-2-Nitrobenzaldehyde (3)3-Methoxy-4-Nitrobenzoic Acid (4)3-Methyl-5-Nitropyridine (4)3-Nitroaniline (98)3-Nitrobenzaldehyde (49)3-Nitrobenzamide (17)3-Nitrobenzene-1,2-Diol (6)3-Nitrobenzenesulfonamide (8)3-Nitrobenzoic Acid (109)3-Nitrobenzonitrile (59)3-Nitrophenol (72)3-Nitropyridin-2-Ol (11)3-Nitropyridin-4-Amine (5)3-Nitropyridine (54)3-Nitrothiophene (6)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(2-Nitrophenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)4-Fluoro-1-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene (12)4-Fluoro-2-Nitroaniline (14)4-Hydroxy-3-Nitrobenzaldehyde (5)4-Methyl-3-Nitroaniline (8)4-Methyl-3-Nitropyridine (8)4-Nitro-1H-Indazole (10)4-Nitro-1H-Indole (6)4-Nitro-1H-Pyrazole (8)4-Nitroaniline (65)4-Nitrobenzaldehyde (18)4-Nitrobenzene-1,3-Diol (5)4-Nitrobenzoic Acid (35)4-Nitrobenzonitrile (25)4-Nitrophenol (67)4-Nitropyridine (11)5-(4-Nitrophenyl)Oxazole (3)5-Methoxy-2-Nitroaniline (7)5-Methyl-2-Nitroaniline (6)5-Nitro-1H-Indazole (5)5-Nitro-1H-Indole (6)5-Nitro-1H-Pyrazole (9)5-Nitro-1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-B]Pyridine (3)5-Nitro-2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran (3)5-Nitrobenzo[D][1,3]Dioxole (4)5-Nitrobenzo[D]Thiazole (3)5-Nitroisoquinoline (7)5-Nitronicotinic Acid (5)5-Nitropyridin-2-Amine (6)6-Nitro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)6-Nitro-1H-Indazole (9)6-Nitro-1H-Indole (8)6-Nitrobenzo[D]Thiazole (3)7-Nitro-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (3)7-Nitro-1H-Indazole (11)7-Nitro-1H-Indole (11)Ethyl 2-Nitrobenzoate (9)Ethyl 3-Nitrobenzoate (22)Ethyl Cinnamate (26)Methyl 2-Nitrobenzoate (54)Methyl 3-Nitrobenzoate (109)Methyl 4-Amino-3-Nitrobenzoate (9)Methyl 4-Nitrobenzoate (29)N-(2-Nitrophenyl)Acetamide (11)N-Methyl-2-Nitroaniline (20)N-Methyl-4-Nitroaniline (6)Nitrobenzene (2309)
Phenols (1786)
Aminophenol (9)Bromophenol (13)Chlorophenol (28)Dibromophenol (9)Dichlorophenol (17)Difluorophenol (36)Dihydroxybenzaldehyde (16)Dihydroxybenzamide (6)Dihydroxybenzoate (15)Dihydroxybenzoic (17)Dihydroxybenzonitrile (6)Dihydroxyphenyl (98)Dihydroxystyryl (4)Diiodophenol (7)Fluorophenol (73)Hydroxyacetophenone (16)Hydroxybenzaldehyde (88)Hydroxybenzamide (24)Hydroxybenzenesulfonic (4)Hydroxybenzenesulfonic Acid (3)Hydroxybenzoate (113)Hydroxybenzohydrazide (4)Hydroxybenzoic (89)Hydroxybenzonitrile (60)Hydroxybenzoyl (1)Hydroxyphenoxy (7)Hydroxyphenylacetic (7)Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid (7)Hydroxyphenylboronic (8)Hydroxypropiophenone (3)Iodophenol (41)Nitrophenol (134)Tetrafluorophenol (9)Trifluorophenol (5)Trihydroxybenzaldehyde (5)Trihydroxybenzoate (12)Trihydroxybenzoic (5)Trihydroxybenzoic Acid (4)Trihydroxyphenyl (10)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-5-Ol (3)1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinolin-6-Ol (6)1-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (73)1-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)Ethan-1-One (19)1-Hydroxyanthracene-9,10-Dione (11)2,3-Dichlorophenol (9)2,3-Difluorophenol (36)2,4-Dibromophenol (16)2,4-Difluorophenol (21)2,5-Dichlorophenol (7)2,6-Dibromophenol (21)2,6-Dichlorophenol (16)2,6-Difluorophenol (24)2,6-Diiodophenol (16)2,6-Dimethylphenol (19)2-(2-Hydroxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (8)2-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)Acetic Acid (7)2-(Benzyloxy)Phenol (5)2-(Difluoromethoxy)Phenol (5)2-(Tert-Butyl)Phenol (56)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenol (8)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenol (23)2-Amino-3-Bromophenol (3)2-Amino-3-Chlorophenol (4)2-Aminophenol (107)2-Benzylphenol (8)2-Bromo-3-Methylphenol (4)2-Bromo-6-Methylphenol (7)2-Bromobenzene-1,3-Diol (7)2-Bromobenzene-1,4-Diol (4)2-Chloro-4-Fluorophenol (9)2-Chloro-4-Nitrophenol (5)2-Chloro-6-Methylphenol (5)2-Chloro-6-Nitrophenol (7)2-Chlorobenzene-1,3-Diol (4)2-Chlorophenol (163)2-Ethylphenol (10)2-Hydroxy-N-Phenylbenzamide (3)2-Hydroxybenzamide (14)2-Hydroxybenzonitrile (45)2-Iodobenzene-1,3-Diol (3)2-Iodophenol (63)2-Isopropylphenol (28)2-Methoxyphenol (197)3,4-Dibromophenol (3)3,4-Difluorophenol (19)3-(Benzyloxy)Phenol (5)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenol (12)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenol (43)3-Bromo-2-Fluorophenol (5)3-Bromo-4-Chlorophenol (5)3-Bromo-4-Fluorophenol (11)3-Bromobenzene-1,2-Diol (8)3-Chloro-4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (7)3-Chlorobenzene-1,2-Diol (6)3-Chlorophenol (112)3-Fluorophenol (180)3-Hydroxybenzonitrile (40)3-Iodophenol (21)3-Nitrobenzene-1,2-Diol (6)3-Nitrophenol (72)4-(Benzyloxy)Phenol (2)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenol (18)4-Amino-2-Fluorophenol (9)4-Amino-3-Chlorophenol (5)4-Benzylphenol (14)4-Chlorobenzene-1,3-Diol (6)4-Fluorophenol (111)4-Hydroxybenzenesulfonic Acid (5)4-Nitrobenzene-1,3-Diol (5)4-Nitrophenol (67)6-Hydroxy-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Inden-1-One (3)Ethyl 2-Hydroxybenzoate (18)Ethyl 3-Hydroxybenzoate (12)M-Cresol (147)Methyl 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)Acetate (10)Methyl 2-Hydroxybenzoate (74)Methyl 3-Hydroxybenzoate (58)O-Cresol (164)P-Cresol (71)Pyrocatechol (131)Resorcinol (146)
Phosphoruses (827)
Diethoxyphosphoryl (5)Diisopropylphosphoramidite (4)Dimethoxyphosphoryl (4)Dimethoxyphosphoryl (4)Dimethylphosphine (28)Dioxaphosphepine (146)Diphosphonic (9)Phosphorothioate (1)1,1,1-Trifluoro-N-(4-Oxido-2,6-Diphenyldinaphtho[2,1-D:1',2'-F][1,3,2]Dioxaphosphepin-4-Yl)Methanesulfonamide (16)Diethyl Benzylphosphonate (17)Dimethyl(Phenyl)Phosphine Oxide (20)Ethyltriphenylphosphonium (2)Methyltriphenylphosphonium (3)Phenyl Phosphate (3)Phenylphosphonic Acid (6)
Silicon Compounds (450)
Butyldimethylsilyl (94)Butyldimethylsilyl (94)Butyldimethylsilyloxy (8)Dimethylsilane (16)Dimethylsilane (16)Dimethylsilyl (4)Tetramethyldisiloxane (3)Tetramethyldisiloxane (3)Triethoxysilyl (13)Triethoxysilyl (13)Triisopropylsilyl (22)Triisopropylsilyl (22)Trimethoxysilane (19)Trimethoxysilane (19)Trimethylsilane (155)1-(Triisopropylsilyl)-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (8)Tert-Butyldimethyl(Phenoxy)Silane (17)Tetraphenylsilane (7)Trimethoxy(Phenyl)Silane (6)Trimethyl(Phenyl)Silane (22)Trimethyl(Phenylethynyl)Silane (23)
Sulfamides (10218)
Dimethylsulfamoyl (5)Dimethylsulfamoyl (5)Methanesulfonamide (54)Methanesulfonamide (54)Methylmethanesulfonamide (3)Methylmethanesulfonamide (3)Methylsulfonamido (4)Methylsulfonamido (4)Sulfinamide (55)Sulfinamide (55)2-Fluoro-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (6)2-Fluorobenzenesulfonamide (12)2-Methylbenzenesulfonamide (8)3-Nitrobenzenesulfonamide (8)4-Amino-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (3)4-Bromo-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (23)4-Chloro-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (4)4-Methoxy-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (3)4-Methoxybenzenesulfonamide (5)4-Methyl-N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (13)N,N-Diethylbenzenesulfonamide (8)N,N-Dimethylbenzenesulfonamide (23)N-(2-Phenoxyphenyl)Methanesulfonamide (4)N-(3-Chlorophenyl)Benzenesulfonamide (6)N-(O-Tolyl)Benzenesulfonamide (4)N-(Tert-Butyl)Benzenesulfonamide (14)N-Ethylbenzenesulfonamide (8)N-Isopropylbenzenesulfonamide (8)N-Methyl-N-(4-Phenylpyrimidin-2-Yl)Methanesulfonamide (7)N-Methylbenzenesulfonamide (15)N-Phenylbenzenesulfonamide (81)N-Phenylmethanesulfonamide (37)Phenylmethanesulfonamide (13)Pyridine-2-Sulfonamide (6)
Sulfides (10123)
Methylthio (432)(S)-2-(Phenylthio)Tetrahydro-2H-Pyran (5)1,2-Diphenyldisulfane (19)2-((Pyridin-2-Ylmethyl)Thio)-1H-Benzo[D]Imidazole (7)2-(Methylthio)Benzo[D]Thiazole (6)2-(Methylthio)Pyridine (5)2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidin-4-Amine (10)2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (19)2-(Methylthio)Thiazole (5)2-(Propylthio)Pyrimidine (5)4,6-Dichloro-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (9)4-Chloro-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (29)4-Methyl-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (7)5-Bromo-2-(Methylthio)Pyrimidine (6)Benzyl(Phenyl)Sulfane (5)Ethyl(Phenyl)Sulfane (8)Pentafluoro(Phenyl)-L6-Sulfane (19)Phenyl(Trifluoromethyl)Sulfane (23)
Sulfones (3927)
(4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(Ethylsulfonyl)Benzene (8)1-(Methylsulfonyl)-3-Nitrobenzene (7)1-(Methylsulfonyl)Piperazine (5)1-(Methylsulfonyl)Piperidine (6)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,4-Triazole (6)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-1H-Imidazole (5)1-(Phenylsulfonyl)Azetidine (7)1-Bromo-2-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzene (4)1-Bromo-4-(Phenylsulfonyl)Benzene (7)1-Fluoro-2-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzene (5)1-Fluoro-3-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzene (10)1-Methyl-3-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzene (5)2-(Methylsulfonyl)Aniline (3)2-(Methylsulfonyl)Pyridine (11)2-(Methylsulfonyl)Pyrimidine (25)3-(Methylsulfonyl)Aniline (7)3-(Methylsulfonyl)Benzoic Acid (6)3-(Methylsulfonyl)Pyridine (5)Benzenesulfonyl Fluoride (51)Tetrahydro-2H-Thiopyran 1,1-Dioxide (8)Tetrahydrothiophene 1,1-Dioxide (13)
Sulfonic Acids (1261)
Aminobenzenesulfonic (4)Bromobenzenesulfonic Acid (4)Disulfonic (9)Disulfonic (9)Ethanesulfonic (3)Methanesulfonic (2)Methanesulfonic (2)Methylbenzenesulfonate (144)Propanesulfonic Acid (2)Trifluoromethanesulfonic (4)2-Aminobenzenesulfonic Acid (9)2-Methylbenzenesulfonic Acid (8)3-Aminobenzenesulfonic Acid (6)4-Chlorobenzenesulfonic Acid (4)4-Hydroxybenzenesulfonic Acid (5)Naphthalene-2-Sulfonic Acid (4)Pyridine-3-Sulfonic Acid (6)
Sulfonyl Chlorides (4029)
Fluorobenzenesulfonyl (12)1H-Pyrazole-4-Sulfonyl Chloride (8)2-Bromobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (8)2-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (24)2-Fluorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (31)2-Methoxybenzenesulfonyl Chloride (15)2-Methylbenzenesulfonyl Chloride (22)3-(Chlorosulfonyl)Benzoic Acid (15)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzenesulfonyl Chloride (13)3-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (21)3-Fluorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (22)4-Chlorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (12)4-Fluorobenzenesulfonyl Chloride (26)Isoquinoline-5-Sulfonyl Chloride (3)Methyl 2-(Chlorosulfonyl)Benzoate (7)Phenylmethanesulfonyl Chloride (20)
Trifluoromethyls (28951)
Trifluoromethyl-Picolinamide (7)Trifluoromethylaniline (3)(2,2,2-Trifluoroethoxy)Benzene (18)(2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (5)(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (20)(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Methanol (10)(2-Fluoro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (9)(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Methanol (4)(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (41)(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Methanol (21)(4-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (22)(Perfluoropropane-2,2-Diyl)Dibenzene (7)(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (1336)1,3-Bis(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (70)1-(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Ethan-1-One (9)1-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (6)1-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (25)1-(4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Ethan-1-Amine (6)1-(Bromomethyl)-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (13)1-(Bromomethyl)-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (17)1-Bromo-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (22)1-Bromo-2-Fluoro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (4)1-Bromo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (100)1-Chloro-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (20)1-Chloro-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (81)1-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (18)1-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (101)1-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (8)1-Fluoro-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (20)1-Fluoro-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (126)1-Fluoro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (98)1-Fluoro-4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (14)1-Fluoro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (53)1-Iodo-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (13)1-Iodo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (30)1-Methoxy-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (21)1-Methoxy-3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (9)1-Methoxy-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (40)1-Methoxy-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (18)1-Methyl-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (5)1-Methyl-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (43)1-Methyl-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (22)1-Nitro-2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (8)1-Nitro-2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (32)1-Nitro-3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzene (9)1-Nitro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (82)1-Phenoxy-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (2)1-Phenoxy-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (2)1-Phenyl-3-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Pyrazole (5)2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-Phenylethan-1-Amine (48)2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-Phenylethan-1-Ol (27)2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-Phenylethan-1-One (51)2-(2,2,2-Trifluoroethoxy)Pyridine (8)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Aniline (18)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzaldehyde (7)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzoic Acid (8)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzonitrile (7)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenol (8)2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Pyridine (6)2-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,1'-Biphenyl (8)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (58)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzaldehyde (27)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzamide (6)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoic Acid (33)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzonitrile (35)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenol (23)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrazine (6)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidine (27)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Quinazoline (4)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Thiazole (11)2-(Trifluoromethyl)Thiophene (11)2-Bromo-1-Fluoro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzene (4)2-Bromo-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (9)2-Bromo-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (5)2-Chloro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (3)2-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidine (6)2-Chloro-6-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (4)2-Methoxy-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (6)2-Methoxy-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (4)2-Phenoxy-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (7)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (3)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Aniline (22)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzaldehyde (10)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzoic Acid (19)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Benzonitrile (11)3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenol (12)3-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Pyrrolo[2,3-B]Pyridine (3)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (102)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzaldehyde (31)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzenesulfonyl Chloride (13)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoic Acid (52)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzonitrile (47)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenol (43)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridazine (3)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Ol (5)3-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (52)3-Chloro-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (5)4,4,4-Trifluoro-1-Phenylbutane-1,3-Dione (10)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)4-(Trifluoromethoxy)Aniline (26)4-(Trifluoromethyl)-2H-Chromen-2-One (6)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenol (18)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridine (14)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidin-2-Amine (6)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyrimidine (12)4-(Trifluoromethyl)Thiazole (7)4-Bromo-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (7)5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Amine (5)5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Ol (8)6-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Indazole (6)6-(Trifluoromethyl)-1H-Indole (5)6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-2-Amine (11)6-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-3-Amine (5)Methyl 2-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoate (14)Methyl 3-(Trifluoromethyl)Benzoate (22)N-Phenyl-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Aniline (3)Phenyl(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Methanone (3)Phenyl(Trifluoromethyl)Sulfane (23)
Organometallic Reagents
Organoborons (34729)
Fluorene-Phenyl-Boronic Acid/Ester (4)Hydroxymethyl-Phenyl-Boronic-Acid (31)Methoxyphenylboronic-Acid (32)Phenyl-Naphthalene-Boronic Acid/Ester (9)(1-(Tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-1H-Indol-2-Yl)Boronic Acid (17)(1-Phenyl-1H-Pyrazol-4-Yl)Boronic Acid (4)(1H-Indazol-4-Yl)Boronic Acid (3)(1H-Indazol-6-Yl)Boronic Acid (4)(1H-Indol-2-Yl)Boronic Acid (3)(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (11)(2,3-Difluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (33)(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(2,6-Difluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (28)(2-(Phenoxymethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (3)(2-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (5)(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (20)(2-Bromophenyl)Boronic Acid (39)(2-Chloro-3-Methoxyphenyl)Boronic Acid (5)(2-Chloro-6-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (9)(2-Fluoro-3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(2-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (229)(2-Nitrophenyl)Boronic Acid (13)(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (10)(3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenyl)Methanol (7)(3-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (9)(3-(Phenoxymethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (3)(3-(Phenylcarbamoyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (3)(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (9)(3-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (41)(3-Bromo-2-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (7)(3-Bromo-2-Methoxyphenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(3-Bromophenyl)Boronic Acid (65)(3-Chloro-2-Methoxyphenyl)Boronic Acid (4)(3-Chloro-4-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (8)(3-Chlorophenyl)Boronic Acid (121)(3-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (169)(3-Iodophenyl)Boronic Acid (5)(3-Nitrophenyl)Boronic Acid (32)(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (26)(4-(Methylsulfonyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(4-(Phenoxymethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (6)(4-(Phenylcarbamoyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (11)(4-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)Boronic Acid (22)(4-Cyclohexylphenyl)Boronic Acid (7)(4-Fluorophenyl)Boronic Acid (93)(5-(Trifluoromethyl)Pyridin-3-Yl)Boronic Acid (4)(6-Phenoxypyridin-3-Yl)Boronic Acid (5)(9H-Fluoren-2-Yl)Boronic Acid (6)(E)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-Styryl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (16)1,3,2-Dioxaborinane (6)1-(4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzyl)Piperazine (4)1-(4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenyl)Piperazine (10)1-(5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridin-2-Yl)Piperazine (6)1-Methyl-4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole (6)2,7-Bis(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-9H-Fluorene (7)2-(1,3,2-Dioxaborinan-2-Yl)Benzonitrile (4)2-(1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1-Methyl-1H-Indole (6)2-(2-(Bromomethyl)Phenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (9)2-(2-Bromophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)2-(3-Chlorophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (8)2-(3-Cyclopropylphenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)2-(3-Isopropoxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzonitrile (14)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenol (7)2-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)2-(4-(Benzyloxy)Phenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (10)2-(4-Bromophenyl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (8)2-(4-Cyclopropylphenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (8)2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborinane (5)2-([1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Yl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (10)2-(Cyclohex-1-En-1-Yl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (16)2-(Furan-2-Yl)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (6)2-(M-Tolyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborinane (4)2-Benzyl-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (12)2-Chloro-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (4)2-Chloro-4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (14)2-Chloro-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)2-Fluoro-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (7)2-Methoxy-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (7)2-Methoxy-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-Methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)2-Methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (3)3-(1,3,2-Dioxaborinan-2-Yl)Aniline (3)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzonitrile (25)3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (74)3-Chloro-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)3-Fluoro-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (7)3-Methyl-5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (6)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(2-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(2-Nitrophenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(3-(Trifluoromethoxy)Phenyl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (5)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(Naphthalen-1-Yl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (19)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(Naphthalen-2-Yl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (12)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(Thiophen-2-Yl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (23)4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(Thiophen-3-Yl)-1,3,2-Dioxaborolane (10)4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine (11)4-Methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridine (5)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Indole (5)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Indoline (5)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Nicotinonitrile (4)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyridin-2-Amine (9)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Pyrimidine (27)5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Thiazole (7)[1,1'-Biphenyl]-4-Ylboronic Acid (29)Benzo[B]Thiophen-2-Ylboronic Acid (5)Benzofuran-2-Ylboronic Acid (8)Benzyl (4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Phenyl)Carbamate (5)Cyclohex-1-En-1-Ylboronic Acid (4)Ethyl 3-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Benzoate (6)Isoquinolin-4-Ylboronic Acid (3)Methyl 5-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Nicotinate (4)N,N-Diphenyl-4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)Aniline (6)Naphthalen-1-Ylboronic Acid (4)Naphthalen-2-Ylboronic Acid (8)Phenylboronic Acid (1286)Pyridin-2-Ylboronic Acid (9)Pyridin-3-Ylboronic Acid (49)Pyridin-4-Ylboronic Acid (21)Pyrimidin-5-Ylboronic Acid (9)Tert-Butyl 2-(1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Indole-1-Carboxylate (6)Tert-Butyl 4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-Dioxaborolan-2-Yl)-1H-Pyrazole-1-Carboxylate (3)Tetraphenylborate (8)Thiophen-2-Ylboronic Acid (20)
Inhibitors/Agonists
Anti-Infection (4763)
3CLpro (41)Antibacterial (2101)Antifungal (525)Antiparasitic (648)Antiprotozoal (2)Antiviral (48)Arenavirus (5)BVDV (3)CMV (30)Dengue Virus (36)EBV (14)Enterovirus (33)FCoV (3)Filovirus (14)Flavivirus (64)GraR (1)HBV (151)HCV (222)HHV (1)HIV (447)HIV Integrase (39)HIV Protease (68)HPV (10)HRV (3)HSV (75)Influenza Virus (251)LpxC (2)M2 proton channel (2)MERS-CoV (1)Neuraminidase (4)NNRTI (12)NRTI (22)Orthopoxvirus (28)Penicillin-Binding Protein (7)PLP (13)Prion (1)Protein Synthesis (4)Reverse Transcriptase (99)RSV (43)SAMHD1 (1)SARS-CoV (298)SQLE (5)TMV (12)Viral MTase (3)Virus Protease (62)VSV (1)β-lactamase (51)
Apoptosis (2443)
Apoptosis (2143)Apoptosis Inducer (1407)Bcl-2 (195)Bcl-6 (6)BRK (3)c-Myc (47)c-RET (64)C/EBP (2)Caspase (170)DAPK (12)Ferroptosis (109)FKBP (15)GDNF Receptor (1)IAP (48)IDO (70)MDM2 (143)MRCK (2)Necroptosis (33)p32 (1)p53 (41)PERK (35)PKD (10)Pyroptosis (13)RIP Kinase (84)Survivin (12)Thymidylate Synthase (24)TNF (22)TNF Receptor (117)TNF-alpha (30)
Cell Cycle (4595)
Antifolate (31)APC (6)Aurora Kinase (87)BUB (3)Casein Kinase (101)CDK (475)Chk (46)CRISPR/Cas9 (7)CRM1 (17)DHFR (55)DNA polymerase θ (2)DNA/RNA Synthesis (620)DOCK (3)DYRK (60)E2F (2)eIF (43)Endonuclease (3)FOXM1 (3)G-quadruplex (6)Haspin Kinase (8)HDAC (336)HGF (1)HSF (4)HSP (161)IRE1 (27)Kinesin (35)Lats kinase (1)LIMK (17)Mad2 (1)Microtubule/Tubulin (305)MKLP (1)Mps1 (21)MTH2 (1)Nucleoside Antimetabolite/Analog (1441)p21 (1)PAK (30)PDI (1)PKMYT1 (2)PLK (50)PPAR (193)PTEN (5)RAD51 (18)Rho (14)RNA polymerase 2 (1)RNA polymerase 1 (2)ROCK (90)Separase (1)Sirtuin (129)SRPK (51)STK33 (2)TACC (3)Telomerase (21)TOPK (1)Topoisomerase (271)Wee1 (16)YB-1 (5)
DNA Damage (3023)
ADAR (1)AP endonuclease (1)ATAD5 (1)ATM/ATR (67)Aurora Kinase (87)Casein Kinase (101)ClpP (5)CRISPR/Cas9 (7)DNA Alkylator/Crosslinker (75)DNA-PK (39)DNA/RNA Synthesis (620)HDR (1)HSP (161)MRE11 (1)MTH1 (8)Nucleoside Antimetabolite/Analog (1441)OGG (3)p97 (15)PARP (175)RAD51 (18)RAD52 (3)Telomerase (21)Topoisomerase (271)WRN (5)YB-1 (5)
Endocrinology/Hormones (826)
5 Alpha Reductase (2)ACE (76)Adrenergic Receptor (184)Androgen Receptor (96)Aromatase (8)ERR (218)GHSR (21)Glucocorticoid Receptor (44)GNRH Receptor (19)Mineralocorticoid Receptor (12)Opioid Receptor (54)Progesterone Receptor (9)PTHR (1)Renin (18)Sepiapterin reductase (2)SSTR (28)Taste receptor (3)Thyroid Hormone Receptor (7)TPO (4)TRHR (1)TSH Receptor (17)TTR (7)
Epigenetics (2366)
AMPK (105)Aurora Kinase (87)DNA Methyltransferase (43)Epigenetic Reader Domain (396)FTO (15)HDAC (336)HIF (112)Histone Acetyltransferase (95)Histone Demethylase (147)Histone Methyltransferase (294)JAK (245)MBD-containing protein (1)METTL3 (10)MicroRNA (16)PAD (24)PARP (175)Pim (58)PKC (157)SF3B1 (3)Sirtuin (129)TET (8)
GPCR/G Protein (3483)
5-HT Receptor (402)Adenosine Receptor (169)Adenylyl Cyclase (1)Adiponectin Receptor (2)Adrenergic Receptor (184)Amylin receptor (1)Angiotensin Receptor (72)Apelin Receptor (22)Bombesin Receptor (7)Bradykinin Receptor (17)cAMP (34)Cannabinoid Receptor (65)CaSR (23)CCR (89)CGRP Receptor (14)Chemerin Receptor (2)Cholecystokinin Receptor (32)CRF Receptor (19)CXCR (112)Dopamine Receptor (170)Endothelin Receptor (47)Epac (9)G protein (2)GHSR (21)GLP Receptor (25)Glucagon Receptor (50)GNRH Receptor (19)GPCR (203)GPCR19 (2)GPR109A (1)GPR119 (2)GPR139 (3)GPR24 (1)GPR35 (1)GPR40 (7)GPR52 (4)GPR6 (3)GPR68 (2)GPR84 (1)GPR88 (10)Guanylate Cyclase (31)HCAR (2)Histamine Receptor (239)ICMT (61)Kisspeptin Receptor (2)LHCGR (39)LPA Receptor (11)LPL Receptor (118)Melanocortin Receptor (31)mGluR (226)Motilin Receptor (1)MRGPR (13)Neuropeptide Y receptor (8)Neurotensin Receptor (13)NMUR (2)NPFF receptor (3)Opioid Receptor (54)OXTR (10)P2Y Receptor (77)PACAP Receptor (3)PAFR (38)PAR (55)Prostaglandin Receptor (217)Ras (275)RGS (6)RXFP Receptor (14)Sigma Receptor (53)SOS (7)SRPK (51)SSTR (28)SUCNR1 (4)TAAR (8)TSH Receptor (17)Urotensin Receptor (7)Vasopressin Receptor (23)β-arrestin (17)
Immunology/Inflammation (2700)
AIM2 (5)AP-1 (14)Arginase (15)Calcineurin (8)CCR (89)CD19 (1)CD20 (2)CD22 (2)CD28 (2)CD28-B7 (1)CD3 (3)CD38 (10)CD47 (6)CD6 (1)CD73 (26)CD80 (1)cGAS (8)Complement System (45)COX (344)CRTH2 (9)CTLA-4 (2)CXCR (112)CYPA (1)FAP (17)FKBP (15)FLAP (17)FPR (17)Galectin (3)Glucocorticoid Receptor (44)Glycoprotein VI (3)GM-CSF (2)Histamine Receptor (239)HMGB (1)IFNAR (24)IL (172)IL Receptor (9)Immunology & Inflammation Related (75)IRAK (71)IRF3 (1)LAG-3 (1)LanC-like protein (1)Legumain (1)LTA4H (3)LTR (71)MALT1 (24)MIF (18)MyD88 (6)NADPH Oxidase (32)NFAT (11)NLR (73)NO Synthesis (6)NOS (186)NOT (1)Nrf2 (99)PD-1/PD-L1 (80)PG Synthase (30)PSMA (13)Pyroptosis (13)ROS (398)Ros1 (18)S100A9 (1)Scavenger receptor (1)SIK (15)SOD (4)SPHK (27)STING (98)TENT (1)Thrombopoietin Receptor (11)Tim3 (4)TLR (163)TSPO (2)VISTA (1)XBP1 (1)
Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel (1711)
ABC Transporter (2)AKK1 (3)ANT (1)AQP (5)AQP3 (1)ARF (2)ATP synthase (19)ATPase (41)BCRP (23)Calcium Channel (269)CFTR (61)Chloride Channel (30)CRAC Channel (14)CRM1 (17)EAAT (3)Efflux pump (1)ENT (2)Ferroportin (2)GABA Receptor (188)GLUT (32)Glutamate transporter (21)Glycine transporter (23)HCN Channel (2)IBAT (10)ITPKA (2)MAT (24)MCT (17)Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger (15)Na+/K+ ATPase (16)Na/HCO3 cotransporter (1)NKCC (1)Oct (11)OCTN (1)Organic Anion Transporter (1)P-gp (53)P2X Receptor (79)Piezo (4)Potassium Channel (287)Proton Pump (54)SEO1 (1)SGLT (44)SLC (6)Sodium Channel (195)SV2 (2)TRP Channel (182)URAT1 (18)Urea Transporter (2)VDAC (6)VRAC (1)
Metabolic Enzyme (3492)
15-PGDH (2)2OG Oxygenase (1)3-PGDH (2)3MST (1)6PGD (2)ACAT (38)ACC (22)ACMSD (2)Aconitate hydratase (1)ACS (3)Adenosine Deaminase (12)Adenosylhomocysteinase (8)ADP-ribosyltransferase (1)AhR (49)AKR (15)ALDH (30)Aldose Reductase (54)Aminopeptidase (28)Antifolate (31)AO (1)ApoE (1)Arginase (15)Asparagine synthetase (1)ATF/CREB proteins (2)ATP Citrate Lyase (6)ATP synthase (19)BDK (1)Beta-glucuronidase (3)Carbonic Anhydrase (121)Carboxylesterase (23)Carboxypeptidase (7)Cardiolipin Peroxidase (1)Cathepsin (98)Ceramidase (4)CETP (15)Cholesterol Transporter (1)CPA (5)CPSI (2)Creatine kinase (1)Cryptochrome (5)CSE (2)CYP51 (1)D-amino acid oxidase (3)D6D (1)DAPA synthase (1)Decarboxylase (8)Dehydrogenase (156)DGAT (62)DGK (20)Dopamine β-hydroxylase (8)E-NTPDase (1)Elastase (32)Enolase (7)Enteropeptidase (5)ERAP (3)FABP (8)Factor Xa (45)Farnesyl Transferase (4)FAS (35)FBPase (4)Ferroptosis (109)FOXO (3)FPR (17)FTO (15)Fumarate hydratase (2)FVII (2)FXR (71)G0/G1 switch protein 2 (2)Galactosidases (5)GCN (1)GCS (3)GGTase (6)Glucokinase (26)Glucosidase (131)GLUT (32)Glutaminase C (2)Glutathione Reductase (1)Glyoxalase (14)GOAT (1)GPx (25)GSNOR (3)GST (16)Hexokinase (8)HMGCR (45)HPSE (2)Hydrolase (12)Hydroxylase (24)IDH (37)IDO (70)Ketohexokinase (5)LDL (11)LDLR (1)Lipase (93)Lipoxygenase (109)LOX (4)LRH-1 (4)LXR (27)MAGL (2)MASTL (1)MDH (3)MetAP (10)MGAT (7)Mineralocorticoid Receptor (12)Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain (3)Mitochondrial Metabolism (98)MPC (3)NAMPT (33)Neprilysin (20)NNMT (8)NPP (2)NPR (15)NQO (2)OGT (2)OPA1 (1)P448 (1)P450 (261)PAI-1 (25)PARG (12)PDE (366)PDHK (12)PEPCK (2)PGAM1 (1)PGC-1α (4)PHGDH (5)Phospholipase (108)Phosphorylase (10)PI5P4K (11)PKM1 (2)PKM2 (6)Procollagen C Proteinase (1)Proprotein convertases (5)Pyruvate Kinase (28)QR (2)RAR/RXR (86)RBP (3)REV-ERB (4)ROR (67)SCD (18)sEH (33)SGK (15)SHMT (7)Sialyltransferase (1)Sphingosine acyltransferase (2)SQOR (2)Srx (1)Steroid Sulfatase (8)TDO (3)TGH (1)Thioredoxin (12)Thrombin (43)Thymidylate Synthase (24)Transferase (80)Transketolase (7)TrxR (11)Trypanothione reductase (1)UGT (3)VD/VDR (47)Xanthine Oxidase (49)αKGD (2)
Neuronal Signaling (3852)
5-HT Receptor (402)AAK1 (17)AChE (43)AChR (348)Adenosine Kinase (5)Adrenergic Receptor (184)AMPAR (54)Amylin receptor (1)Amyloid-β (172)Calcium Channel (269)CaMK (54)Cannabinoid Receptor (65)CGRP Receptor (14)Cholecystokinin Receptor (32)Cholinesterase (235)CHT (1)COMT (16)DAT (21)Dopamine Receptor (170)Endorphin (1)Enkephalinase (3)FAAH (45)GABA Receptor (188)Glucosylceramide Synthase (13)GluR (208)GPR119 (2)GPR139 (3)GPR24 (1)Histamine Receptor (239)Huntingtin (3)Imidazoline Receptor (14)Kainate receptor (5)MAO (195)Melanocortin Receptor (31)mGluR (226)MT Receptor (12)NET (3)Neuropeptide Y receptor (8)Neurotensin Receptor (13)NGF (3)NK Receptor (57)NMDA (1)NMDAR (50)Notch (26)Nurr1 (7)OLIG2 (1)Opioid Receptor (54)OX Receptor (50)P2X Receptor (79)Proprotein convertases (5)QC (3)RAGE (3)REST (1)Ryanodine Receptor-1 (1)S100β (1)Secretase (112)SERT (27)Sigma Receptor (53)SMS (4)SSRIs (5)Substance P (2)TAAR (8)Tau Protein (28)TLX (1)Trk Receptor (80)TRP Channel (182)TTR (7)α-synuclein (1)
Protein Tyrosine Kinase/RTK (2741)
Ack1 (5)ALK (86)Bcr-Abl (105)BMX Kinase (3)BRK (3)BTK (149)c-FMS (60)c-Kit (87)c-Met/HGFR (131)c-RET (64)DDR1/DDR2 Receptor (22)DYRK (60)EGFR (403)Ephrin Receptor (16)ErbB (6)FAK (56)FGF (2)FGFR (136)FLT3 (134)GAK (624)HER2 (31)IGF-1R (28)Insulin Receptor (26)ITK (18)JAK (245)MRCK (2)PDGFR (127)PTK (7)Pyk2 (4)Ros1 (18)SHP2 (48)Src (110)Syk (40)TAM Receptor (50)Tie-2 (16)Trk Receptor (80)VEGFR (271)
Other Inhibitors/Agonists (3218)
20-HETE (2)AIMP2-DX2 (2)Amino Acids and Amino Acid Derivatives (126)Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase (18)Anesthetic (3)Anti-inflammation (30)Anti-Thyroid Agent (1)Anti-tumor (7)Anti-ulcer (1)Antioxidant (33)Antispasmodic Agent (3)ASGPR (11)Bcat (11)c-RET (64)Cancer Stem Cells (2)CAR (5)Cardiac transcription factor (2)CBFβ-SMMHC (1)CD20 (2)CD52 (1)CD73 (26)CerK (1)Chelating Agent (15)Choleretic (1)Choline Kinase (3)CNT (1)CRTH2 (9)CSE (2)DCLK (1)DcpS (1)Decarboxylase (8)Dehydrogenase (156)Diabetes (2)Diuretic (1)Drug Metabolite (286)DUE-B (1)E2F (2)ECE (2)Endogenous Metabolite (1247)ERO1 (2)FAP (17)FATP (3)Fer/FerT (1)FPP synthase (1)Fucosyltransferase (4)Fungicide (60)G protein (2)Galectin (3)Galectin-3 (12)GBF1 (1)GCase (4)Glucocorticoid Receptor (44)GRK (21)Herbicide (17)HIPK2 (3)Histidine kinase (1)HNF4α (1)HPPD (3)HRGP (1)Hydroxylase (24)IgE (2)IMP1 (1)Importin β (1)Insecticide (27)ITPKA (2)LAT1 (3)LDL (11)Lipase (93)Lipocalin-2 (1)LYTACs (8)MALAT1 (1)MITF (1)MLKL (4)Molecular Glues (41)MPO (5)MTTP (8)Muscle Relaxant (1)MYOF (1)NAADP (1)Neuroprotection/neurogenic Agent (4)NMD (1)NT (2)Nur77 (8)O-GlcNAcase (9)O-glycosylation (1)OSBP (1)OSBPL (1)OSC (2)Osteoclasts/Bone/Osteogenesis (15)OxPhos (4)PAM complex (1)PANK (2)PAX2 (1)PBR (4)PCA1 (1)PCSK9 (7)PDX1 (1)PEPT (1)PFKFB3 (7)Phosphatase (248)Phosphorylase (10)Photosensitizer (6)PIN1 (10)PKG (10)Platelet (5)PME-1 (2)PMO/MNA (4)PNP (1)PREP (20)Protein Synthesis (4)PXR (3)Quorum Sensing (57)RasGAP (2)Rev-ErbA (3)RUNX (7)SAP (1)SMARC (6)SQS (4)SREBP (5)SRPK (51)Sweetener (3)Tgase (2)Thioredoxin (12)TIR1 (1)TNIK (8)TNK (4)TNNI3K (1)UGT1A1 (1)Urease (5)vanin (4)VDA (1)Vitamin (61)VPS (3)XOR (1)α-amylase (15)Others (2611)
Inhibitory Monoclonal Antibody
Human Inhibitory Monoclonal Antibody (62)
Amyloid-β/monoclonal antibody (2)CA Ⅸ/monoclonal antibody (1)CCR/monoclonal antibody (1)CD19/monoclonal antibody (1)CD20/monoclonal antibody (2)CD22/monoclonal antibody (1)CD25/monoclonal antibody (1)CD3/monoclonal antibody (1)CD38/monoclonal antibody (1)CD4/monoclonal antibody (1)CD40/monoclonal antibody (1)CD47/monoclonal antibody (1)CD52/monoclonal antibody (1)CD6/monoclonal antibody (1)CD62p/monoclonal antibody (1)CD73/monoclonal antibody (1)CGRP Receptor/monoclonal antibody (2)Complement System/monoclonal antibody (1)CTLA-4/monoclonal antibody (1)EGFR/monoclonal antibody (2)HER2/monoclonal antibody (2)IFNAR/monoclonal antibody (1)IgE/monoclonal antibody (2)IGF-1R/monoclonal antibody (1)IL-13/monoclonal antibody (1)IL-17a/monoclonal antibody (1)IL-1β/monoclonal antibody (1)IL-23/monoclonal antibody (2)IL-4Ra/monoclonal antibody (1)IL-5/monoclonal antibody (1)IL-5Rα/monoclonal antibody (1)IL-6/monoclonal antibody (3)Integrin/monoclonal antibody (1)KIR/monoclonal antibody (1)LAG-3/monoclonal antibody (1)PCSK9/monoclonal antibody (2)PD-1/PD-L1/monoclonal antibody (4)RANKL /monoclonal antibody (1)Sclerostin/monoclonal antibody (1)SLAMF7/monoclonal antibody (1)TIGIT/monoclonal antibody (1)Tim3/monoclonal antibody (1)TNF Receptor/monoclonal antibody (3)TNF-alpha/monoclonal antibody (2)TROP2/monoclonal antibody (1)VEGFR/monoclonal antibody (1)
Animal Modeling Reagents
Immune and Inflammatory Disease Models (29)
Arthritis Model (1)Cystitis Model (1)Dermatitis Model (1)Ear Edema Model (1)Encephalomyelitis Model (2)Foot Edema Model (2)Gastrointestinal Inflammation and Ulcer Model (8)Gouty Arthritis Model (1)Liver Inflammation Model (2)Myocarditis Model (2)Nephritis Model (1)Pancreatitis Model (5)Psoriasis Model (3)Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Model (2)
Cancer
Tumor Epigenetics and Gene Regulation (2861)
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase (18)ATM/ATR (67)DNA Methyltransferase (43)DNA/RNA Synthesis (620)Epigenetic Reader Domain (396)HDAC (336)HIF (112)Histone Acetyltransferase (95)Histone Demethylase (147)Histone Methyltransferase (294)METTL3 (10)MicroRNA (16)PAD (24)PARP (175)Pim (58)PKC (157)RNA polymerase 1 (2)Sirtuin (129)TET (8)Topoisomerase (271)
Enzymology
Enzyme Inhibitors (206)
Acetaldehyde Dehydrogenase Inhibitor (1)Acyltransferase Inhibitor (4)Alkaline Phosphatase Inhibitor (2)Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor (4)ATP Enzyme Inhibitor (7)Calcineurin Inhibitor (1)Carbonic Acid Dehydratase Inhibitor (2)Caspase Inhibitor (2)Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibitor (47)DNA Topoisomerase II Inhibitor (11)Hypoxia Inducible Factor (HIF) Inhibitor (3)Inosine Monophosphate (IMP) Dehydrogenase Inhibitor (10)Leukotriene A4 Hydrolase Inhibitor (3)Lipoxygenase Inhibitor (11)Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (4)NADH Peroxidase Inhibitor (2)Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitor (2)Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor (20)Protease Inhibitor (20)Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor (16)Starch Glucosidase Inhibitor (3)Thromboxane Synthase Inhibitor (2)Topoisomerase I Inhibitor (8)Tyrosine / EGF Receptor Protein Kinase Inhibitor (33)
Fluorescent Probe / Staining
Cell Biology Fluorescent Dyes (61)
Apoptosis Dyes (6)BODIPY (21)Cytoplasm Dyes (5)Cytotoxicity Analysis Dyes (12)Endocytosis and pinocytosis Dyes (5)Endoplasmic Reticulum Dyes (2)Exosome Dyes (4)Lipid Droplet Dyes (3)Lysosome Dyes (4)Membrane Dyes (4)Mitochondrial Dyes (5)NOS Dyes (6)Nucleic Acid Dyes (1)Nucleus Dyes (10)PH Indicators (18)ROS Dyes (27)
Natural Products
Asteraceae (228)
Achillea (3)Ageratum (1)Ambrosia (2)Arctium (2)Arnica (1)Artemisia (25)Aster (2)Atractylodes (9)Aucklandia (5)Bellis (1)Blumea (4)Cacalia (1)Carpesium (1)Carthamus (7)Centaurea (5)Centipeda (4)Chrysactinia (4)Chrysanthemum (6)Cichorium (2)Cirsium (2)Conyza (1)Coreopsis (1)Cosmos (1)Crepis (3)Cynara (1)Dahlia (2)Dittrichia (1)Doronicum (1)Echinacea (2)Eclipta (6)Elephantopus (1)Erigeron (3)Eupatorium (20)Gnaphalium (1)Gynura (2)Helianthus (4)Heterotheca (1)Inula (8)Kalimeris (1)Laggera (13)Laurentia (1)Ligularia (4)Matricaria (2)Petasites (2)Pulicaria (4)Saussurea (3)Scorzonera (2)Senecio (9)Siegesbeckia (2)Silybum (5)Smallanthus (1)Stevia (10)Tagetes (4)Telekia (1)Tessaria (1)Tussilago (2)Verbesina (1)Vernonia (5)Wedelia (2)Xanthium (6)Zinnia (1)
Fabaceae (348)
Abrus (1)Acacia (9)Adenanthera (1)Albizia (1)Ammothamnus (1)Antheroporum (1)Astragalus (23)Butea (1)Caesalpinia (18)Cajanus (3)Campylotropis (1)Cassia (26)Cicer (1)Crotalaria (5)Cytisus (3)Dalbergia (10)Derris (13)Desmodium (3)Erythrina (13)Flemingia (3)Genista (1)Glycine (22)Glycyrrhiza (41)Griffonia (1)Hedysarum (1)Lespedeza (5)Leucaena (3)Lotus (5)Lupinus (8)Maackia (4)Medicago (1)Millettia (6)Mimosa (1)Mucuna (2)Ononis (2)Parochetus (2)Phyllodium (1)Pisum (1)Pongamia (1)Prosopis (2)Psoralea (18)Pterocarpus (1)Pterolobium (1)Pueraria (25)Robinia (2)Saraca (1)Senna (1)Sophora (36)Spartium (1)Spatholobus (2)Styphnolobium (1)Trifolium (6)Trigonella (2)Vicia (2)Wisteria (2)
Rutaceae (162)
Aegle (1)Boenninghausenia (2)Cedrelopsis (1)Citrus (38)Clausena (7)Dictamnus (8)Euodia (1)Evodia (13)Flindersia (1)Fortunella (1)Glycosmis (3)Haplophyllum (3)Melicope (1)Micromelum (11)Murraya (21)Phebalium (2)Phellodendron (8)Ptaeroxylon (1)Ruta (3)Skimmia (1)Tetradium (1)Toddalia (14)Zanthoxylum (20)
Vesicle
Parkinson'S Disease and Alzheimer'S Disease (5789)
Akt (207)AMPAR (54)Apoptosis (2143)Caspase (170)CDK (475)CREB (5)Dopamine Receptor (170)Dopamine β-hydroxylase (8)ERK (166)Glucagon Receptor (50)GPCR (203)GSK-3 (126)IL (172)JAK (245)JNK (79)LRRK2 (32)MyD88 (6)NF-κB (419)Notch (26)p53 (41)PI3K (340)PKA (59)PTEN (5)RAGE (3)Ras (275)Rho (14)ROCK (90)ROS (398)Secretase (112)STAT (160)STING (98)Tau Protein (28)TLR (163)TNF (22)Tyrosinase (100)Tyrosine / EGF Receptor Protein Kinase Inhibitor (33)Wnt (104)α-synuclein (1)β-catenin (71)